Secondary systemic amyloidosis
Amyloidosis - secondary systemic
Secondary systemic amyloidosis is a disorder in which abnormal proteins build up in tissues and organs. Clumps of the abnormal proteins are called amyloid deposits.
Secondary means it occurs because of another disease or situation. For example, this condition usually occurs as a result of chronic infection or chronic inflammatory disease. Primary amyloidosis means there is no disease that is causing the condition.
Chronic
Chronic refers to something that continues over an extended period of time. A chronic condition is usually long-lasting and does not easily or quick...

Systemic means that the disease affects the entire body.
Causes
The exact cause of amyloidosis is unknown. You are more likely to develop secondary systemic amyloidosis if you have a long-term infection or inflammation.
Amyloidosis
Primary amyloidosis is a disorder in which abnormal proteins build up in tissues and organs. Clumps of the abnormal proteins are called amyloid depo...
This condition may occur with:
-
Ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic form of arthritis. It mostly affects the bones and joints at the base of the spine where it connects with t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
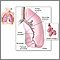
Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is a disease in which the large airways in the lungs are damaged. This causes the airways to become wider. Bronchiectasis can be pres...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chronic
osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is a bone infection. It is mainly caused by bacteria or other germs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is a disease that causes thick, sticky mucus to build up in the lungs, digestive tract, and other areas of the body. It is one of th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Familial Mediterranean fever
Familial Mediterranean fever
Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) is a rare disorder passed down through families (inherited). It involves repeated fevers and inflammation that of...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hairy cell leukemia
Hairy cell leukemia
Hairy cell leukemia (HCL) is an unusual cancer of the blood. It affects B cells, a type of white blood cell (lymphocyte).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hodgkin disease
Hodgkin disease
Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer of lymph tissue. Lymph tissue is found in the lymph nodes, spleen, liver, bone marrow, and other sites.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Juvenile chronic arthritis
-
Kidney dialysis
Kidney dialysis
Dialysis treats end-stage kidney failure. It removes harmful substances from the blood when the kidneys cannot. This article focuses on peritoneal d...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a blood cancer that starts in the plasma cells in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue found inside most bone...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Reiter syndrome
Reiter syndrome
Reactive arthritis is a group of conditions that may involve the joints, eyes, and urinary and genital systems. These areas become swollen and infla...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term disease. It leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It can also affect other organs....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Sjogren syndrome
Sjogren syndrome
Sjögren syndrome is an autoimmune disorder in which the glands that produce tears and saliva are destroyed. This causes dry mouth and dry eyes. The...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
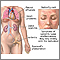
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. In this disease, the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. It can af...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
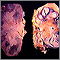
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs. It may spread to other organs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Symptoms of secondary systemic amyloidosis depend on which body tissue is affected by the protein deposits. These deposits damage normal tissues, leading to the symptoms or signs of this illness:
- Bleeding in the skin
-
Fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
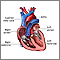
Irregular heartbeat
Irregular heartbeat
Palpitations are feelings or sensations that your heart is pounding or racing. They can be felt in your chest, throat, or neck. You may:Have an unpl...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Numbness
of hands and feet
Numbness
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Rash
-
Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathingUncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swallowing difficulties
- Swollen arms or legs
- Swollen tongue
- Weak hand grip
- Weight loss
Exams and Tests
Tests that may be done include:
-
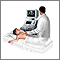
Abdominal ultrasound
(may show a swollen liver or spleen)
Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, and...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Biopsy or
aspiration
of fat just beneath the skin (subcutaneous fat)
Aspiration
Aspiration means to draw in or out using a sucking motion. It has two meanings:Breathing in a foreign object (sucking food into the airway). A medic...
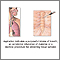 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Biopsy of rectum
Biopsy of rectum
A rectal biopsy is a procedure to remove a small piece of tissue from the rectum for examination.
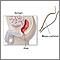 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Biopsy of skin
Biopsy of skin
A skin lesion biopsy is when a small amount of skin is removed so it can be examined. The skin is tested to look for skin conditions or diseases. A...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Biopsy of bone marrow
Biopsy of bone marrow
A bone marrow biopsy is the removal of marrow from inside bone. Bone marrow is the soft tissue inside bones that helps form blood cells. It is foun...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blood tests, including
creatinine
and
BUN
Creatinine
The creatinine blood test measures the level of creatinine in the blood. This test is done to see how well your kidneys are working. Creatinine can ...
