Ketones blood test
Acetone bodies; Ketones - serum; Nitroprusside test; Ketone bodies - serum; Ketones - blood
A serum ketone test measures how many ketones are there in the blood.
How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed.
Blood sample
Venipuncture is the collection of blood from a vein. It is most often done for laboratory testing.

How to Prepare for the Test
No preparation is needed.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel slight pain. Others feel a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or a slight bruise. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
Ketones are substances produced in the liver when fat cells break down in the blood. This test is used to diagnose ketoacidosis . This is a life-threatening problem that affects people who:
Ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a life-threatening problem that affects people with diabetes. It occurs when the body cannot use sugar (glucose) as a fuel ...
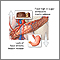
- Have diabetes. It occurs when the body cannot use sugar (glucose) as a fuel source because there is no insulin or not enough insulin. Fat is used for fuel instead. When fat breaks down, waste products called ketones build up in the body.
- Drink large amounts of alcohol.
Normal Results
A normal test result is negative. This means there are no ketones in the blood.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your health care provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
A test result is positive if ketones are found in the blood. This may indicate:
-
Alcoholic ketoacidosis
Alcoholic ketoacidosis
Alcoholic ketoacidosis is the buildup of ketones in the blood. Ketones are a type of acid that form when the body breaks down fat for energy. The co...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a life-threatening problem that affects people with diabetes. It occurs when the body cannot use sugar (glucose) as a fuel ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Starvation
- Uncontrolled blood glucose in persons with diabetes
A diet low in carbohydrates can increase ketones.
Risks
Veins and arteries vary in size from one patient to another and from one side of the body to the other. Drawing blood from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
References
Ghosh S, Collier A. Acute metabolic complications. In: Ghosh S, Collier A. Churchill's Pocketbook of Diabetes . 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2012:chap 4.
Khan MI, Weinstock RS. Carbohydrates. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods . 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2011:chap 16.
-
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
-
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
-
Diabetes - type 1
(In-Depth)
-
Diabetes - type 2
(In-Depth)
Review Date: 1/31/2015
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Medical Director and Director of Didactic Curriculum, MEDEX Northwest Division of Physician Assistant Studies, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seatttle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

