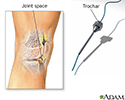
Synovial biopsy
Biopsy - synovial membrane; Rheumatoid arthritis - synovial biopsy; Gout - synovial biopsy; Joint infection - synovial biopsy; Synovitis - synovial biopsy
A synovial biopsy is the removal of a piece of tissue lining a joint for examination. The tissue is called the synovial membrane.
How the Test is Performed
The test is done in the operating room, often during an arthroscopy. During this procedure:
-
You will receive
general anesthesia
. This means you'll be pain free and asleep during the procedure.
General anesthesia
General anesthesia is treatment with certain medicines that puts you into a deep sleep so you do not feel pain during surgery. After you receive the...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - The surgeon makes a tiny cut in the skin near the joint.
- An instrument called a trocar is inserted through the cut into the joint.
- A tiny camera with a light is used to look inside the joint.
- A tool called a biopsy grasper is then inserted through the trocar. The grasper is used to cut a small piece of tissue.
- The surgeon removes the grasper along with the tissue. The trocar and any other instruments are removed. The skin cut is closed and a bandage is applied.
- The sample is sent to a lab for examination.
How to Prepare for the Test
Follow your health care provider's instructions on how to prepare. This may include not eating and drinking anything for several hours before the procedure.
How the Test will Feel
With the local anesthetic, you will feel a prick and a burning sensation. As the trocar is inserted, there will be some discomfort. If the surgery is performed under regional or general anesthesia, you will not feel the procedure.
Why the Test is Performed
Synovial biopsy helps diagnose gout and bacterial infections, or rule out other infections. It can be used to diagnose autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, or uncommon infections like tuberculosis.
Gout
Gout is a type of arthritis. It occurs when uric acid builds up in blood and causes inflammation in the joints. Acute gout is a painful condition th...

Normal Results
The synovial membrane structure is normal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Synovial biopsy may identify the following conditions:
- Chronic synovitis (inflammation of the synovial membrane)
-
Coccidioidomycosis
(a fungal infection)
Coccidioidomycosis
Valley fever is an infection that occurs when the spores of the fungus Coccidioides immitis enter your body through the lungs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fungal arthritis
Fungal arthritis
Fungal arthritis is swelling and irritation (inflammation) of a joint by a fungal infection. It is also called mycotic arthritis.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Gout
-
Hemochromatosis
(abnormal buildup of iron deposits)
Hemochromatosis
Hemochromatosis is a condition in which there is too much iron in the body. It is also called iron overload.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Systemic lupus erythematosus
(autoimmune disease that affects the skin, joints, and other organs)
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. In this disease, the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. It can af...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs. It may spread to other organs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Synovial
cancer
(very rare type of soft tissue cancer)
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term disease. It leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It can also affect other organs....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
There is a very slight chance of infection and bleeding.
Considerations
Follow instructions for keeping the wound clean and dry until your provider says it is OK to get it wet.
References
El-Gabalawy HS. Synovial fluid analyses, synovial biopsy, and synovial pathology. In: Firestein GS, Budd RC, Gabriel SE, McInnes IB, O'Dell JR, eds. Kelley and Firestein's Textbook of Rheumatology . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 53.
West SG. Synovial biopsies. In: West SG, ed. Rheumatology Secrets. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2015:chap 9.
-
Synovial biopsy - illustration
A synovial biopsy takes a sample of synovial tissue which is tissue that lines the joint. The test is performed to help diagnose gout, bacterial infections, and other infections.
Synovial biopsy
illustration
Review Date: 9/22/2016
Reviewed By: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.