Esophageal stricture - benign
Benign esophageal stricture is a narrowing of the esophagus (the tube from the mouth to the stomach). It causes swallowing difficulties.
Benign means that it is not caused by cancer of the esophagus .
Cancer of the esophagus
Esophageal cancer is cancer that starts in the esophagus. This is the tube that moves food from the mouth to the stomach.

Causes
Esophageal stricture can be caused by:
-
Gastroesophageal reflux
(GERD).
Gastroesophageal reflux
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a condition in which the stomach contents leak backwards from the stomach into the esophagus (the tube from...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Eosinophilic esophagitis.
-
Injuries caused by an
endoscope
.
Endoscope
An endoscope is a medical device with a light attached. It is used to look inside a body cavity or organ. The scope is inserted through a natural o...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Long-term use of a nasogastric (NG) tube (tube through the nose into the stomach).
- Swallowing substances that harm the lining of the esophagus. These may include household cleaners, lye, disc batteries, or battery acid.
-
Treatment of
esophageal varices
.
Esophageal varices
The esophagus is the tube that connects your throat to your stomach. Varices are enlarged veins that may be found in the esophagus. These veins may...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Trouble swallowing
-
Pain with swallowing
Pain with swallowing
Swallowing pain is any pain or discomfort while swallowing. You may feel it high in the neck or lower down behind the breastbone. Most often, the p...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Unintentional weight loss
Unintentional weight loss
Unexplained weight loss is a decrease in body weight, when you did not try to lose the weight on your own. Many people gain and lose weight. Uninten...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Regurgitation of food
Exams and Tests
You may need the following tests:
-
Barium swallow
to look for narrowing of the esophagus
Barium swallow
An upper GI and small bowel series is a set of x-rays taken to examine the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine. Barium enema is a related test....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Endoscopy
to look for narrowing of the esophagus
Endoscopy
Endoscopy is a way of looking inside the body using a flexible tube that has a small camera and light on the end of it. This instrument is called an...
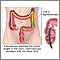 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Dilation (stretching) of the esophagus is the main treatment for acid reflux related strictures. You may need to have this treatment repeated after a period of time to prevent the stricture from narrowing again.
Proton pump inhibitors (acid-blocking medicines) can keep a peptic stricture from returning. Surgery is rarely needed.
If you have eosinophilic esophagitis, you may need to take medicines or make changes to your diet to reduce the inflammation. In some cases, dilation is done.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The stricture may come back in the future. This would require a repeat dilation.
Possible Complications
Swallowing problems may keep you from getting enough fluids and nutrients. Solid food, especially meat, can get stuck above the stricture. If this happens, endoscopy would be needed to remove the lodged food.
There is also a higher risk of having food, fluid, or vomit enter the lungs with regurgitation. This can cause choking or aspiration pneumonia .
Aspiration pneumonia
Pneumonia is a breathing condition in which there is swelling or an infection of the lungs or large airways. Aspiration pneumonia occurs when food, ...

When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you have swallowing problems that do not go away.
Prevention
Use safety measures to avoid swallowing substances that can harm your esophagus. Keep dangerous chemicals out of the reach of children. See your provider if you have GERD.
References
Penman ID, Lees CW. Alimentary tract and pancreatic disease. In: Walker BR, Colledge NR, Ralston SH, Penman ID, eds. Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine . 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone; 2014:chap 22.
Pfau PR, Hancock SM. Foreign bodies, bezoards, and caustic ingestions. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 27.
Ricthter JE, Friendenberg FK. Gastroesophageal reflux disease. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 44.
-
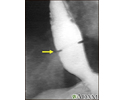
Schatzki ring - x-ray - illustration
A solution containing a dye (barium), which is visible on x-rays, has been swallowed (upper GI series) and x-rays have been taken of the esophagus. There is a narrowing near the stomach (indicated by the arrow). This non-cancerous ring of tissue (Shatzki ring) may cause swallowing problems (dysphagia) and can be treated with dilation of the stricture.
Schatzki ring - x-ray
illustration
-
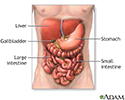
Digestive system organs - illustration
The digestive system organs in the abdominal cavity include the liver, gallbladder, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.
Digestive system organs
illustration
-
Schatzki ring - x-ray - illustration
A solution containing a dye (barium), which is visible on x-rays, has been swallowed (upper GI series) and x-rays have been taken of the esophagus. There is a narrowing near the stomach (indicated by the arrow). This non-cancerous ring of tissue (Shatzki ring) may cause swallowing problems (dysphagia) and can be treated with dilation of the stricture.
Schatzki ring - x-ray
illustration
-
Digestive system organs - illustration
The digestive system organs in the abdominal cavity include the liver, gallbladder, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.
Digestive system organs
illustration
Review Date: 8/2/2016
Reviewed By: Raymond S. Koff, MD, Clinical Professor of Medicine, University of Connecticut School of Medicine, Farmington, CT. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.