Upper GI and small bowel series
GI series; Barium swallow x-ray; Upper GI series
An upper GI and small bowel series is a set of x-rays taken to examine the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine.
x-rays
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray particles through the body. The im...

Barium enema is a related test.
Barium enema
Barium enema is a special x-ray of the large intestine, which includes the colon and rectum.
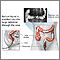
How the Test is Performed
An upper GI and small bowel series is done in a health care office or hospital radiology department.
You may get an injection of a medicine that slows muscle movement in the small intestine. This makes it easier to see the structures of your organs on the x-rays.
Before the x-rays are taken, you must drink 16 to 20 ounces (480 to 600 milliliters) of a milkshake-like drink. The drink contains a substance called barium, which shows up well on x-rays.
An x-ray method called fluoroscopy tracks how the barium moves through your esophagus, stomach, and small intestine. Pictures are taken while you sit or stand in different positions.
The test most often takes around 3 hours but can take as long as 6 hours to complete.
A GI series may include this test or a barium enema.
How to Prepare for the Test
You may have to change your diet for 2 or 3 days before the test. In most cases, you will not be able to eat for a period of time before the test.
Be sure to ask your health care provider if you need to change how you take any of your medicines. Often you can continue taking the medicines you take by mouth. Never make any changes in your medicines without first talking to your provider.
You will be asked to remove all jewelry on your neck, chest, or abdomen before the test.
How the Test will Feel
The x-ray may cause mild bloating but no discomfort most of the time. The barium milkshake feels chalky as you drink it.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to look for a problem in the structure or function of your esophagus, stomach, or small intestine.
Normal Results
A normal result shows that the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine are normal in size, shape, and movement.
Normal value ranges may vary depending on the lab doing the test. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results in the esophagus may indicate the following problems:
-
Achalasia
Achalasia
The tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach is the esophagus. Achalasia makes it harder for the esophagus to move food into the stomach...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Diverticula
Diverticula
Diverticula are small, bulging sacs or pouches that form on the inner wall of the intestine. Diverticulitis occurs when these pouches become inflame...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer is cancer that starts in the esophagus. This is the tube that moves food from the mouth to the stomach.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Esophageal narrowing (stricture) - benign
Esophageal narrowing (stricture) - beni...
Benign esophageal stricture is a narrowing of the esophagus (the tube from the mouth to the stomach). It causes swallowing difficulties. Benign mean...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hiatal hernia
Hiatal hernia
Hiatal hernia is a condition in which part of the stomach extends through an opening of the diaphragm into the chest. The diaphragm is the sheet of ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Ulcers
Ulcers
An ulcer is a crater-like sore on the skin or mucous membrane. Ulcers form when the top layers of skin or tissue have been removed. They can occur ...
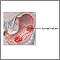 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Abnormal results in the stomach may indicate the following problems:
-
Gastric cancer
Gastric cancer
Stomach cancer is cancer that starts in the stomach.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Gastric ulcer
- benign
Gastric ulcer
A peptic ulcer is an open sore or raw area in the lining of the stomach or intestine. A gastric ulcer occurs in the stomach. A duodenal ulcer occurs ...
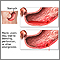 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Gastritis
Gastritis
Gastritis occurs when the lining of the stomach becomes inflamed or swollen. Gastritis can last for only a short time (acute gastritis). It may als...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Polyps (a tumor that is usually noncancerous and grows on the
mucus membrane
)
Mucus membrane
Mucosa is moist tissue that lines certain parts of the inside of your body. It is in your: NoseMouthLungsUrinary and digestive tracts Glands in this...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pyloric stenosis
(narrowing)
Pyloric stenosis
Pyloric stenosis is a narrowing of the pylorus, the opening from the stomach into the small intestine. This article describes the condition in infan...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Abnormal results in the stomach may indicate the following problems:
-
Malabsorption
syndrome
Malabsorption
Malabsorption involves problems with the body's ability to take in nutrients from food.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swelling and irritation of the small intestines
- Tumors
- Ulcers
The test may also be done for the following conditons:
-
Annular pancreas
Annular pancreas
An annular pancreas is a ring of pancreatic tissue that encircles the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). The normal position of the p...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Duodenal ulcer
Duodenal ulcer
A peptic ulcer is an open sore or raw area in the lining of the stomach or intestine. A gastric ulcer occurs in the stomach. A duodenal ulcer occurs ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a condition in which the stomach contents leak backwards from the stomach into the esophagus (the tube from...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Gastroparesis
Gastroparesis
Gastroparesis is a condition that reduces the ability of the stomach to empty its contents. It does not involve a blockage (obstruction).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Intestinal obstruction
Intestinal obstruction
Intestinal obstruction is a partial or complete blockage of the bowel. The contents of the intestine cannot pass through it.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Lower esophageal ring
Lower esophageal ring
A lower esophageal ring is an abnormal ring of tissue that forms where the esophagus (the tube from the mouth to the stomach) and stomach meet....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Primary or idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction
Primary or idiopathic intestinal pseudo...
