Esophageal culture
Culture - esophageal
Esophageal culture is a laboratory test that checks for infection-causing germs in a sample of tissue from the esophagus.
How the Test is Performed
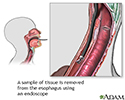
A sample of tissue from your esophagus is needed. The sample is taken during a procedure called esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) .
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a test to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and first part of the small intestine.
The sample is sent to a lab. There, it is placed in a special dish (culture) and watched for the growth of bacteria, fungi, or viruses.
Other tests may be done to determine what medicine can best treat the organism.
How to Prepare for the Test
Follow your health care provider's instructions on how to prepare for EGD.
How the Test will Feel
During EGD, you will receive medicine to relax you. You may have some discomfort or feel like gagging as the endoscope is passed through your mouth and throat into the esophagus. This feeling will go away shortly.
Why the Test is Performed
Your doctor may order this test if you have signs or symptoms of an esophageal infection or disease. You may also have the test if an ongoing infection does not get better with treatment.
Normal Results
A normal result means that no germs grew in the laboratory dish.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal result means germs grew in the laboratory dish. This is a sign of an infection of the esophagus, which may be due to bacteria, a virus, or a fungus.
Risks
Risks are related to the EGD procedure. Your health care provider can explain these risks.
References
Graman PS. Esophagitis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 99.
Katzka DA. Esophageal disorders caused by medications, trauma, and infection. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 46.
-
Esophageal tissue culture - illustration
A sample biopsy of esophageal tissue is obtained by placing a tube through the mouth into the esophagus where small instruments grab a portion of esophageal tissue for examination. The test is performed when infection or other diseases of the esophagus are suspected, or an ongoing infection does not respond to treatment.
Esophageal tissue culture
illustration
-
Esophageal tissue culture - illustration
A sample biopsy of esophageal tissue is obtained by placing a tube through the mouth into the esophagus where small instruments grab a portion of esophageal tissue for examination. The test is performed when infection or other diseases of the esophagus are suspected, or an ongoing infection does not respond to treatment.
Esophageal tissue culture
illustration
Review Date: 8/20/2015
Reviewed By: Subodh K. Lal, MD, gastroenterologist at Gastrointestinal Specialists of Georgia, Austell, GA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.