Gram stain of skin lesion
Skin lesion gram stain
A gram stain of a skin lesion is a laboratory test that uses special stains to detect and identify bacteria in a sample from a skin sore. The gram stain method is one of the most commonly used techniques to quickly diagnose bacterial infections.
How the Test is Performed
Your health care provider will remove a sample of tissue from the skin sore. For information on how this is done, see the article on skin lesion biopsy .
Skin lesion biopsy
A skin lesion biopsy is when a small amount of skin is removed so it can be examined. The skin is tested to look for skin conditions or diseases. A...
The sample is sent to a laboratory, where it is applied in a very thin layer to a glass slide. A series of different colored stains is applied to the sample. A laboratory team member examines the stained slide under a microscope, checking for bacteria. The color, size, and shape of the cells help identify the germ causing the infection.
How to Prepare for the Test
No preparation is needed for the laboratory test.
How the Test Will Feel
The laboratory test is painless. For information on what it feels like to have the skin sample removed, see: Skin lesion biopsy .
Skin lesion biopsy
A skin lesion biopsy is when a small amount of skin is removed so it can be examined. The skin is tested to look for skin conditions or diseases. A...

Why the Test is Performed
Your provider may order this test if you have signs of an infected skin sore. The test is done to determine which bacteria caused the infection.
Normal Results
The test is normal if no bacteria are found.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal result means bacteria have been found in the skin lesion. Further tests are needed to confirm the results.
Risks
There are no risks related to the laboratory test. For information on risks related to removing a skin sample, see: Skin lesion biopsy .
Skin lesion biopsy
A skin lesion biopsy is when a small amount of skin is removed so it can be examined. The skin is tested to look for skin conditions or diseases. A...

Considerations
A skin or mucosal culture may be done along with this test. Other studies are often done on a skin sample to determine if cancer is present.
Skin or mucosal culture
A skin or nail culture is a laboratory test to look for and identify germs that cause problems with the skin or nails. It is called a mucosal culture...

Viral skin lesions like herpes simplex are examined by other tests or a viral culture.
References
Hall GS, Woods GL. Medical bacteriology. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods . 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2011:chap 57.
-
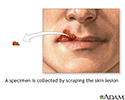
Viral lesion culture - illustration
A viral lesion culture is performed to confirm herpes simplex virus present in a skin lesion. The specimen is collected by scraping the suspected skin lesion or aspirating fluid from the lesion. Results are available within 16 hours to 7 days of receipt of the specimen, depending on the culture method used.
Viral lesion culture
illustration
-
Viral lesion culture - illustration
A viral lesion culture is performed to confirm herpes simplex virus present in a skin lesion. The specimen is collected by scraping the suspected skin lesion or aspirating fluid from the lesion. Results are available within 16 hours to 7 days of receipt of the specimen, depending on the culture method used.
Viral lesion culture
illustration
Review Date: 11/3/2014
Reviewed By: Richard J. Moskowitz, MD, dermatologist in private practice, Mineola, NY. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.