Poisoning first aid
Poisoning is caused by exposure to a harmful substance. This can be due to swallowing, injecting, breathing in, or other means. Most poisonings occur by accident.
Immediate first aid is very important in a poisoning emergency. The first aid you give before getting medical help can save a person's life.
This article is for information only. DO NOT use it to treat or manage an actual poison exposure. If you or someone you are with has an exposure, call your local emergency number (such as 911), or your local poison center can be reached directly by calling the national toll-free Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) from anywhere in the United States.
Considerations
Millions of poisonings are reported to United States poison control centers every year. Many result in death.
It is important to note that just because a package does not have a warning label does not mean a substance is safe. You should consider poisoning if someone suddenly becomes sick for no apparent reason. Poisoning should also be considered if the person is found near a furnace, car, fire, or in an area that is not well ventilated.
Symptoms of poisoning may take time to develop. However, if you think someone has been poisoned, DO NOT wait for symptoms to develop. Get medical help right away.
Causes
Items that can cause poisoning include:
- Carbon monoxide gas (from furnaces, gas engines, fires, space heaters)
-
Certain foods
Certain foods
Food poisoning occurs when you swallow food or water that contains bacteria, parasites, viruses, or the toxins made by these germs. Most cases are c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chemicals in the workplace
-
Drugs, including over-the-counter and prescription medicines (such as an
aspirin overdose
) and illicit drugs such as cocaine
Aspirin overdose
An overdose of aspirin means you have too much aspirin in your body. This can happen in two ways:If a person accidentally or intentionally takes a ve...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Household
detergents
and cleaning products
Detergents
Detergents are powerful cleaning products that may contain strong acids, alkalis, or phosphates. Cationic detergents are often used as germ-killing ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Household and outdoor plants (eating toxic plants)
-
Insecticides
Insecticides
Insecticide is a chemical that kills bugs. Insecticide poisoning occurs when someone swallows or breathes in this substance or it is absorbed throug...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Paints
Symptoms
Symptoms vary according to the poison, but may include:
-
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bluish lips
-
Chest pain
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Confusion
-
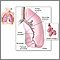
Cough
Cough
Coughing is an important way to keep your throat and airways clear. But too much coughing may mean you have a disease or disorder. Some coughs are d...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Diarrhea
-
Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
Difficulty breathing or shortness of br...
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathingUncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Dizziness
Dizziness
Dizziness is a term that is often used to describe 2 different symptoms: lightheadedness and vertigo. Lightheadedness is a feeling that you might fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Double vision
Double vision
There are many types of eye problems and vision disturbances, such as: HalosBlurred vision (the loss of sharpness of vision and the inability to see ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Drowsiness
Drowsiness
Drowsiness refers to feeling abnormally sleepy during the day. People who are drowsy may fall asleep in inappropriate situations or at inappropriate...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fever
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
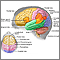
Headache
Headache
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
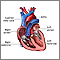
Heart palpitations
Heart palpitations
Palpitations are feelings or sensations that your heart is pounding or racing. They can be felt in your chest, throat, or neck. You may:Have an unpl...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Irritability
-
Loss of appetite
Loss of appetite
A decreased appetite is when your desire to eat is reduced. The medical term for a loss of appetite is anorexia.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
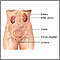
Loss of bladder control
Loss of bladder control
Urinary (or bladder) incontinence happens when you are not able to keep urine from leaking out of your urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Muscle twitching
Muscle twitching
Muscle twitches are fine movements of a small area of muscle.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up is forcing the contents of the stomach ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Numbness and tingling
Numbness and tingling
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical findings or changes in behavior that occur after an episode of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term "seizure...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Skin rash
or
burns
Skin rash
Rashes involve changes in the color, feeling or texture of your skin.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleBurns
Burns commonly occur by direct or indirect contact with heat, electric current, radiation, or chemical agents. Burns can lead to cell death....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Stupor
Stupor
Decreased alertness is a state of reduced awareness. A coma is a state of decreased alertness from which a person cannot be awakened. A long-term co...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Unconsciousness
Unconsciousness
Unconsciousness is when a person is unable to respond to people and activities. Doctors often call this a coma or being in a comatose state. Other c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Unusual
breath odor
Breath odor
Breath odor is the scent of the air you breathe out of your mouth. Unpleasant breath odor is commonly called bad breath.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Weakness
First Aid
Seek immediate medical help.
For poisoning by swallowing:
Check and monitor the person's airway, breathing, and pulse. If necessary, begin rescue breathing and CPR .
CPR
CPR stands for cardiopulmonary resuscitation. It is an emergency lifesaving procedure that is done when someone's breathing or heartbeat has stopped...
- Try to make sure that the person has indeed been poisoned. It may be hard to tell. Some signs include chemical-smelling breath, burns around the mouth, difficulty breathing, vomiting, or unusual odors on the person. If possible, identify the poison.
- DO NOT make a person throw up unless told to do so by poison control or a health care professional.
