Pericardial fluid culture
Culture - pericardial fluid
Pericardial fluid culture is a test performed on a sample of fluid from the sac surrounding the heart. It is done to identify organisms that cause infection.
Pericardial fluid gram stain is a related topic.
Pericardial fluid gram stain
Pericardial fluid Gram stain is a method of staining a sample of fluid taken from the sac surrounding the heart to diagnose a bacterial infection. T...
How the Test is Performed
Some people may have a cardiac monitor placed before the test to check for heart disturbances. Patches called electrodes will be placed on the chest, similar to during an ECG. A chest x-ray or ultrasound may be done before the test.
ECG.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.

Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to make images of organs and structures inside the body.
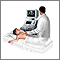
The skin of the chest will be cleaned with antibacterial soap. A doctor inserts a small needle into the chest between the ribs into the thin sac that surrounds the heart (the pericardium). A small amount of fluid is removed.
You may have an ECG and chest x-ray after the test. Sometimes the pericardial fluid is taken during open heart surgery.
The sample is sent to a lab. Bacteria are grown in samples of the fluid. It can take a few hours to several weeks to get the test results.
How to Prepare for the Test
You will be asked not to eat or drink anything for several hours before the test. You may have a chest x-ray or ultrasound before the test to identify the area of fluid collection.
How the Test Will Feel
You will feel some pressure and discomfort when the needle is inserted into the chest and the fluid is removed. Your doctor should be able to give you pain medicine so that the procedure does not hurt very much.
Why the Test is Performed
Your doctor may order this test if you have signs of a heart sac infection or if you have pericardial effusion .
Pericardial effusion
Pericarditis is a condition in which the sac-like covering around the heart (pericardium) becomes inflamed.
The test may also be done if you have pericarditis .
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is a condition in which the sac-like covering around the heart (pericardium) becomes inflamed.

Normal Results
A normal result means no infectious organisms are found in the fluid sample.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may be due to an infection of the pericardium. The specific organism causing the infection may be identified. More tests may be needed to determine the most effective treatments.
Risks
Complications are rare but include:
- Heart or lung puncture
- Infection
References
LeWinter MM, Hopkins WE. Pericardial diseases. In: Mann DL, Zipes DP, Libby P, Bonow RO, Braunwald E, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 71.
-
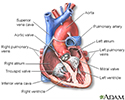
Heart, section through the middle - illustration
The interior of the heart is composed of valves, chambers, and associated vessels.
Heart, section through the middle
illustration
-
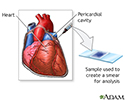
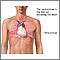
Pericardial fluid culture - illustration
During a pericardial fluid culture, a small needle is inserted into the chest between the ribs into the pericardium (the thin sac that surrounds the heart) and a small amount of fluid is withdrawn. Samples of the fluid are placed in various culture media in the laboratory, and the media is observed for the growth of microorganisms. The test is performed when an infection of the heart is suspected or when a pericardial effusion is present.
Pericardial fluid culture
illustration
-
Heart, section through the middle - illustration
The interior of the heart is composed of valves, chambers, and associated vessels.
Heart, section through the middle
illustration
-
Pericardial fluid culture - illustration
During a pericardial fluid culture, a small needle is inserted into the chest between the ribs into the pericardium (the thin sac that surrounds the heart) and a small amount of fluid is withdrawn. Samples of the fluid are placed in various culture media in the laboratory, and the media is observed for the growth of microorganisms. The test is performed when an infection of the heart is suspected or when a pericardial effusion is present.
Pericardial fluid culture
illustration
Review Date: 12/7/2014
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Assistant Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Assistant in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.