High blood pressure - infants
Hypertension - infants
High blood pressure (hypertension) is an increase in the force of blood against the arteries in the body. This article focuses on high blood pressure in infants.
Causes
Blood pressure measures how hard the heart is working, and how healthy the arteries are. There are 2 numbers in each blood pressure measurement:
- The first (top) number is the systolic blood pressure, which measures the force of blood released when the heart beats.
- The second (bottom) number is the diastolic pressure, which measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest.
Blood pressure measurements are written this way: 120/80. One or both of these numbers can be too high.
Several factors affect blood pressure, including:
- Hormones
- The health of the heart and blood vessels
- The health of the kidneys
High blood pressure in infants may be due to kidney or heart disease that is present at birth (congenital). Common examples include:
-
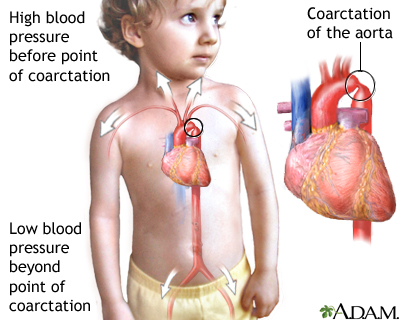
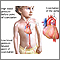
Coarctation of the aorta
(narrowing of the large blood vessel of the heart called the aorta)
Coarctation of the aorta
The aorta carries blood from the heart to the vessels that supply the body with blood. If part of the aorta is narrowed, it is hard for blood to pas...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
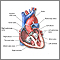
Patent ductus arteriosus
(blood vessel between the aorta and pulmonary artery that should close after birth, but remains open)
Patent ductus arteriosus
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a condition in which the ductus arteriosus does not close. The word "patent" means open. The ductus arteriosus is ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
(lung condition that affects newborn babies who were either put on a breathing machine after birth or were born very early)
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is a chronic lung condition that affects newborn babies who were either put on a breathing machine after birth or we...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney disease involving the kidney tissue
- Renal artery stenosis (narrowing of the major blood vessel of the kidney)
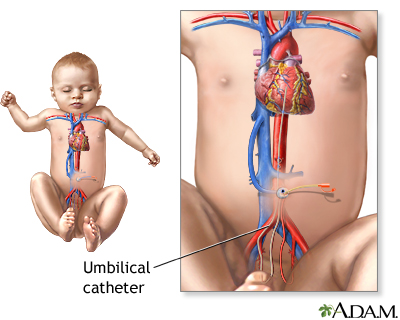
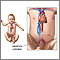
In newborn babies, high blood pressure is often caused by a blood clot in a kidney blood vessel, a complication of having an umbilical artery catheter .
Umbilical artery catheter
The placenta is the link between mother and baby during pregnancy. Two arteries and one vein in the umbilical cord carry blood back and forth. If t...
Other causes of high blood pressure in infants may include:
- Certain medicines
- Exposure to illegal drugs such as cocaine
- Certain tumors
- Inherited conditions (problems that run in families)
- Thyroid problems
Blood pressure rises as the baby grows. The average blood pressure in a newborn is 64/41. The average blood pressure in a child 1 month through 2 years old is 95/58. It is normal for these numbers to vary.
Symptoms
Most babies with high blood pressure will not have symptoms. Instead, symptoms may be related to the condition causing the high blood pressure. These symptoms may include:
-
Bluish skin
Bluish skin
Cyanosis is a bluish color to the skin or mucous membrane that is usually due to a lack of oxygen in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Failure to grow and gain weight
- Frequent urinary tract infections
- Pale skin (pallor)
- Rapid breathing
Symptoms that may appear if the baby has very high blood pressure include:
- Irritability
- Seizures
- Trouble breathing
- Vomiting
Exams and Tests
In most cases, the only sign of high blood pressure is the blood pressure measurement itself.
Signs of very high blood pressure include:
-
Heart failure
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
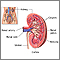
Kidney failure
Kidney failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Rapid pulse
Blood pressure in infants is measured with an automatic device.
If coarctation of the aorta is the cause, there may be decreased pulses or blood pressure in the legs. A click may be heard if a bicuspid aortic valve occurs with the coarctation.
Coarctation of the aorta
The aorta carries blood from the heart to the vessels that supply the body with blood. If part of the aorta is narrowed, it is hard for blood to pas...

