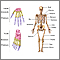
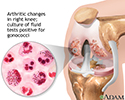
Gonococcal arthritis
Disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI); Disseminated gonococcemia
Gonococcal arthritis is inflammation of a joint due to a gonorrhea infection.
Causes
Gonococcal arthritis is an infection of a joint. It occurs in people who have gonorrhea caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae . Gonococcal arthritis affects women more often than men. It is most common among sexually active teen girls.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI).
There are two forms of gonococcal arthritis:
- One form involves skin rashes and many joints, usually large joints such as the knee, wrist, and ankle.
- The second, less common form involves the spread of the bacteria through the blood (disseminated gonococcemia), which leads to infection of a joint, sometimes more than one joint.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
-
Fever
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Lower
abdominal pain
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Joint pain for 1 to 4 days
- Pain in the hands or wrists due to tendon inflammation
-
Pain or burning during urination
Pain or burning during urination
Painful urination is any pain, discomfort, or burning sensation when passing urine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Single joint pain
- Skin rash (sores are slightly raised, pink to red, and may later contain pus or appear purple)
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical examination and ask about the symptoms.
Tests will be done to check for a gonorrhea infection. This may involve taking samples of tissue, stool, joint fluids, or other body material and sending them to a lab for examination under a microscope. Examples of such tests include:
-
Cervical gram stain
Cervical gram stain
Endocervical Gram stain is a method to identify bacteria on tissue from the cervix using a special series of stains.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Culture of joint aspirate
Culture of joint aspirate
Joint fluid culture is a laboratory test to detect infection-causing organisms in a sample of fluid surrounding a joint.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Joint fluid gram stain
Joint fluid gram stain
Joint fluid Gram stain is a laboratory test to identify bacteria in a sample of joint fluid using a special series of stains (colors). The Gram stai...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Throat culture
Throat culture
A throat swab culture is a laboratory test that is done to identify germs that may cause infection in the throat. It is most often used to diagnose ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urine test for gonorrhea
Treatment
The gonorrhea infection must be treated.
There are two aspects of treating a sexually transmitted disease, especially one as easily spread as gonorrhea. The first is to cure the infected person. The second is to locate, test, and treat all sexual contacts of the infected person. This is done to prevent further spread of the disease.
Some locations allow you to take counseling information and treatment to your partner(s) yourself. In other locations, the health department will contact your partner(s).
A treatment routine is recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Your provider will determine the best and most up-to-date treatment. A follow-up visit 7 days after treatment is important, if the infection was complicated, to recheck blood tests, and confirm that the infection was cured.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Symptoms usually improve within 1 to 2 days of starting treatment. Full recovery can be expected.
Possible Complications
Untreated, this condition may lead to persistent joint pain.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if you have symptoms of gonorrhea or gonococcal arthritis.
Prevention
Not having sexual intercourse (abstinence) is the only sure method to prevent gonorrhea. A monogamous sexual relationship with a person who you know does not have any sexually transmitted disease (STD) can reduce your risk. Monogamous means you and your partner do not have sex with any other people.
You can greatly lower your risk of infection with an STD by practicing safer sex. This means using a condom every time you have sex. Condoms are available for both men and women, but they are most commonly worn by the man. A condom must be used properly every time.
Treating all sexual partners is essential to prevent re-infection.
References
Cook PP, Siraj DS. Bacterial arthritis. In: Firestein GS, Budd RC, Gabriel SE, et al., eds. Kelly's Textbook of Rheumotology . 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2013:chap 109.
Marrazzo JM, Apicella MA. Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonnorrhea). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 215.
-
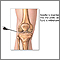
Gonoccocal arthritis - illustration
Gonococcal arthritis is an infection, usually of a single joint, that occurs following infection with gonorrhea. If the strain of bacteria is not antibiotic-resistant, recovery is expected.
Gonoccocal arthritis
illustration
Review Date: 5/1/2015
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Assistant Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Assistant in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.