Extremity x-ray
An extremity x-ray is an image of the hands, wrist, feet, ankle, leg, thigh, forearm humerus or upper arm, hip, shoulder or all of these areas. The term "extremity" often refers to a human limb.
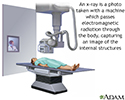
x-ray
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray particles through the body. The im...

X-rays are a form of radiation that passes through the body to form an image on film. Structures that are dense (such as bone) will appear white. Air will be black, and other structures will be shades of gray.
How the Test is Performed
The test is done in a hospital radiology department or in the health care provider's office. X-ray is done by an x-ray technologist.
You will need to hold still as the x-ray is taken. You may be asked to change position, so more x-rays can be taken.
How to Prepare for the Test
Tell your provider if you are pregnant. Remove all jewelry from the area being imaged.
In general, there is no discomfort. You may be slightly uncomfortable while the leg or arm is put in place for the x-ray.
Why the Test is Performed
Your provider may order this test if you have signs of:
-
A
fracture
Fracture
If more pressure is put on a bone than it can stand, it will split or break. A break of any size is called a fracture. If the broken bone punctures...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tumor
-
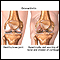
Arthritis
(inflammation of the joints)
Arthritis
Arthritis is inflammation of one or more joints. A joint is the area where 2 bones meet. There are more than 100 different types of arthritis....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Normal Results
The x-ray shows normal structures for the age of the person.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may be due to:
- Bone conditions that get worse over time (degenerative)
-
Bone tumor
Bone tumor
A bone tumor is an abnormal growth of cells within a bone. A bone tumor may be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Broken bone (fracture)
- Dislocated bone
-
Osteomyelitis
(infection)
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is a bone infection. It is mainly caused by bacteria or other germs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Arthritis
Other conditions for which the test may be performed:
-
Clubfoot
Clubfoot
Clubfoot is when the foot turns inward and downward. It is a congenital condition, which means it is present at birth.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - To detect foreign objects in the body
Risks
There is low-level radiation exposure. X-rays are monitored and regulated to provide the smallest amount of radiation exposure needed to make the image. Most experts feel that the risk is low compared with the benefits.
Pregnant women and children are more sensitive to the risks of an x-ray.
References
Kelly DM. Congenital anomalies of the lower extremity. In: Canale ST, Beaty JH, eds. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics . 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2013:chap 29.
Spouge A. Imaging overview. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR, eds. DeLee and Drez's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine . 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 10.
Thomas SH, Goodloe JM. Foreign bodies. In: Marx JA, Hockberger RS, Walls RM, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2014:chap 60.
-
X-ray - illustration
X-rays are a form of ionizing radiation that can penetrate the body to form an image on film. Structures that are dense (such as bone) will appear white, air will be black, and other structures will be shades of gray depending on density. X-rays can provide information about obstructions, tumors, and other diseases, especially when coupled with the use of barium and air contrast within the bowel.
X-ray
illustration
-
X-ray - illustration
X-rays are a form of ionizing radiation that can penetrate the body to form an image on film. Structures that are dense (such as bone) will appear white, air will be black, and other structures will be shades of gray depending on density. X-rays can provide information about obstructions, tumors, and other diseases, especially when coupled with the use of barium and air contrast within the bowel.
X-ray
illustration
Review Date: 7/3/2016
Reviewed By: Jason Levy, MD, Northside Radiology Associates, Atlanta, GA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.