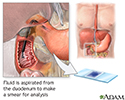
Smear of duodenal fluid aspirate
Duodenal aspirated fluid smear
Smear of duodenal fluid aspirate is an exam of fluid from the duodenum to check for signs of an infection (such as giardia or strongyloides ). Rarely, this test is also done in a newborn to check for biliary atresia.
Duodenum
The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine. It is located between the stomach and the middle part of the small intestine, or jejunum. Aft...

Giardia
Giardia, or giardiasis, is an infection of the small intestine. A tiny parasite called Giardia lamblia causes it.

Strongyloides
Strongyloidiasis is an infection with the roundworm Strongyloides stercoralis (S stercoralis).
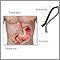
How the Test is Performed
A sample is taken during a procedure called an esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) .
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a test to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and first part of the small intestine.
How to Prepare for the Test
Do not eat or drink anything for 12 hours before the test.
How the Test will Feel
You may feel like you have to gag as the tube is passed, but the procedure is most often not painful. You can get medicines to help you relax and be free of pain. If you get anesthesia, you cannot drive for the rest of the day.
Why the Test is Performed
The test is done to look for infection of the small bowel. However, it is not often needed. In most cases, this test is only done when a diagnosis cannot be made with other tests.
Normal Results
There should be no disease-causing organisms in the duodenum. Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
The results may show the presence of giardia protozoa, the intestinal parasite strongyloides, or another infectious organism.
Risks
The risks of this test include:
- Bleeding
- Perforation of (poking a hole in) the gastrointestinal tract by the scope
- Infection
Some people may not be able to have this test because of other medical conditions.
Considerations
Other tests that are less invasive can often find the source of the infection.
References
Beavis KG, Charnot-Katsikas A. Specimen collection and handling for diagnosis of infectious diseases. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods . 23rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 64.
Dupont HL. Approach to the patient with suspected enteric infection. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 283.
Fritsche TR, Pritt BS. Medical parasitology. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods . 23rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 63.
Gerding DN, Johnson S. Clostridial infections. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 296.
Gerding DN, Young VB. Clostridium difficle infection. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 245.
Haines CF, Sears CL. Infectious enteritis and proctocolitis. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 110.
Semrad CE. Approach to the patient with diarrhea and malabsorption. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 140.
Siddiqi HA, Salwen MJ, Shaikh MF, Bowne WB. Laboratory diagnosis of gastrointestinal and pancreatic disorders. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods . 23rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 22.
-
Duodenum tissue smear - illustration
A duodenal tissue smear is performed by inserting a special tube through the mouth down into the duodenum. When the tube is in place, it suctions out some of the fluid located in the duodenum. When the procedure is over the tube is removed. The sample is sent to the laboratory for testing. The test is performed to diagnose infection or parasitic infestation of the small bowel.
Duodenum tissue smear
illustration
-
Duodenum tissue smear - illustration
A duodenal tissue smear is performed by inserting a special tube through the mouth down into the duodenum. When the tube is in place, it suctions out some of the fluid located in the duodenum. When the procedure is over the tube is removed. The sample is sent to the laboratory for testing. The test is performed to diagnose infection or parasitic infestation of the small bowel.
Duodenum tissue smear
illustration
Review Date: 5/11/2016
Reviewed By: Subodh K. Lal, MD, gastroenterologist with Gastrointestinal Specialists of Georgia, Austell, GA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.