Bronchiectasis
Acquired bronchiectasis; Congenital bronchiectasis; Chronic lung disease - brochiectasis
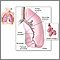
Bronchiectasis is a disease in which the large airways in the lungs are damaged. This causes the airways to become wider.
Bronchiectasis can be present at birth or infancy or develop later in life.
Causes
Bronchiectasis is often caused by inflammation or infection of the airways that keeps coming back.
Sometimes it begins in childhood after having a severe lung infection or inhaling a foreign object . Breathing in food particles can also lead to this condition.
Inhaling a foreign object
If you breathe a foreign object into your nose, mouth, or respiratory tract, it may become stuck and cause breathing problems or choking. It can als...
Other causes of bronchiectasis can include:
-
Cystic fibrosis
, a disease that causes thick, sticky mucus to build up in the lungs
Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is a disease that causes thick, sticky mucus to build up in the lungs, digestive tract, and other areas of the body. It is one of th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis or
Crohn disease
Crohn disease
Crohn disease is a disease where parts of the digestive tract become inflamed. It most often involves the lower end of the small intestine and the be...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Allergic lung diseases
- Leukemia and related cancers
Symptoms
Symptoms develop over time. They may occur months or years after the event that causes the bronchiectasis.
Long-term (chronic) cough with large amounts of foul smelling sputum is the main symptom of bronchiectasis. Other symptoms may include:
-
Breath odor
Breath odor
Breath odor is the scent of the air you breathe out of your mouth. Unpleasant breath odor is commonly called bad breath.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
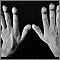
Clubbing
of fingers (rare)
Clubbing
Clubbing is changes in the areas under and around the toenails and fingernails that occur with some disorders. The nails also show changes.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Coughing up blood
Coughing up blood
Coughing up blood is the spitting up of blood or bloody mucus from the lungs and throat (respiratory tract). Hemoptysis is the medical term for cough...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Paleness
Paleness
Paleness is an abnormal loss of color from normal skin or mucous membranes.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Shortness of breath
that gets worse with exercise
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathingUncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Weight loss
Weight loss
Unexplained weight loss is a decrease in body weight, when you did not try to lose the weight on your own. Many people gain and lose weight. Uninten...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Wheezing
Wheezing
Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound during breathing. It occurs when air moves through narrowed breathing tubes in the lungs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Low grade fever and night sweats
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam. When listening to the chest with a stethoscope, the provider may hear small clicking, bubbling, wheezing, rattling, or other sounds, usually in the lower lungs.
Tests that may be done include:
- Aspergillosis precipitin test (to check for signs of an allergic reaction to fungus)
-
Alpha-1 antitrypsin blood test
Alpha-1 antitrypsin blood test
Alpha-1 antitrypsin is a laboratory test to measure the amount of alpha-1 antitrypsin (A1AT) in your blood.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
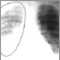
Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest CT
Chest CT
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Sputum culture
Sputum culture
Routine sputum culture is a laboratory test that looks for germs that cause infection. Sputum is the material that comes up from air passages when y...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Complete blood count
(CBC)
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The tota...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Genetic testing, including
sweat test
for cystic fibrosis and tests for other diseases
Sweat test
Sweat electrolytes is a test that measures the level of chloride in sweat. Sweat chloride test is the standard test used to diagnose cystic fiborsis...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
PPD skin test
to check for a past tuberculosis infection
PPD skin test
The PPD skin test is a method used to diagnose silent (latent) tuberculosis (TB) infection. PPD stands for purified protein derivative.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Serum immunoglobulin electrophoresis
to measure proteins called immunoglobulins in the blood
Serum immunoglobulin electrophoresis
Serum immunoelectrophoresis is a lab test that measures proteins called immunoglobulins in the blood. Immunoglobulins are proteins that function as ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Lung function tests
to measure breathing and how well the lungs are functioning
Lung function tests
Pulmonary function tests are a group of tests that measure breathing and how well the lungs are functioning.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment is aimed at controlling infections and sputum, relieving airway blockage , and preventing the problem from becoming worse.
Airway blockage
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathingUncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air

Daily drainage to remove sputum is part of treatment. A respiratory therapist can show the person coughing exercises that will help.
Medicines are often prescribed. These include:
- Antibiotics to treat infections
- Bronchodilators to open up airways
- Expectorants to help loosen and cough up thick sputum
Surgery to remove ( resect ) the lung may be needed if medicine does not work and the disease is in a small area, or if the person has a lot of bleeding in the lungs.
Resect
Lung surgery is surgery done to repair or remove lung tissue. There are many common lung surgeries, including:Biopsy of an unknown growthLobectomy, ...
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outlook depends on the specific cause of the disease. With treatment, most people live without major disability.
Possible Complications
Complications of bronchiectasis may include:
-
Cor pulmonale
Cor pulmonale
Cor pulmonale is a condition that causes the right side of the heart to fail. Long-term high blood pressure in the arteries of the lung and right ve...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Coughing up blood
- Low oxygen levels (in severe cases)
-
Recurrent
pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a breathing (respiratory) condition in which there is an infection of the lung. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). ...
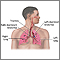 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Depression
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if:
-
Chest pain
or shortness of breath gets worse
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
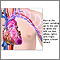 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - There is a change in the color or amount of phlegm you cough up, or if it is bloody
- Other symptoms get worse or do not improve with treatment
Prevention
You can reduce your risk by promptly treating lung infections.
Childhood vaccines and a yearly flu vaccine help reduce the chance of some infections. Avoiding upper respiratory infections, smoking, and pollution may also reduce your risk of getting this infection.
Vaccines
Vaccines are used to boost your immune system and prevent serious, life-threatening diseases.
References
Chan ED, Iseman MD. Bronchiectasis. In: Broaddus VC, Mason RJ, Ernst JD, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 48.
O'Donnell AE. Bronchiectasis, atelectasis, cysts, and localized lung disorders. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 90.
-
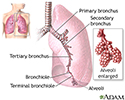
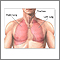
Lungs - illustration
The major features of the lungs include the bronchi, the bronchioles and the alveoli. The alveoli are the microscopic blood vessel-lined sacks in which oxygen and carbon dioxide gas are exchanged.
Lungs
illustration
-
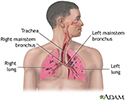
Respiratory system - illustration
Air is breathed in through the nasal passageways, travels through the trachea and bronchi to the lungs.
Respiratory system
illustration
-
Lungs - illustration
The major features of the lungs include the bronchi, the bronchioles and the alveoli. The alveoli are the microscopic blood vessel-lined sacks in which oxygen and carbon dioxide gas are exchanged.
Lungs
illustration
-
Respiratory system - illustration
Air is breathed in through the nasal passageways, travels through the trachea and bronchi to the lungs.
Respiratory system
illustration
Review Date: 8/21/2016
Reviewed By: Denis Hadjiliadis, MD, MHS, Paul F. Harron, Jr. Associate Professor of Medicine, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.