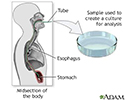
Gastric tissue biopsy and culture
Culture - gastric tissue; Culture - stomach tissue; Biopsy - gastric tissue; Biopsy - stomach tissue; Upper endoscopy - gastric tissue biopsy; EGD - gastric tissue biopsy
Gastric tissue biopsy is the removal of stomach tissue for examination. A culture is a laboratory test that examines the tissue sample for bacteria and other organisms that can cause disease.
Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for laboratory examination.
How the Test is Performed
The tissue sample is removed during a procedure called upper endoscopy (or EGD) . It is done with a flexible tube with a small camera (flexible endoscope) at the end. The scope is inserted down the throat into the stomach.
Upper endoscopy (or EGD)
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a test to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and first part of the small intestine.
The health care provider sends the tissue sample to a laboratory where it is examined for signs of cancer, certain infections, or other problems.
How to Prepare for the Test
Follow instructions on how to prepare for the procedure. You will likely be asked not to eat or drink anything for 6 to 12 hours before the procedure.
How the Test will Feel
Your provider will tell you what to expect during the procedure.
Why the Test is Performed
This test may be done to diagnose a stomach ulcer or the cause of other stomach symptoms. These symptoms may include:
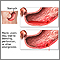
Stomach ulcer
A peptic ulcer is an open sore or raw area in the lining of the stomach or intestine. A gastric ulcer occurs in the stomach. A duodenal ulcer occurs ...
- Loss of appetite or weight loss
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pain in the upper part of the belly
- Black stools
- Vomiting blood or coffee ground-like material
A gastric tissue biopsy and culture can help detect:
- Cancer
- Infections, most commonly Helicobacter pylori , the bacteria that can cause stomach ulcers
Normal Results
A gastric tissue biopsy is normal if it does not show cancer, other damage to the lining of the stomach, or signs of organisms that cause infection.
A gastric tissue culture may be considered normal if it does not show certain bacteria. Stomach acids normally prevent too much bacteria from growing.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may be due to:
-
Stomach (gastric) cancer
Stomach (gastric) cancer
Stomach cancer is cancer that starts in the stomach.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Gastritis
, when the lining of the stomach becomes inflamed or swollen
Gastritis
Gastritis occurs when the lining of the stomach becomes inflamed or swollen. Gastritis can last for only a short time (acute gastritis). It may als...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Helicobacter pylori infection
Risks
Your provider can discuss the risks of the upper endoscopy procedure with you.
References
Bhattacharya B. Non-neoplastic disorders of the stomach. In: Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Montgomery E, eds. Gastrointestinal and Liver Pathology . 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:chap 3.
Feldman M, Lee EL. Gastritis. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 52.
Park JY, Fenton HH, Lewin MR, Dilworth HP. Epithelial neoplasms of the stomach. In: Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Montgomery E, eds. Gastrointestinal and Liver Pathology . 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012: chap 4.
Vargo JJ. Preparation for and complications of GI endoscopy. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 41.
-
Culture of gastric tissue biopsy - illustration
A flexible fiberoptic tube is passed through the mouth and down the esophagus until it enters the stomach. The tube allows the health care provider to see the various parts and take a biopsy (sample). The sample is taken to the laboratory to be examined. The procedure is used to determine the cause of bleeding, and to diagnose tumors, ulcers, inflammatory disease, and structural abnormalities of the stomach.
Culture of gastric tissue biopsy
illustration
-
Culture of gastric tissue biopsy - illustration
A flexible fiberoptic tube is passed through the mouth and down the esophagus until it enters the stomach. The tube allows the health care provider to see the various parts and take a biopsy (sample). The sample is taken to the laboratory to be examined. The procedure is used to determine the cause of bleeding, and to diagnose tumors, ulcers, inflammatory disease, and structural abnormalities of the stomach.
Culture of gastric tissue biopsy
illustration
Review Date: 10/27/2015
Reviewed By: Subodh K. Lal, MD, gastroenterologist with Gastrointestinal Specialists of Georgia, Austell, GA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.