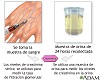 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleBUN
BUN stands for blood urea nitrogen. Urea nitrogen is what forms when protein breaks down. A test can be done to measure the amount of urea nitrogen ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Echocardiogram
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
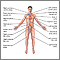 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Electrocardiogram (
ECG
)
ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Nerve conduction velocity
Nerve conduction velocity
Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a test to see how fast electrical signals move through a nerve.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
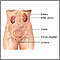 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The condition that is causing the amyloidosis should be treated. In some cases, the drug colchicine or a biologic drug (medicine that treats the immune system) is prescribed.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well a person does depends on which organs are affected and whether the disease that is causing it can be controlled. If the disease involves the heart and kidneys, it may lead to organ failure and death.
Possible Complications
Health problems that may result from secondary systemic amyloidosis include:
-
Endocrine
failure
Endocrine
Endocrine glands release (secrete) hormones into the bloodstream. The endocrine glands include:AdrenalHypothalamusIslets of Langerhans in the pancrea...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Heart failure
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
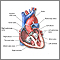 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Kidney failure
Kidney failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...
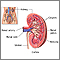 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Respiratory
failure
Respiratory
The words "respiratory" and "respiration" refer to the lungs and breathing.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you have symptoms of this condition. The following are serious symptoms that need prompt medical attention:
- Bleeding
- Irregular heartbeat
- Numbness
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling
- Weak grip
Prevention
If you have a disease that is known to increase your risk for this condition, make sure you get it treated. This may help prevent amyloidosis.
References
Gertz MA. Amyloidosis. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 188.
-
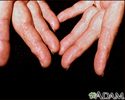
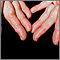
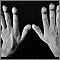
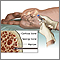
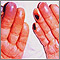
Amyloidosis on the fingers - illustration
Amyloidosis refers to the extracellular deposition of a protein called amyloid. This protein deposition can affect multiple organs. The deposition of amyloid may be a by-product of normal aging, or may occur with several other conditions. In this picture, we see how amyloidosis can affect the skin as nodular deposits on the fingers.
Amyloidosis on the fingers
illustration
-
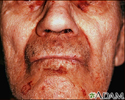
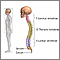
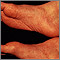
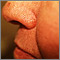
Amyloidosis on the face - illustration
Amyloidosis refers to deposits of a protein (called amyloid) in the tissues. This condition can affect multiple organs. The deposition of amyloid may be a by-product of normal aging. In this picture, we see how amyloidosis can cause a patchy, bruised appearance to the skin. Bruises of the skin around the eyes are referred to as the characteristic "pinched purpura".
Amyloidosis on the face
illustration
-
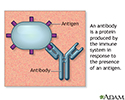
Antibodies - illustration
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
Antibodies
illustration
-
Amyloidosis on the fingers - illustration
Amyloidosis refers to the extracellular deposition of a protein called amyloid. This protein deposition can affect multiple organs. The deposition of amyloid may be a by-product of normal aging, or may occur with several other conditions. In this picture, we see how amyloidosis can affect the skin as nodular deposits on the fingers.
Amyloidosis on the fingers
illustration
-
Amyloidosis on the face - illustration
Amyloidosis refers to deposits of a protein (called amyloid) in the tissues. This condition can affect multiple organs. The deposition of amyloid may be a by-product of normal aging. In this picture, we see how amyloidosis can cause a patchy, bruised appearance to the skin. Bruises of the skin around the eyes are referred to as the characteristic "pinched purpura".
Amyloidosis on the face
illustration
-
Antibodies - illustration
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
Antibodies
illustration
-
Amyloidosis
(Alt. Medicine)
Review Date: 5/3/2015
Reviewed By: Laura J. Martin, MD, MPH, ABIM Board Certified in Internal Medicine and Hospice and Palliative Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.