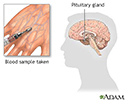
Growth hormone stimulation test
Arginine test; Arginine-GHRH test
The growth hormone (GH) stimulation test measures the ability of the body to produce GH.
How the Test is Performed
Blood is drawn several times. Blood samples are taken through an intravenous (IV) line instead of re-inserting the needle each time. The test takes between 2 to 5 hours.
The procedure is done the following way:
- An IV is usually placed in a vein, most often the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. The site is first cleaned with germ-killing medicine (antiseptic).
- The first sample is drawn early in the morning.
- Medicine is given through the vein. This medicine stimulates the pituitary gland to release GH. Several medicines are available. The doctor will decide which medicine is best.
- Additional blood samples are drawn over the next few hours.
- After the last sample is taken, the IV line is removed. Pressure is applied to stop any bleeding.
How to Prepare for the Test
DO NOT eat for 10 to 12 hours before the test. Eating food can change the test results.
Some medicines can affect the test results. Ask your health care provider if you should stop taking any of your medicines before the test.
If your child will have this test, explain how the test will feel. You may want to demonstrate on a doll. The more familiar your child is with what will happen and the purpose of the procedure, the less anxiety he or she will feel.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging sensation. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or a slight bruise. These soon go away.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is most often done to find out whether a growth hormone deficiency (GH deficiency) is causing slowed growth.
Growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency means the pituitary gland does not make enough growth hormone.

Normal Results
Normal results include:
- Normal peak value, at least 10 nanogram per milliliter (ng/mL) or 10 microgram/L
- Indeterminate, 5 to 10 ng/mL or 5 to 10 microgram/L
- Subnormal, 5 ng/mL or 5 microgram/L
(A normal value rules out hGH deficiency; in some laboratories, the normal level is 7 ng/mL or 7 microgram/L.)
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
If this test does not raise GH levels, there is a reduced amount of hGH stored in the anterior pituitary.
Anterior
Anterior means "in front of" or "the front surface of. " It usually refers to the front side of the body. For example, your knee caps are on the ant...
In children, this results in GH deficiency . In adults, it may be linked to panhypopituitarism or adult GH deficiency.
GH deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency means the pituitary gland does not make enough growth hormone.

Panhypopituitarism
Growth hormone deficiency means the pituitary gland does not make enough growth hormone.

Risks
Veins and arteries vary in size from one patient to another and from one side of the body to the other. Obtaining a blood sample from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
-
Hematoma
(blood accumulating under the skin)
Hematoma
Bleeding into the skin can occur from broken blood vessels that form tiny red dots (called petechiae). Blood also can collect under the tissue in la...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
Medicines that stimulate the pituitary during the test may cause side effects. The doctor can tell you more about this.
References
Alatzoglou KS, Dattani MT. Growth hormone deficiency in children. In: Jameson JL, De Groot LJ, de Kretser DM, et al, eds. Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric . 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 23.
Parks JS, Felner EI. Hypopituitarism. In: Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St. Geme JW, Schor NF, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics . 20th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 557.
-
Growth hormone stimulation test - illustration
The growth hormone stimulation test is usually performed to identify if hGH (human growth hormone) is deficient. The test is performed by administering the amino acid arginine in a vein to raise hGH levels. The test measures the ability of the pituitary to secrete growth hormone in response to the arginine. Lack of hGH can cause growth retardation in infants and children.
Growth hormone stimulation test
illustration
-
Growth hormone stimulation test - illustration
The growth hormone stimulation test is usually performed to identify if hGH (human growth hormone) is deficient. The test is performed by administering the amino acid arginine in a vein to raise hGH levels. The test measures the ability of the pituitary to secrete growth hormone in response to the arginine. Lack of hGH can cause growth retardation in infants and children.
Growth hormone stimulation test
illustration
-
Diabetes - type 2
(In-Depth)
-
Amenorrhea
(Alt. Medicine)
-
Angina
(Alt. Medicine)
-
Epilepsy
(In-Depth)
-
Fibromyalgia
(In-Depth)
-
Rubella
(Alt. Medicine)
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
(In-Depth)
-
Insomnia
(In-Depth)
Review Date: 7/10/2015
Reviewed By: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.