Intestinal pseudo-obstruction is a condition in which there are symptoms of blockage of the intestine (bowels) without any physical blockage....
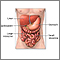 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
You are exposed to a low level of radiation during this test, which carries a very small risk of cancer. X-rays are monitored and regulated to provide the minimum amount of radiation exposure needed to produce the image. Most experts feel that the risk is low compared with the benefits.
Pregnant women should not have this test in most cases. Children are more sensitive to the risks of x-rays.
Barium may cause constipation. Talk to your provider if the barium has not passed through your system by 2 or 3 days after the exam.
Considerations
The upper GI series should be done after other x-ray procedures, because the barium that remains in the body may block details in other imaging tests.
References
Caroline DF, Dass C, Agusto O. In: Adam A, Dixon AK, eds. Grainger & Allison's Diagnostic Radiology: A Textbook of Medical Imaging . 6th ed. New York, NY: Churchill Livingstone; 2015:chap 27.
Kim DH, Pickhardt PJ. Diagnostic imaging procedures in gastroenterology. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2011:chap 135.
-
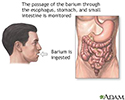
Barium ingestion - illustration
An upper GI series is performed to examine the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine. The purpose of the test is to detect abnormalities in those areas.
Barium ingestion
illustration
-
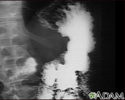
Stomach cancer, X-ray - illustration
An upper GI series in a patient with cancer of the stomach (gastric carcinoma).
Stomach cancer, X-ray
illustration
-
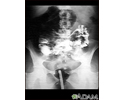
Stomach ulcer, X-ray - illustration
This is an example of a procedure called an upper GI series. The person swallows a substance called barium which allows for illumination of the organs in question. In this case, an ulceration is present in the stomach, seen on the right of the screen. This method is a means of diagnosing stomach ulcers as well as other anomalies along the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Stomach ulcer, X-ray
illustration
-
Volvulus - X-ray - illustration
A GI series in a patient with a twisted bowel (volvulus).
Volvulus - X-ray
illustration
-
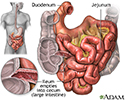
Small intestine - illustration
The small intestine is the portion of the digestive system most responsible for absorption of nutrients from food into the bloodstream. The pyloric sphincter governs the passage of partly digested food from the stomach into the duodenum. This short first portion of the small intestine is followed by the jejunum and the ileum. The ileocecal valve of the ileum passes digested material into the large intestine.
Small intestine
illustration
-
Barium ingestion - illustration
An upper GI series is performed to examine the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine. The purpose of the test is to detect abnormalities in those areas.
Barium ingestion
illustration
-
Stomach cancer, X-ray - illustration
An upper GI series in a patient with cancer of the stomach (gastric carcinoma).
Stomach cancer, X-ray
illustration
-
Stomach ulcer, X-ray - illustration
This is an example of a procedure called an upper GI series. The person swallows a substance called barium which allows for illumination of the organs in question. In this case, an ulceration is present in the stomach, seen on the right of the screen. This method is a means of diagnosing stomach ulcers as well as other anomalies along the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Stomach ulcer, X-ray
illustration
-
Volvulus - X-ray - illustration
A GI series in a patient with a twisted bowel (volvulus).
Volvulus - X-ray
illustration
-
Small intestine - illustration
The small intestine is the portion of the digestive system most responsible for absorption of nutrients from food into the bloodstream. The pyloric sphincter governs the passage of partly digested food from the stomach into the duodenum. This short first portion of the small intestine is followed by the jejunum and the ileum. The ileocecal valve of the ileum passes digested material into the large intestine.
Small intestine
illustration
Review Date: 11/20/2014
Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Frankford-Torresdale Hospital, Aria Health System, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.