Culture - joint fluid
Joint fluid culture
Joint fluid culture is a laboratory test to detect infection-causing organisms in a sample of fluid surrounding a joint.
How the Test is Performed
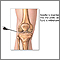
A sample of joint fluid is needed. This may be done in a doctor's office using a needle, or during an operating room procedure. Removing the sample is called joint fluid aspiration .
Joint fluid aspiration
Synovial fluid analysis is a group of tests that examine joint (synovial) fluid. The tests help diagnose and treat joint-related problems.
The fluid sample is sent to a laboratory where it is placed in a special dish and watched to see if bacteria, fungi, or viruses grow. This is called a culture.
If these germs are detected, other tests may be done to further identify the infection-causing substance and determine the best treatment.
How to Prepare for the Test
There is no special preparation needed for the lab culture. How to prepare for the removal of joint fluid .
Removal of joint fluid
Synovial fluid analysis is a group of tests that examine joint (synovial) fluid. The tests help diagnose and treat joint-related problems.

How the Test will Feel
The joint fluid culture is done in a laboratory and does not involve the person.
For information on how the procedure to remove joint fluid feels, see joint fluid aspiration .
Joint fluid aspiration
Synovial fluid analysis is a group of tests that examine joint (synovial) fluid. The tests help diagnose and treat joint-related problems.

Why the Test is Performed
Your doctor may order this test if you have unexplained pain and inflammation of a joint or a suspected joint infection.
Normal Results
The test result is considered normal if no organisms (bacteria, fungi, or viruses) grow in the laboratory dish.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results are a sign of infection in the joint. Infections may include:
-
Bacterial arthritis
Bacterial arthritis
Septic arthritis is inflammation of a joint due to a bacterial or fungal infection. Septic arthritis that is due to the bacteria that cause gonorrhe...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fungal arthritis
Fungal arthritis
Fungal arthritis is swelling and irritation (inflammation) of a joint by a fungal infection. It is also called mycotic arthritis.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Gonococcal arthritis
Gonococcal arthritis
Gonococcal arthritis is inflammation of a joint due to a gonorrhea infection.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Turberculous arthritis
Risks
There are no risks to the patient associated with a lab culture. For risks related to the removal of joint fluid, see joint fluid aspiration .
Joint fluid aspiration
Synovial fluid analysis is a group of tests that examine joint (synovial) fluid. The tests help diagnose and treat joint-related problems.

References
Matteson EL, Osmon DR. Infections of bursae, joints, and bones. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2011:chap 280.
Ohl CA, Forster D. Infectious arthritis of native joints. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglass, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2014:chap 105.
-
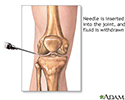
Joint aspiration - illustration
Synovial fluid analysis is a series of tests performed on synovial (joint) fluid to help diagnose and treat joint-related abnormalities. To obtain a synovial fluid sample, a needle is inserted into the knee between the joint space. When the needle is in place the synovial fluid is then withdrawn. The sample is sent to the lab for analysis.
Joint aspiration
illustration
-
Joint aspiration - illustration
Synovial fluid analysis is a series of tests performed on synovial (joint) fluid to help diagnose and treat joint-related abnormalities. To obtain a synovial fluid sample, a needle is inserted into the knee between the joint space. When the needle is in place the synovial fluid is then withdrawn. The sample is sent to the lab for analysis.
Joint aspiration
illustration
Review Date: 11/24/2014
Reviewed By: Daniel Levy, MD, PhD, Infectious Diseases, Lutherville Personal Physicians, Lutherville, MD. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.