Gum biopsy
Biopsy - gingiva (gums)
A gum biopsy is a surgery in which a small piece of gingival (gum) tissue is removed and examined.
Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for laboratory examination.
How the Test is Performed
A painkiller is sprayed into the mouth in the area of the abnormal gum tissue. You may also have an injection of numbing medicine. A small piece of gum tissue is removed and checked for problems in the lab. Sometimes stitches are used to close the opening created for the biopsy.
How to Prepare for the Test
You may be told not to eat for a few hours before the biopsy.
How the Test will Feel
The painkiller put in your mouth should numb the area during the procedure. You may feel some tugging or pressure. If there is bleeding, the blood vessels may be sealed off with an electric current or laser. This is called electrocauterization . After the numbness wears off, the area may be sore for a few days.
Electrocauterization
Electrocauterization is the process of heating tissue with electricity.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to look for the cause of abnormal gum tissue.
Normal Results
This test is only done when gum tissue looks abnormal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may indicate:
-
Amyloid
Amyloid
Primary amyloidosis is a disorder in which abnormal proteins build up in tissues and organs. Clumps of the abnormal proteins are called amyloid depo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Noncancerous
mouth sores
(the specific cause can be determined in many cases)
Mouth sores
There are different types of mouth sores. They can occur anywhere in the mouth including bottom of the mouth, inner cheeks, gums, lips, and tongue....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Oral cancer
(for example,
squamous cell carcinoma
)
Oral cancer
Oral cancer is cancer that starts in the mouth.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
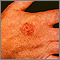
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleSquamous cell carcinoma
Squamous cell cancer is the second most common type of cancer in the United States. Other common types of skin cancer are:Basal cellMelanoma
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
Risks for this procedure include:
- Bleeding from the biopsy site
- Infection of the gums
- Soreness
Considerations
Avoid brushing the area where the biopsy was performed for 1 week.
References
Eusterman VD. History and Physical Examination, Screening and Diagnostic Testing. Otolaryngol Clin North Am . Feb 2011;44(1):1-29. PMID: 21093621 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21093621 .
-
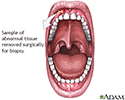
Gum biopsy - illustration
Gum biopsy is a diagnostic procedure in which a small piece of gingival (gum) tissue is removed for examination. The test is performed when examination of the mouth reveals abnormal-appearing gum tissue.
Gum biopsy
illustration
-
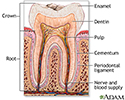
Tooth anatomy - illustration
The structure of the tooth includes dentin, pulp and other tissues, blood vessels and nerves imbedded in the bony jaw. Above the gum line, the tooth is protected by the hard enamel covering.
Tooth anatomy
illustration
-
Gum biopsy - illustration
Gum biopsy is a diagnostic procedure in which a small piece of gingival (gum) tissue is removed for examination. The test is performed when examination of the mouth reveals abnormal-appearing gum tissue.
Gum biopsy
illustration
-
Tooth anatomy - illustration
The structure of the tooth includes dentin, pulp and other tissues, blood vessels and nerves imbedded in the bony jaw. Above the gum line, the tooth is protected by the hard enamel covering.
Tooth anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 2/9/2015
Reviewed By: Alan Lipkin, MD, Otolaryngologist, private practice, Denver, CO. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.