Exercise and activity for weight loss
Weight loss - activity; Weight loss - exercise; Obesity - activity
An active lifestyle and exercise routine, along with eating healthy foods, is the best way to lose weight.
The Weight-loss Formula
Calories used in exercise > calories eaten = weight loss.
This means that to lose weight, the number of calories you burn by exercising needs to be greater than the number of calories from the foods you eat and drink. Even if you work out a lot, if you eat more calories than you burn, you will gain weight.
Another way to look at this is that a woman ages 30 to 50 years who does not exercise needs about 1,800 calories a day to maintain her normal weight. A man ages 30 to 50 years who does not exercise needs about 2,200 calories to maintain his normal weight.
For every hour of exercise they do, they would burn:
- 240 to 300 calories doing light activity such as cleaning house or playing baseball or golf.
- 370 to 460 calories doing activity such as a brisk walk (3.5 mph), gardening, biking (5.5 mph), or dancing.
- 580 to 730 calories doing activity such as jogging at a pace of 9 minutes per mile, playing football, or swimming laps.
- 740 to 920 calories doing activity such as running at a pace of 7 minutes per mile, playing racquetball, and skiing.
Even if you don't change the amount of calories in your diet, but you do add activity to your daily life, you'll lose weight or gain less weight.
Benefits of Weight Loss
An exercise weight-loss program that works needs to be fun and keep you motivated. It helps to have a specific goal. Your goal might be managing a health condition, reducing stress, improving your stamina, or being able to buy clothes in a smaller size. Your exercise program may also be a way for you to be with other people. Exercise classes or exercising with a buddy are both good social outlets.
You may have a hard time starting an exercise routine, but once you do, you will begin to notice other benefits. Improved sleep and self-esteem might be a couple of them. Other benefits you may not notice include increased bone and muscle strength and a lower risk for heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
Getting Started
You do not need to join a gym to get exercise. If you have not exercised or been active in a long time, be sure to start off slowly to prevent injuries. Taking a brisk 10-minute walk twice a week is a good start.
You can also try joining a dance, yoga, or karate class. You could also join a baseball or bowling team, or even a mall-walking group. The social aspects of these groups can be rewarding and motivating.
The most important thing is that you do exercises that you enjoy.
Build Physical Activity into Your Regular Routine
Simple lifestyle changes can make a big difference over time.
- At work, try taking the stairs instead of the elevator, walking down the hall to talk with a co-worker instead of sending an e-mail, or adding a 10- to 20-minute walk during lunch.
- When you are running errands, try parking at the far end of the parking lot or down the street. Even better, try walking to the store.
- At home, try taking on common chores such as vacuuming, washing a car, gardening, raking leaves, or shoveling snow.
- If you ride the bus, get off the bus one stop before your usual stop and walk the rest of the way.
Reduce Your Screen Time
Sedentary behaviors are things you do while you are sitting still. Decreasing your sedentary behaviors can help you lose weight. For most people, the best way to decrease sedentary behavior is to reduce the time they spend watching TV and using a computer and other electronic devices. All of these activities are called "screen time."
Some ways to decrease the harm of too much screen time are:
- Choose one or two TV programs to watch, and turn off the TV when they are over.
- DO NOT keep the TV on all the time for background noise -- you might end up sitting down and watching it. Turn on the radio instead. You can be up doing things around the house and still listen to the radio.
- DO NOT eat while you are watching TV.
- Before you turn on the TV, take your dog for a walk. If you are going to miss your favorite show, record it.
- Find activities to replace TV-watching. Read a book, play a board game with family or friends, or take an evening class.
- Work out on an exercise mat while you watch TV. You will burn calories.
- Ride a stationary bike or use a treadmill while you watch TV.
If you like playing video games, try games that require you to move your whole body, not just your thumbs.
How Much Exercise Do You Need?
Aim to exercise about 2.5 hours a week. Do moderate-intensity aerobic and muscle-strengthening activities. Depending on your schedule, you could exercise 30 minutes 5 days a week or 45 to 60 minutes 3 days a week.
You do not have to do your total daily exercise all at once. If your goal is to exercise for 30 minutes, you can break that up into shorter time periods that add up to 30 minutes.
As you become more fit, you can challenge yourself by increasing the intensity of your exercise by going from light activity to moderate activity. You can also increase the amount of time you exercise.
References
Dempsey PC, Howard BJ, Lynch BM, Owen N, Dunstan DW. Associations of television viewing time with adults' well-being and vitality. Prev Med . 2014;69:69-74. PMID: 25230366 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25230366 .
Fitch A, Everling L, Fox C, et al. Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement. Prevention and management of obesity for adults. Updated May 2013. www.icsi.org/guidelines__more/catalog_guidelines_and_more/catalog_guidelines/catalog_endocrine_guidelines/obesity__adults . Accessed October 27, 2016.
Jensen MD. Obesity. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 220.
Moyer VA, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for and management of obesity in adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med . 2012;157(5):373-378. PMID: 22733087 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22733087 .
-
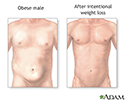
Weight loss - illustration
Losing excess weight by eating a healthy diet is one of the best ways of helping to prevent disease. Obesity increases the risk of illness and death due to diabetes, stroke, coronary artery disease, and kidney and gallbladder disorders. The more overweight, the higher the risk becomes.
Weight loss
illustration
-
Weight loss - illustration
Losing excess weight by eating a healthy diet is one of the best ways of helping to prevent disease. Obesity increases the risk of illness and death due to diabetes, stroke, coronary artery disease, and kidney and gallbladder disorders. The more overweight, the higher the risk becomes.
Weight loss
illustration
-
Exercise
(In-Depth)
-
Weight control and diet
(In-Depth)
-
Obesity
(Alt. Medicine)
-
Heart-healthy diet
(In-Depth)
-
Diabetes diet
(In-Depth)
-
Diabetes
(Alt. Medicine)
-
Diabetes - type 2
(In-Depth)
-
Anorexia nervosa
(Alt. Medicine)
-
Osteoarthritis
(Alt. Medicine)
-
Coronary artery disease
(In-Depth)
Review Date: 8/22/2016
Reviewed By: Laura J. Martin, MD, MPH, ABIM Board Certified in Internal Medicine and Hospice and Palliative Medicine, Atlanta, GA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.