Skin lesion KOH exam
Potassium hydroxide examination of skin lesion
The skin lesion KOH exam is a test to diagnose a fungal infection of the skin .
Fungal infection of the skin
Candida infection of the skin is a yeast infection of the skin. The medical name of the condition is cutaneous candidiasis.

How the Test is Performed
The health care provider scrapes the problem area of your skin, using a blunt edge, such as the edge of a microscope slide. The scrapings from the skin are placed in liquid containing the chemical potassium hydroxide (KOH). The liquid is examined under the microscope. KOH destroys all non-fungal cells. This makes it easier to see if there is any fungus present.
Potassium hydroxide
This article discusses poisoning from swallowing or touching potassium hydroxide or products that contain this chemical. This article is for informat...
How to Prepare for the Test
There is no special preparation for the test.
How the Test will Feel
You may feel pressure or pain when the provider scrapes your skin.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to diagnose a fungal infection of the skin.
Normal Results
No fungus is present.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Fungus is present. The fungus may be related to ringworm , athlete's foot , jock itch , or another fungal infection.
Ringworm
Ringworm is a skin infection due to a fungus or yeast. Often, there are several patches of ringworm on the skin at once. The medical name for ringw...
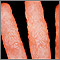
Athlete's foot
Athlete's foot is an infection of the feet caused by fungus or yeast. The medical term is tinea pedis, or ringworm of the foot.
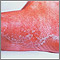
Jock itch
Jock itch is an infection of the groin area caused by fungus or yeast. The medical term is tinea cruris, or ringworm of the groin.

Risks
There is a small risk of bleeding or infection from scraping the skin.
References
Elewski BE, Hughey LC, Sobera JO, Hay R. Fungal diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology . 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:chap 77.
-
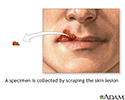
Viral lesion culture - illustration
A viral lesion culture is performed to confirm herpes simplex virus present in a skin lesion. The specimen is collected by scraping the suspected skin lesion or aspirating fluid from the lesion. Results are available within 16 hours to 7 days of receipt of the specimen, depending on the culture method used.
Viral lesion culture
illustration
-
Viral lesion culture - illustration
A viral lesion culture is performed to confirm herpes simplex virus present in a skin lesion. The specimen is collected by scraping the suspected skin lesion or aspirating fluid from the lesion. Results are available within 16 hours to 7 days of receipt of the specimen, depending on the culture method used.
Viral lesion culture
illustration
Review Date: 4/14/2015
Reviewed By: Kevin Berman, MD, PhD, Atlanta Center for Dermatologic Disease, Atlanta, GA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.