Anti-smooth muscle antibody
Anti-smooth muscle antibody is a blood test that detects the presence of antibodies against smooth muscle. The antibody is useful in making a diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis.
Antibodies
An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens. Examples of antigens include micr...

How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed. This may be taken through a vein. The procedure is called a venipuncture .
Venipuncture
Venipuncture is the collection of blood from a vein. It is most often done for laboratory testing.

How to Prepare for the Test
No special steps are needed to prepare for this test.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain, while others feel only a prick or stinging sensation. Afterward, there may be some throbbing.
Why the Test is Performed
You may need this test if you have signs of certain diseases, such as hepatitis and cirrhosis . These conditions can trigger the body to form antibodies against smooth muscle.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is swelling and inflammation of the liver.
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is scarring of the liver and poor liver function. It is the last stage of chronic liver disease.
Normal Results
Normally, there are no antibodies present.
Note: Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your health care provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
A positive test may be due to:
- Chronic active autoimmune hepatitis
- Cirrhosis
-
Infectious mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis
Mononucleosis, or mono, is a viral infection that causes fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph glands, most often in the neck.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
The test also helps distinguish autoimmune hepatitis from systemic lupus erythematosus .
Autoimmune hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis is inflammation of the liver. It occurs when immune cells mistake the liver's normal cells for harmful invaders and attack them...

Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. In this disease, the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. It can af...
Risks
Risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
References
Czaja AJ. Autoimmune hepatitis. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger & Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2010:chap 88.
-
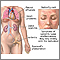
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
-
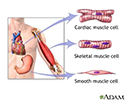
Types of muscle tissue - illustration
The 3 types of muscle tissue are cardiac, smooth, and skeletal. Cardiac muscle cells are located in the walls of the heart, appear striated, and are under involuntary control. Smooth muscle fibers are located in walls of hollow visceral organs, except the heart, appear spindle-shaped, and are also under involuntary control. Skeletal muscle fibers occur in muscles which are attached to the skeleton. They are striated in appearance and are under voluntary control.
Types of muscle tissue
illustration
-
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
-
Types of muscle tissue - illustration
The 3 types of muscle tissue are cardiac, smooth, and skeletal. Cardiac muscle cells are located in the walls of the heart, appear striated, and are under involuntary control. Smooth muscle fibers are located in walls of hollow visceral organs, except the heart, appear spindle-shaped, and are also under involuntary control. Skeletal muscle fibers occur in muscles which are attached to the skeleton. They are striated in appearance and are under voluntary control.
Types of muscle tissue
illustration
-
Psoriasis
(In-Depth)
-
Scleroderma
(In-Depth)
-
Stress
(In-Depth)
-
Melanoma and other skin cancers
(In-Depth)
-
Asthma in adults
(In-Depth)
-
Hypothyroidism
(In-Depth)
-
Asthma in children and adolescents
(In-Depth)
-
Pneumonia
(In-Depth)
Review Date: 1/20/2015
Reviewed By: Gordon A. Starkebaum, MD, Professor of Medicine, Division of Rheumatology, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.