Peritoneal fluid analysis
Peritoneal fluid analysis is a lab test to look at fluid that has built up in the space in the abdomen around the internal organs. This area is called the peritoneal space.
How the Test is Performed
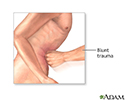
The sample of fluid is removed from the peritoneal space using a needle and syringe.
Your health care provider will clean and numb a small area of your belly area (abdomen). A needle is inserted through the skin of your abdomen and a fluid sample is pulled out. The fluid is collected into a tube (syringe) attached to the end of the needle.
The fluid is sent to a lab where it is examined. Tests will be done on the fluid to measure:
- Albumin
- Protein
- Red and white blood cell counts
Tests will also check for bacteria and other types of infection.
The following tests may also be done:
- Alkaline phosphatase
- Amylase
- Cytology (appearance of cells)
- Glucose
- LDH
How to Prepare for the Test
Let your health care provider know if you:
- Are taking any medicines (including herbal remedies)
- Have any allergies to medicines or numbing medicine
- Have any bleeding problems
- Might be pregnant
How the Test will Feel
You may feel a stinging sensation from the numbing medicine, or pressure as the needle is placed.
If a large amount of fluid is taken out, you may feel dizzy or light-headed. Tell the health care provider if you feel dizzy.
Why the Test is Performed
The test is done to:
-
Detect
peritonitis
Peritonitis
Peritonitis is an inflammation (irritation) of the peritoneum. This is the thin tissue that lines the inner wall of the abdomen and covers most of t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Find the cause of fluid in the abdomen
- Remove large amounts of fluid from the peritoneal space in people who have liver disease
- See whether an injury to the abdomen has caused internal bleeding
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may mean:
- Bile-stained fluid may mean you have a gallbladder or liver problem.
-
Bloody fluid may be a sign of
tumor
or injury.
Tumor
A tumor is an abnormal growth of body tissue. Tumors can be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
High white blood cell counts may be a sign of
peritonitis
.
Peritonitis
Peritonitis is an inflammation (irritation) of the peritoneum. This is the thin tissue that lines the inner wall of the abdomen and covers most of t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Milk-colored peritoneal fluid may be a sign of
carcinoma
,
cirrhosis
of the liver,
lymphoma
, tuberculosis, or infection.
Carcinoma
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleCirrhosis
Cirrhosis is scarring of the liver and poor liver function. It is the last stage of chronic liver disease.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleLymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer of lymph tissue. Lymph tissue is found in the lymph nodes, spleen, liver, bone marrow, and other sites.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other abnormal test results may be due to a problem in the intestines or organs of the abdomen. Large differences between the amount of albumin in the peritoneal fluid and in your blood may point to heart, liver, or kidney failure. Small differences may be a sign of cancer or infection.
Risks
Risks may include:
- Damage to the bowel, bladder, or a blood vessel in the abdomen from a needle puncture
- Infection
- Low blood pressure
-
Shock
Shock
Shock is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body is not getting enough blood flow. Lack of blood flow means that the cells and organs...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Garcia-Tsao G. Cirrhosis and its sequelae. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 153.
Runyon BA. Ascites and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease . 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2010:chap 91.
-
Indication
Presentation
-
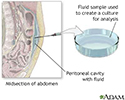
Peritoneal culture - illustration
A peritoneal culture is a procedure where peritoneal fluid is withdrawn with a needle from the peritoneal cavity. The peritoneal cavity is the space between the two membranes lining the abdominal cavity. The test is done to determine the cause of ascites, fluid accumulation in the peritoneal space.
Peritoneal culture
illustration
-
Indication
Presentation
-
Peritoneal culture - illustration
A peritoneal culture is a procedure where peritoneal fluid is withdrawn with a needle from the peritoneal cavity. The peritoneal cavity is the space between the two membranes lining the abdominal cavity. The test is done to determine the cause of ascites, fluid accumulation in the peritoneal space.
Peritoneal culture
illustration
Review Date: 2/11/2015
Reviewed By: Subodh K. Lal, MD, Gastroenterologist at Gastrointestinal Specialists of Georgia, Austell, GA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.