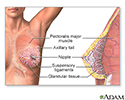
Breast ultrasound
Ultrasonography of the breast; Sonogram of the breast
Breast ultrasound is a test that uses sound waves to examine the breasts.
How the Test is Performed
You will be asked to undress from the waist up. You will be given a gown to wear.
During the test, you will lie on your back on an examining table.
Your health care provider will place a gel on the skin of your breast. A hand-held device, called a transducer, is moved over the breast area. You may be asked to raise your arms above your head and turn to the left or right.
The device sends sound waves to the breast tissue. The sound waves help create a picture that can be seen on a computer screen on the ultrasound machine.
The number of people involved in the test will be limited to protect your privacy.
How to Prepare for the Test
You may want to wear a two-piece outfit, so you do not have to completely undress.
On the day of your test, DO NOT use any lotion or powder on your breasts. DO NOT use deodorant under your arms. Remove jewelry from your neck and chest area.
How the Test will Feel
This test usually does not cause any discomfort, although the gel may feel cool.
Why the Test is Performed
Breast ultrasound is usually ordered when more information is needed after other tests are done. These tests may include mammogram or breast MRI .
Mammogram
A mammogram is an x-ray picture of the breasts. It is used to find breast tumors and cancer.
Breast MRI
A breast MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the breast and sur...
Your provider may order this test if you have:
-
A
breast lump
found during a breast exam
Breast lump
A breast lump is swelling, a growth, or a lump in the breast. Breast lumps in both men and women raise concern for breast cancer, even though most l...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - An abnormal mammogram
-
Clear or bloody
nipple discharge
Nipple discharge
Nipple discharge is any fluid that comes out of the nipple area in your breast.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
A breast ultrasound can:
-
Help tell the difference between a solid mass or a
cyst
Cyst
A cyst is a closed pocket or pouch of tissue. It can be filled with air, fluid, pus, or other material.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Help look for a growth if you have clear or bloody fluid coming from your nipple
-
Guide a needle during a
breast biopsy
Breast biopsy
A breast biopsy is the removal of breast tissue to examine it for signs of breast cancer or other disorders. There are several types of breast biopsi...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Normal Results
A normal result means the breast tissue appears normal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Ultrasound can help show noncancerous growths such as:
- Cysts, which are, fluid-filled sacs
-
Fibroadenomas
, which are, noncancerous solid growths
Fibroadenomas
Fibroadenoma of the breast is a benign tumor. Benign tumor means it is not caused by cancer.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Lipomas, which are, noncancerous fatty lumps that can occur anywhere in the body, including the breasts
Breast cancers can also be seen with ultrasound.
Breast cancers
Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the tissues of the breast. There are 2 main types of breast cancer:Ductal carcinoma starts in the tubes (duct...

Follow-up tests to determine whether treatment may be needed include:
-
Breast lump removal (lumpectomy)
Breast lump removal (lumpectomy)
Breast lump removal is surgery to remove a lump that may be breast cancer. Tissue around the lump is also removed. This surgery is called a lumpect...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Open (surgical) breast biopsy
-
Stereotactic (needle) breast biopsy
Stereotactic (needle) breast biopsy
A breast biopsy is the removal of breast tissue to examine it for signs of breast cancer or other disorders. There are several types of breast biops...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Ultrasound-guided breast biopsy
Ultrasound-guided breast biopsy
A breast biopsy is the removal of breast tissue to examine it for signs of breast cancer or other disorders. There are several types of breast biopsi...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
There are no risks associated with breast ultrasound. There is no radiation exposure.
References
Hacker NF, Friedland ML. Breast disease. In: Hacker NF, Gambone JC, Hobel CJ, eds. Hacker and Moore's Essentials of Obstetrics and Gynecology . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 30.
Harvey JA, Mahoney MC, Newell MS, et al. ACR appropriateness criteria palpable breast masses. J Am Coll Radiol . 2013;10:742-9.e1-3. PMID: 24091044 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24091044 .
Hooley RJ, Scoutt LM, Philpotts LE. Breast ultrasonography: state of the art. Radiology . 2013;268:642-59. PMID: 23970509 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23970509 .
Wolfe AC, Domchek SM, Davidson NE, Sacchini V, McCormick B. Cancer of the breast. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Doroshow JH, Kastan MB, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology . 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone; 2014:chap 91.
Review Date: 10/2/2015
Reviewed By: Debra G. Wechter, MD, FACS, general surgery practice specializing in breast cancer, Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.