Lymph node culture
Culture - lymph node
Lymph node culture is a laboratory test done on a sample from a lymph node to identify germs that cause infection.
How the Test is Performed
A sample is needed from a lymph node. The sample may be taken using a needle to draw fluid (aspiration) from the lymph node or during a lymph node biopsy .
Lymph node biopsy
A lymph node biopsy is the removal of lymph node tissue for examination under a microscope. The lymph nodes are small glands that make white blood ce...
The sample is sent to a laboratory. There, it is placed in a special dish and watched to see if bacteria, fungi, or viruses grow. This process is called a culture. Sometimes, special stains are also used to identify specific cells or microorganisms before culture results are available.
If needle aspiration does not provide a good enough sample, the entire lymph node may be removed and sent for culture and other testing.
How to Prepare for the Test
Your health care provider will instruct you on how to prepare for the lymph node sampling .
Lymph node sampling
A lymph node biopsy is the removal of lymph node tissue for examination under a microscope. The lymph nodes are small glands that make white blood ce...

How the Test will Feel
When local anesthetic is injected, you will feel a prick and a mild stinging sensation. The site will likely be sore for a few days after the test.
Why the Test is Performed
Your doctor may order this test if you have swollen glands and infection is suspected.
Normal Results
A normal result means there was no growth of microorganisms on the lab dish.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results are a sign of a bacterial, fungal, or viral infection.
Risks
Risks may include:
- Bleeding
- Infection (in rare cases, the wound may get infected and you may need to take antibiotics)
- Nerve injury if the biopsy is done on a lymph node close to nerves (the numbness usually goes away in a few months)
References
Armitage JO, Bierman PJ. Approach to the patient with lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 168.
Pasternik MS, Swartz MN. Lymphadenitis and lymphangitis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 97.
-
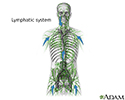
Lymphatic system - illustration
The lymphatic system filters fluid from around cells. It is an important part of the immune system. When people refer to swollen glands in the neck, they are usually referring to swollen lymph nodes. Common areas where lymph nodes can be easily felt, especially if they are enlarged, are: the groin, armpits (axilla), above the clavicle (supraclavicular), in the neck (cervical), and the back of the head just above hairline (occipital).
Lymphatic system
illustration
-
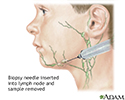
Lymph node culture - illustration
To obtain a sample of lymph tissue for biopsy, a needle is inserted within the lymph node and a sample of fluid is sent to the laboratory. The laboratory test isolates and identifies organisms that cause infection. The test may be performed if plague is suspected, but it is rarely done otherwise.
Lymph node culture
illustration
-
Lymphatic system - illustration
The lymphatic system filters fluid from around cells. It is an important part of the immune system. When people refer to swollen glands in the neck, they are usually referring to swollen lymph nodes. Common areas where lymph nodes can be easily felt, especially if they are enlarged, are: the groin, armpits (axilla), above the clavicle (supraclavicular), in the neck (cervical), and the back of the head just above hairline (occipital).
Lymphatic system
illustration
-
Lymph node culture - illustration
To obtain a sample of lymph tissue for biopsy, a needle is inserted within the lymph node and a sample of fluid is sent to the laboratory. The laboratory test isolates and identifies organisms that cause infection. The test may be performed if plague is suspected, but it is rarely done otherwise.
Lymph node culture
illustration
Review Date: 12/10/2015
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Assistant Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Assistant in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.