Schirmer test
Tear test; Tearing test; Dry eye test; Basal secretion test; Sjögren - Schirmer; Schirmer's test
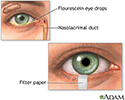
The Schirmer test determines whether the eye produces enough tears to keep it moist.
How the Test is Performed
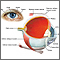
The health care provider will place the end of a special paper strip inside the lower eyelid of each eye. Both eyes are tested at the same time. Before the test, you will be given numbing eyedrops to prevent your eyes from tearing due to irritation from the paper strips.
The exact procedure may vary. Most often, the eyes are closed for 5 minutes. Close your eyes gently. Closing the eyes tightly or rubbing the eyes during the test can cause abnormal test results.
After 5 minutes, the doctor removes the paper and measures how much of it has become moist.
Sometimes the test is done without numbing drops to test for other types of tear problems.
The phenol red thread test is similar to the Schirmer test, except that red strips of special thread are used instead of paper strips. Numbing drops are not needed. The test takes 15 seconds.
How to Prepare for the Test
You will be asked to remove your glasses or contact lenses before the test.
How the Test will Feel
Some people find that holding the paper against the eye is irritating or mildly uncomfortable. The numbing drops often sting at first.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is used when the eye doctor suspects you have dry eye. Symptoms include dryness of the eyes or excessive watering of the eyes.
Normal Results
More than 10 mm of moisture on the filter paper after 5 minutes is a sign of normal tear production. Both eyes normally release the same amount of tears.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Dry eyes may result from:
- Aging
-
Blepharitis
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is inflamed, irritated, itchy, and reddened eyelids. It most often occurs where the eyelashes grow. Dandruff-like debris builds up at t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Climate changes
-
Corneal ulcers and infections
Corneal ulcers and infections
The cornea is the clear tissue at the front of the eye. A corneal ulcer is an open sore in the outer layer of the cornea. It is often caused by inf...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Eye infections (for example,
conjunctivitis
)
Conjunctivitis
The conjunctiva is a clear layer of tissue lining the eyelids and covering the white of the eye. Conjunctivitis occurs when the conjunctiva becomes...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Laser vision correction
Laser vision correction
LASIK is eye surgery that permanently changes the shape of the cornea (the clear covering on the front of the eye). It is done to improve vision and...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of blood cancer that begins in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft tissue in the center of the bones, where blood cells are ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lymphoma
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Previous eyelid or facial surgery
-
Sjögren syndrome
Sjögren syndrome
Sjögren syndrome is an autoimmune disorder in which the glands that produce tears and saliva are destroyed. This causes dry mouth and dry eyes. The...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Vitamin A deficiency
Vitamin A deficiency
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is stored in the liver. There are two types of vitamin A that are found in the diet. Preformed vitamin A is...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
There are no risks with this test.
Considerations
DO NOT rub the eyes for at least 30 minutes after the test. Leave contact lenses out for at least 2 hours after the test.
Even though the Schirmer test has been available for more than 100 years, several studies show that it does not properly identify a large group of people with dry eye. Newer and better tests are being developed. One test measures a molecule called lactoferrin. People with low tear production and dry eye have low levels of this molecule.
Another test measures tear osmolarity, or how concentrated the tears are. The higher the osmolarity, the more likely it is that you have dry eye.
References
American Academy of Ophthalmology Preferred Practice Patterns Committee. Preferred Practice Pattern Guidelines. Comprehensive Adult Medical Eye Evaluation -- 2010. Available at: one.aao.org/preferred-practice-pattern/comprehensive-adult-medical-eye-evaluation--octobe. Accessed February 26, 2015.
American Academy of Ophthalmology Cornea/External Disease Panel. Preferred Practice Pattern Guidelines. Dry Eye Syndrome Summary Benchmark -- 2014. Available at: one.aao.org/summary-benchmark-detail/dry-eye-syndrome-summary-benchmark--october-2012. Accessed February 26, 2015.
Lemp MA, Foulks GN. Diagnosis and management of dry eye disease. In: Tasman W, Jaeger EA, eds. Duane's Ophthalmology . Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2013:vol 4,chap 14.
-
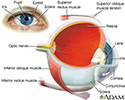
Eye - illustration
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer or tunic (sclera, or white, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle tunic layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (the retina) is nervous or sensory. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
Eye
illustration
-
Schirmer's test - illustration
Schirmer's test is used to determine whether the eye produces enough tears to keep it moist. The test is performed by placing filter paper inside the lower lid of the eye. After 5 minutes, the paper is removed and the length of the paper that has become wet is measured.
Schirmer's test
illustration
-
Eye - illustration
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer or tunic (sclera, or white, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle tunic layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (the retina) is nervous or sensory. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
Eye
illustration
-
Schirmer's test - illustration
Schirmer's test is used to determine whether the eye produces enough tears to keep it moist. The test is performed by placing filter paper inside the lower lid of the eye. After 5 minutes, the paper is removed and the length of the paper that has become wet is measured.
Schirmer's test
illustration
Review Date: 2/23/2015
Reviewed By: Franklin W. Lusby, MD, ophthalmologist, Lusby Vision Institute, La Jolla, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.