Amylase - urine
This is a test that measures the amount of amylase in urine. Amylase is an enzyme that helps digest carbohydrates. It is produced mainly in the pancreas and the glands that make saliva.
Enzyme
Enzymes are complex proteins that cause a specific chemical change in all parts of the body. For example, they can help break down the foods we eat ...
Amylase may also be measured with a blood test .
Measured with a blood test
Amylase is an enzyme that helps digest carbohydrates. It is made in the pancreas and the glands that make saliva. When the pancreas is diseased or ...

How the Test is Performed
A urine sample is needed. The test may be performed using:
-
Clean-catch urine test
Clean-catch urine test
A urine culture is a lab test to check for bacteria or other germs in a urine sample. It can be used to check for a urinary tract infection in adults...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
24-hour urine collection
24-hour urine collection
The urine 24-hour volume test measures the amount of urine produced in a day. The amount of creatinine, protein, and other chemicals released into t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
How to Prepare for the Test
Many medicines can interfere with test results.
- Your health care provider will tell you if you need to stop taking any medicines before you have this test.
- DO NOT stop or change your medicines without talking to your provider first.
How the Test will Feel
The test involves only normal urination. There is no discomfort.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to diagnose pancreatitis and other diseases that affect the pancreas.
Normal Results
The normal range is 2.6 to 21.2 international units per hour (IU/h).
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
The example above shows the common measurement range for results for these tests. Some laboratories use different measurements or may test different specimens.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An increased amount of amylase in the urine is called amylasuria. Increased urine amylase levels may be a sign of:
-
Acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis is sudden swelling and inflammation of the pancreas.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Alcohol consumption
Alcohol consumption
Alcohol use involves drinking beer, wine, or hard liquor.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cancer of the pancreas
, ovaries, or lungs
Cancer of the pancreas
Pancreatic cancer is cancer that starts in the pancreas.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis is sudden swelling and irritation of the gallbladder. It causes severe belly pain.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Ectopic or ruptured
tubal pregnancy
Tubal pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy that occurs outside the womb (uterus). It is life-threatening to the mother.
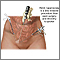 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Gallbladder disease
-
Infection of the salivary glands (called sialoadenitis, may be caused by
mumps
or a blockage)
Mumps
Mumps is a contagious disease that leads to painful swelling of the salivary glands. The salivary glands produce saliva, a liquid that moistens food...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Intestinal obstruction
Intestinal obstruction
Intestinal obstruction is a partial or complete blockage of the bowel. The contents of the intestine cannot pass through it.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pancreatic duct obstruction
Pancreatic duct obstruction
Bile duct obstruction is a blockage in the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder and small intestine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pelvic inflammatory disease
-
Perforated ulcer
Perforated ulcer
A peptic ulcer is an open sore or raw area in the lining of the stomach or intestine. A gastric ulcer occurs in the stomach. A duodenal ulcer occurs ...
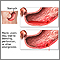 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Decreased amylase levels may be due to:
- Damage to the pancreas
- Kidney disease
-
Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer is cancer that starts in the pancreas.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Toxemia of pregnancy
Toxemia of pregnancy
Preeclampsia is when a pregnant woman develops high blood pressure and protein in the urine after the 20th week of pregnancy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Forsmark CE. Pancreatitis. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 144.
-
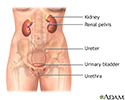
Female urinary tract - illustration
The female and male urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Female urinary tract
illustration
-
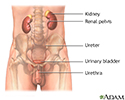
Male urinary tract - illustration
The male and female urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Male urinary tract
illustration
-
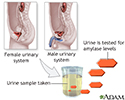
Amylase urine test - illustration
Amylase is an enzyme which helps digest glycogen and starch. It is produced mainly in the pancreas and salivary glands. Amylase is normally secreted from the pancreas through the pancreatic duct to the small intestines.
Amylase urine test
illustration
-
Female urinary tract - illustration
The female and male urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Female urinary tract
illustration
-
Male urinary tract - illustration
The male and female urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Male urinary tract
illustration
-
Amylase urine test - illustration
Amylase is an enzyme which helps digest glycogen and starch. It is produced mainly in the pancreas and salivary glands. Amylase is normally secreted from the pancreas through the pancreatic duct to the small intestines.
Amylase urine test
illustration
Review Date: 5/3/2015
Reviewed By: Laura J. Martin, MD, MPH, ABIM Board Certified in Internal Medicine and Hospice and Palliative Medicine, Atlanta, GA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.