Bicuspid aortic valve
A bicuspid aortic valve (BAV) is an aortic valve that only has 2 leaflets, instead of 3. The aortic valve regulates blood flow from the heart into th...
Other tests in infants with high blood pressure will try to find the cause of the problem. Such tests may include:
- A special type of x-ray that uses a dye to look at blood vessels (angiography)
- Laboratory tests, including blood and urine tests
- X-rays of the chest or abdomen
- Ultrasounds, including an ultrasound of the working heart (echocardiogram) and of the kidneys
- MRI of the blood vessels
Treatment
The treatment depends on the cause of high blood pressure in the infant. Treatment can include:
-
Dialysis
to treat kidney failure
Dialysis
Artificial kidneys - hemodialysis; Dialysis; Renal replacement therapy - hemodialysis; End-stage renal disease - hemodialysis; Kidney failure - hemod...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Medicines to lower blood pressure or help the heart pump better
- Surgery (including transplantation surgery or repair of the coarctation)
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well the baby does depends on the cause of high blood pressure and other factors such as:
- Other health problems in the baby
- Whether damage (such as kidney damage) has occurred as a result of the high blood pressure
Possible Complications
Untreated, high blood pressure may lead to:
- Heart or kidney failure
- Organ damage
- Seizures
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if your baby:
- Fails to grow and gain weight
- Has bluish skin
- Has frequent urinary tract infections
- Seems irritable
- Tires easily
Take your baby to the emergency department if your baby:
- Has seizures
- Is not responding
- Is vomiting constantly
Prevention
Some causes of high blood pressure run in families. Talk to your provider before you get pregnant if you have a family history of:
- Congenital heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
Also talk to your provider before becoming pregnant if you take medicine for a health problem. Exposure to certain drugs in the womb may increase your baby's risk of developing problems that can lead to high blood pressure.
References
Beard L, Neonatology. In: Engorn B, Flerlage J, eds. The Harriet Lane Handbook: A Manual for Pediatric House Officers . 20th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 18.
Lande MB. Systemic hypertension. In: Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St. Geme JW, Schor NF, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics . 20th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 445.
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics . 2004;114 (2 Suppl 4th Report):555-576. PMID: 15286277 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15286277 .
-
Umbilical catheter - illustration
An umbilical catheter is a long, soft plastic tube (usually made of silicone) that is placed in the umbilical cord either through the umbilical artery or umbilical vein to allow IV fluids and medications to be given over an extended period of time.
Umbilical catheter
illustration
-
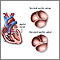
Coarctation of the aorta - illustration
Coarctation of the aorta is a birth defect in which the aorta, the major artery from the heart, is narrowed. The narrowing results in high blood pressure before the point of coarctation and low blood pressure beyond the point of coarctation. Most commonly, coarctation is located so that there is high blood pressure in the upper body and arms and low blood pressure in the lower body and legs. Symptoms can include localized hypertension, cold feet or legs, decreased exercise performance, and heart failure.
Coarctation of the aorta
illustration
-
Umbilical catheter - illustration
An umbilical catheter is a long, soft plastic tube (usually made of silicone) that is placed in the umbilical cord either through the umbilical artery or umbilical vein to allow IV fluids and medications to be given over an extended period of time.
Umbilical catheter
illustration
-
Coarctation of the aorta - illustration
Coarctation of the aorta is a birth defect in which the aorta, the major artery from the heart, is narrowed. The narrowing results in high blood pressure before the point of coarctation and low blood pressure beyond the point of coarctation. Most commonly, coarctation is located so that there is high blood pressure in the upper body and arms and low blood pressure in the lower body and legs. Symptoms can include localized hypertension, cold feet or legs, decreased exercise performance, and heart failure.
Coarctation of the aorta
illustration
-
Diabetes - type 2
(In-Depth)
-
Diabetes
(Alt. Medicine)
-
Coronary artery disease
(In-Depth)
-
Heart failure
(In-Depth)
-
Anemia
(In-Depth)
-
Sickle cell disease
(In-Depth)
-
Vitamin D
(Alt. Medicine)
-
Peripheral artery disease and intermittent claudication
(In-Depth)
-
Potassium
(Alt. Medicine)
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
(In-Depth)
Review Date: 5/6/2016
Reviewed By: Scott I Aydin, MD, Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Division of Pediatric Cardiology and Critical Care Medicine, The Children's Hospital at Montefiore, Bronx, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.