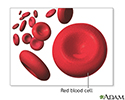
Hypochromia
Hypochromia means that the red blood cells have less color than normal when examined under a microscope. This usually occurs when there is not enough of the pigment that carries oxygen ( hemoglobin ) in the red blood cells.
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. The hemoglobin test measures how much hemoglobin is in your blood.

The most common cause of hypochromia in the United States is not enough iron in the body (iron deficiency). If it is not treated, this can lead to a disorder called iron deficiency anemia .
Iron deficiency anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. There are man...
The cause of hypochromia should be evaluated by your health care provider.
References
Brittenham GM. Disorders of iron homeostasis: iron deficiency and overload. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ Jr, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2013:chap 34.
Ginder GD. Microcytic and hypochromic anemias. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 159.
Review Date: 2/11/2016
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.