Esophagitis - infectious
Infection - esophagus; Esophageal infection
Esophagitis is a general term for any inflammation, irritation, or swelling of the esophagus. This is the tube that carries food and liquids from the mouth to the stomach.
Causes
Infectious esophagitis is rare. It often occurs in people whose immune systems are weakened. People who have strong immune systems don't usually develop the infection.
Common causes of a weakened immune system include:
-
HIV/
AIDS
AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes AIDS. When a person becomes infected with HIV, the virus attacks and weakens the immune ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Diabetes
Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Leukemia
or lymphoma
Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of blood cancer that begins in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft tissue in the center of the bones, where blood cells are ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Medicines that suppress the immune system, such as ones given after organ or bone marrow transplant
- Other conditions that suppress or weaken your immune system
Organisms (germs) that cause esophagitis include fungi, yeast, and viruses. Common organisms include:
- Candida albicans
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
- Human papillomavirus (HPV)
- Tuberculosis bacteria
Symptoms
Symptoms of esophagitis include:
- Difficulty swallowing and painful swallowing
- Fever and chills
-
Yeast infection of the tongue and lining of the mouth (
oral thrush
)
Oral thrush
Thrush is a yeast infection of the tongue and lining of the mouth.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sores in the mouth or back of the throat (with herpes or CMV)
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will ask about your symptoms and examine your mouth and throat. Tests may include:
- Blood and urine tests for CMV
- Culture of cells from the esophagus for herpes or CMV
- Mouth or throat swab culture for candida
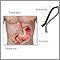
You may need to have an upper endoscopy exam . This is a test to examine the lining of the esophagus.
Upper endoscopy exam
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a test to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and first part of the small intestine.
Treatment
In most people with esophagitis, medicines can control the infection. These include:
- Antiviral medicines such as acyclovir, famciclovir, or valacyclovir can treat a herpes infection.
- Antifungal medicines such as fluconazole (taken by mouth), caspofungin (given by injection), or amphotericin (given by injection) can treat candida infection.
- Antiviral medicines that are given through a vein (intravenously), such as ganciclovir or foscarnet can treat CMV infection. In some cases, a medicine called valganciclovir, which is taken by mouth, can be used for CMV infection.
Some people may also need pain medicine.
Ask your provider for special diet recommendations. For example, there may be foods you need to avoid eating as your esophagitis heals.
Many people who are treated for an episode of infectious esophagitis need other, long-term medicines to suppress the virus or fungus, and to prevent the infection from coming back.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Esophagitis can usually be treated effectively and usually heals in 3 to 5 days. People with a weakened immune system may take longer to get better.
Possible Complications
Health problems that may result from infectious esophagitis include:
- Holes in your esophagus (perforations)
- Infection at other sites
- Recurrent infection
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if you have any condition that can cause reduced immune response and you develop symptoms of infectious esophagitis.
Immune response
The immune response is how your body recognizes and defends itself against bacteria, viruses, and substances that appear foreign and harmful....

Prevention
If you have a weakened immune system, try to avoid contact with people who have an infection with any of the organisms mentioned above.
References
Graman PS. Esophagitis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 99.
Katzka DA. Esophageal disorders caused by medications, trauma, and infection. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 46.
-
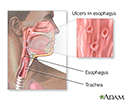
Herpetic esophagitis - illustration
Herpetic esophagitis is a herpes simplex infection causing inflammation and ulcers of the esophagus. Symptoms include difficulty swallowing and pain (dysphagia). Herpetic esophagitis can be effectively treated with antiviral medication if the person is not significantly immunodeficient.
Herpetic esophagitis
illustration
-
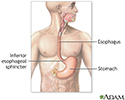
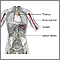
Upper gastrointestinal system - illustration
The upper gastrointestinal organs include the mouth, esophagus and stomach.
Upper gastrointestinal system
illustration
-
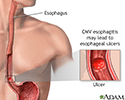
CMV esophagitis - illustration
Cytomegalovirus is a large herpes-type virus commonly found in humans that can cause serious infections in people with impaired immunity. CMV esophagitis, which may lead to ulcers, is treated with antiviral medications, which may stop the replication of the virus but will not destroy it.
CMV esophagitis
illustration
-
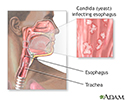
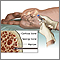
Candidal esophagitis - illustration
Painful swallowing and oral lesions are symptoms of Candidal esophagitis, a fungal infection of the esophagus. Candidal esophagitis is treated with antifungal medications. Recovery is dependent on extent of immunosuppression.
Candidal esophagitis
illustration
-
Herpetic esophagitis - illustration
Herpetic esophagitis is a herpes simplex infection causing inflammation and ulcers of the esophagus. Symptoms include difficulty swallowing and pain (dysphagia). Herpetic esophagitis can be effectively treated with antiviral medication if the person is not significantly immunodeficient.
Herpetic esophagitis
illustration
-
Upper gastrointestinal system - illustration
The upper gastrointestinal organs include the mouth, esophagus and stomach.
Upper gastrointestinal system
illustration
-
CMV esophagitis - illustration
Cytomegalovirus is a large herpes-type virus commonly found in humans that can cause serious infections in people with impaired immunity. CMV esophagitis, which may lead to ulcers, is treated with antiviral medications, which may stop the replication of the virus but will not destroy it.
CMV esophagitis
illustration
-
Candidal esophagitis - illustration
Painful swallowing and oral lesions are symptoms of Candidal esophagitis, a fungal infection of the esophagus. Candidal esophagitis is treated with antifungal medications. Recovery is dependent on extent of immunosuppression.
Candidal esophagitis
illustration
Review Date: 9/10/2015
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Assistant Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Assistant in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.