- If the person vomits, clear the person's airway. Wrap a cloth around your fingers before cleaning out the mouth and throat. If the person has been sick from a plant part, save the vomit. It may help experts identify what medicine can be used to help reverse the poisoning.
-
If the person starts having convulsions, give
convulsion first aid
.
Convulsion first aid
A seizure is the physical findings or changes in behavior that occur after an episode of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term "seizure...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Keep the person comfortable. The person should be rolled onto the left side, and remain there while getting or waiting for medical help.
- If the poison has spilled on the person's clothes, remove the clothing and flush the skin with water.
For inhalation poisoning:
Call for emergency help. Never attempt to rescue a person without notifying others first.
- If it is safe to do so, rescue the person from the danger of the gas, fumes, or smoke. Open windows and doors to remove the fumes.
- Take several deep breaths of fresh air, and then hold your breath as you go in. Hold a wet cloth over your nose and mouth.
- DO NOT light a match or use a lighter because some gases can catch fire.
- After rescuing the person from danger, check and monitor the person's airway, breathing, and pulse. If necessary, begin rescue breathing and CPR.
-
If necessary, perform
first aid for eye injuries
or convulsion first aid.
First aid for eye injuries
Eye emergencies include cuts, scratches, objects in the eye, burns, chemical exposure, and blunt injuries to the eye or eyelid. Certain eye infectio...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - If the person vomits, clear the person's airway. Wrap a cloth around your fingers before cleaning out the mouth and throat.
- Even if the person seems perfectly fine, get medical help.
Do Not
DO NOT:
- Give an unconscious person anything by mouth.
- Induce vomiting unless you are told to do so by the Poison Control Center or a doctor. A strong poison that burns on the way down the throat will also do damage on the way back up.
- Try to neutralize the poison with lemon juice or vinegar, or any other substance, unless you are told to do so by the Poison Control Center or a doctor.
- Use any "cure-all" type antidote.
- Wait for symptoms to develop if you suspect that someone has been poisoned.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Your local poison center can be reached directly by calling the national toll-free Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) from anywhere in the United States. They will give you further instructions.
Poison Help hotline
For a POISON EMERGENCY call:1-800-222-1222ANYWHERE IN THE UNITED STATESThis national hotline number will let you talk to experts in poisoning. This ...

This is a free and confidential service. All local poison control centers in the United States use this national number. You should call if you have any questions about poisoning or poison prevention. It does not need to be an emergency. You can call for any reason, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
After doing first aid steps at home, you may need to go to the emergency room. Take the container with you to the hospital, if possible. At the hospital you will have an exam. You also may need the following tests and treatments.
- Activated charcoal
- Airway support, including oxygen, breathing tube through the mouth (intubation),and ventilator (breathing machine)
- Blood and urine tests
- Chest x-ray
- CT (computerized tomography, or advanced imaging) scan
- EKG (electrocardiogram, or heart tracing)
- Fluids through the vein (IV)
- Laxative
- Medicines to treat symptoms, including antidotes to reverse the effects of the poisoning if one exists
Prevention
Be aware of poisons in and around your home. Take steps to protect young children from toxic substances. Store all medicines , cleaners, cosmetics, and household chemicals out of reach of children, or in cabinets with childproof latches.
Protect young children
Most American children live healthy lives. Car seats, safe cribs, and strollers help protect your child in and near the home. Yet, parents and care...

Be familiar with plants in your home, yard, and vicinity. Keep your children informed, too. Remove any poisonous plants. Never eat wild plants, mushrooms, roots, or berries unless you very familiar with them.
Teach children about the dangers of substances that contain poison. Label all poisons.
DO NOT store household chemicals in food containers, even if they are labeled. Most nonfood substances are poisonous if taken in large doses.
If you are concerned that industrial poisons might be polluting nearby land or water, report your concerns to the local health department or the state or federal Environmental Protection Agency.
References
Kulig K. General approach to the poisoned patient. In: Marx JA, Hockberger RS, Walls RM, et al., eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2014:chap 147.
Mowry JB, Spyker DA, Cantilena LR Jr, McMillan N, Ford M. 2013 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers' National Poison Data System (NPDS): 31st Annual Report. Clin Toxicol (Phila) . 2014 Dec;52(10):1032-283. PMID: 25559822 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25559822 .
-
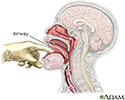
Check airway - illustration
After rescuing a victim from danger, check their airway, breathing and circulation. If there is a visible obstruction of the upper airway which can be removed easily, then follow the procedure for doing so; once that has been accomplished, follow the most recent guidelines for CPR.
Check airway
illustration
-
Check airway - illustration
After rescuing a victim from danger, check their airway, breathing and circulation. If there is a visible obstruction of the upper airway which can be removed easily, then follow the procedure for doing so; once that has been accomplished, follow the most recent guidelines for CPR.
Check airway
illustration
-
Food poisoning
(Alt. Medicine)
Review Date: 1/26/2015
Reviewed By: Jacob L. Heller, MD, MHA, emergency medicine, Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.