Parathyroid biopsy
Biopsy - parathyroid
A parathyroid biopsy is the removal of a small piece of a parathyroid gland for examination under a microscope. The parathyroid glands are found just behind the thyroid gland on each side of the neck.
How the Test is Performed
There are two parathyroid glands on each side of the neck, making a total of 4 glands. The parathyroid glands can't be felt with the hands.
A parathyroid biopsy is done while you're awake.
- Using an ultrasound machine, the health care provider locates the gland that is of concern.
- A thin needle is inserted directly into the gland, and a small piece of tissue is removed.
- The procedure takes 10 to 30 minutes.
The tissue is sent to a laboratory, where it is examined under a microscope. The level of parathyroid hormone (PTH) in your blood will also be checked.
Parathyroid hormone
The PTH test measures the level of parathyroid hormone in the blood. PTH stands for parathyroid hormone. It is a protein hormone released by the par...
How to Prepare for the Test
Tell your provider if you have any drug allergies or bleeding problems, or if you are pregnant.
Make sure the provider knows about all the medicines you're taking, including any herbs or supplements. Tell your provider if you're taking any blood thinning drugs (aspirin, heparin, Lovenox, warfarin). You may have to stop taking them a few days before the procedure. Do NOT stop any medicines on your own. Ask your provider first.
How the Test will Feel
You may feel a sting as the needle is inserted into the gland. Most people do not need any pain medicine.
Why the Test is Performed
The parathyroid glands release PTH. This hormone controls the level of calcium in the body.
This procedure is most often done to rule out the cause of a high parathyroid hormone level.
It may also be done if an ultrasound exam shows an enlarged parathyroid gland.
Normal Results
There is no swelling, PTH level is normal, and cells from the tissue sample are normal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
The test confirms that a parathyroid gland is enlarged if PTH level is too high or cells from the sample are abnormal.
Abnormal results may be due to:
-
Noncancerous tumor of the parathyroid gland (
parathyroid adenoma
)
Parathyroid adenoma
A parathyroid adenoma is a noncancerous (benign) tumor of the parathyroid glands. The parathyroid glands are located in the neck, near or attached t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Parathyroid cancer
(rare)
Parathyroid cancer
Parathyroid cancer is a cancerous (malignant) growth in a parathyroid gland.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Enlargement of all 4 parathyroid glands (
parathyroid hyperplasia
)
Parathyroid hyperplasia
Parathyroid hyperplasia is the enlargement of all 4 parathyroid glands. The parathyroid glands are located in the neck, near or attached to the back...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Disorder in which one or more of the endocrine glands are overactive or form a tumor (multiple endocrine neoplasia) ([
MEN I
] or [
MEN II
])
MEN I
Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) type I is a disease in which one or more of the endocrine glands are overactive or forms a tumor. It is passed do...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMEN II
Multiple endocrine neoplasia, type II (MEN II) is a disorder passed down through families in which one or more of the endocrine glands are overactive...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
The main risks of the procedure are bruising and bleeding into or around the thyroid gland. If bleeding is severe, it may put pressure over the windpipe (trachea). In this case, surgery is needed to correct the problem. This complication is rare.
Some people develop temporary hoarseness when the nerve that runs close to the parathyroid glands is injured. This complication is also rare.
References
Darr EA, Sritharan N, Pellitteri PK, Sofferman RA, Randolph GW. Management of parathyroid disorders. In: Flint PW, Haughey BH, Lund V, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 124.
-
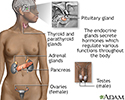
Endocrine glands - illustration
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine the pace of chemical activity in the body (the more hormone in the bloodstream, the faster the chemical activity; the less hormone, the slower the activity).
Endocrine glands
illustration
-
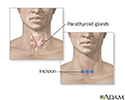
Parathyroid biopsy - illustration
A parathyroid biopsy most often is performed as part of a surgical procedure to examine and/or remove the parathyroid glands because of disease. The parathyroid glands may be removed because of conditions such as a tumor or increased blood calcium levels. The parathyroid glands are located near the thyroid gland. They secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH), which functions primarily in the control of calcium levels.
Parathyroid biopsy
illustration
-
Endocrine glands - illustration
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine the pace of chemical activity in the body (the more hormone in the bloodstream, the faster the chemical activity; the less hormone, the slower the activity).
Endocrine glands
illustration
-
Parathyroid biopsy - illustration
A parathyroid biopsy most often is performed as part of a surgical procedure to examine and/or remove the parathyroid glands because of disease. The parathyroid glands may be removed because of conditions such as a tumor or increased blood calcium levels. The parathyroid glands are located near the thyroid gland. They secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH), which functions primarily in the control of calcium levels.
Parathyroid biopsy
illustration
Review Date: 5/24/2016
Reviewed By: Mary C. Mancini, MD, PhD, Department of Surgery, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center-Shreveport, Shreveport, LA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.