Aminoaciduria
Amino acids - urine; Urine amino acids
Aminoaciduria is an abnormal amount of amino acids in the urine. Amino acids are the building blocks for proteins in the body.
How the Test is Performed
A clean-catch urine sample is needed. This is often done at your doctor's office or health clinic.
Clean-catch urine sample
A urine culture is a lab test to check for bacteria or other germs in a urine sample. It can be used to check for a urinary tract infection in adults...
How to Prepare for the Test
Most of the time you do not need to take special steps before this test. Make sure your doctor knows all of the medicines you recently used. If this test is being done on an infant who is breast-feeding, make sure the health care provider knows what medicines the nursing mother is taking.
How the Test will Feel
The test involves only normal urination.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to measure amino acid levels in the urine. There are many different types of amino acids. It is common for some of each kind to be found in the urine. Increased levels of individual amino acids can be a sign of a problem with metabolism.
Normal Results
The specific value is measured in micromoles per deciliter (micromol/dL) or micromoles per liter (micromol/l).
Alanine
- Children: 65 to 190 micromol/dL or 650 to 1,900 micromol/L
- Adults: 160 to 690 micromol/dL or 1600 to 6,900 micromol/L
Alpha-aminoadipic acid
- Children: 25 to 78 micromol/dL or 250 to 780 micromol/L
- Adults: 0 to 165 micromol/dL or 0 to 1,650 micromol/L
Alpha-amino-N-butyric acid
- Children: 7 to 25 micromol/dL or 70 to 250 micromol/L
- Adults: 0 to 28 micromol/dL or 0 to 280 micromol/L
Arginine
- Children: 10 to 25 micromol/dL or 100 to 250 micromol/L
- Adults: 13 to 64 micromol/dL or 130 to 640 micromol/L
Asparagine
- Children: 15 to 40 micromol/dL or 150 to 400 micromol/L
- Adults: 34 to 100 micromol/dL or 340 to 1,000 micromol/L
Aspartic acid
Aspartic acid is a nonessential amino acids. Amino acids are building blocks of proteins. "Nonessential" means that our bodies produce it even if w...
- Children: 10 to 26 micromol/dL or 100 to 260 micromol/L
- Adults: 14 to 89 micromol/dL or 140 to 890 micromol/L
Beta-alanine
- Children: 0 to 42 micromol/dL or 0 to 420 micromol/L
- Adults: 0 to 93 micromol/dL or 0 to 930 micromol/L
Beta-amino-isobutyric acid
- Children: 25 to 96 micromol/dL or 250 to 960 micromol/L
- Adults: 10 to 235 micromol/dL or 100 to 2,350 micromol/L
Carnosine
- Children: 34 to 220 micromol/dL or 340 to 2,200 micromol/L
- Adults: 16 to 125 micromol/dL or 160 to 1,250 micromol/L
Citrulline
- Children: 0 to 13 micromol/dL or 0 to 130 micromol/L
- Adults: 0 to 11 micromol/dL or 0 to 110 micromol/L
Cystine
- Children: 11 to 53 micromol/dL or 110 to 530 micromol/L
- Adults: 28 to 115 micromol/dL or 280 to 1,150 micromol/L
Glutamic acid
- Children: 13 to 22 micromol/dL or 130 to 220 micromol/L
- Adults: 27 to 105 micromol/dL or 270 to 1,050 micromol/L
Glutamine
- Children: 150 to 400 micromol/dL or 1,500 to 4,000 micromol/L
- Adults: 300 to 1,040 micromol/dL or 3,000 to 10,400 micromol/L
Glycine
- Children: 195 to 855 micromol/dL or 1,950 to 8,550 micromol/L
- Adults: 750 to 2,400 micromol/dL or 7,500 to 24,000 micromol/L
Histidine
- Children: 46 to 725 micromol/dL or 460 to 7,250 micromol/L
- Adults: 500 to 1500 micromol/dL or 5,000 to 15,000 micromol/L
Hydroxyproline
- Children: not measured
- Adults: not measured
Isoleucine
- Children: 3 to 15 micromol/dL or 30 to 150 micromol/L
- Adults: 4 to 23 micromol/dL or 40 to 230 micromol/L
Leucine
- Children: 9 to 23 micromol/dL or 90 to 230 micromol/L
- Adults: 20 to 77 micromol/dL or 200 to 770 micromol/L
Lysine
- Children: 19 to 140 micromol/dL or 190 to 1,400 micromol/L
- Adults: 32 to 290 micromol/dL or 320 to 2,900 micromol/L
Methionine
- Children: 7 to 20 micromol/dL or 70 to 200 micromol/L
- Adults: 5 to 30 micromol/dL or 50 to 300 micromol/L
1-methylhistidine
- Children: 41 to 300 micromol/dL or 410 to 3,000 micromol/L
- Adults: 68 to 855 micromol/dL or 680 to 8,550 micromol/L
3-methylhistidine
- Children: 42 to 135 micromol/dL or 420 to 1,350 micromol/L
- Adults: 64 to 320 micromol/dL or 640 to 3,200 micromol/L
Ornithine
- Children: 3 to 16 micromol/dL or 30 to 160 micromol/L
- Adults: 5 to 70 micromol/dL or 50 to 700 micromol/L
Phenylalanine
Serum phenylalanine screening is a blood test to look for signs of the disease phenylketonuria (PKU). The test detects abnormally high levels of an ...
- Children: 20 to 61 micromol/dL or 200 to 610 micromol/L
- Adults: 36 to 90 micromol/dL or 360 to 900 micromol/L
Phosphoserine
- Children: 16 to 34 micromol/dL or 160 to 340 micromol/L
- Adults: 28 to 95 micromol/dL or 280 to 950 micromol/L
Phosphoethanolamine
- Children: 24 to 66 micromol/dL or 240 to 660 micromol/L
- Adults: 17 to 95 micromol/dL or 170 to 950 micromol/L
Proline
- Children: not measured
- Adults: not measured
Serine
- Children: 93 to 210 micromol/dL or 930 to 2,100 micromol/L
- Adults: 200 to 695 micromol/dL or 2,000 to 6,950 micromol/L
Taurine
- Children: 62 to 970 micromol/dL or 620 to 9,700 micromol/L
- Adults: 267 to 1290 micromol/dL or 2,670 to 12,900 micromol/L
Threonine
- Children: 25 to 100 micromol/dL or 250 to 1,000 micromol/L
- Adults: 80 to 320 micromol/dL or 800 to 3,200 micromol/L
Tyrosine
- Children: 30 to 83 micromol/dL or 300 to 830 micromol/L
- Adults: 38 to 145 micromol/dL or 380 1,450 micromol/L
Valine
- Children: 17 to 37 micromol/dL or 170 to 370 micromol/L
- Adults: 19 to 74 micromol/dL or 190 to 740 micromol/
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your health care provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
The examples above show the common measurements for results for these tests. Some laboratories use different measurements or may test different specimens.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Increased total urine amino acids may be due to:
- Alkaptonuria
- Canavan disease
- Cystinosis
- Cystathioninuria
- Fructose intolerance
-
Galactosemia
Galactosemia
Galactosemia is a condition in which the body is unable to use (metabolize) the simple sugar galactose.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hartnup disease
- Homocystinuria
- Hyperammonemia
-
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is a disorder in which the parathyroid glands in your neck produce too much parathyroid hormone (PTH).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Maple syrup urine disease
-
Methylmalonic acidemia
Methylmalonic acidemia
Methylmalonic acidemia is a disorder in which the body cannot break down certain proteins and fats. The result is a buildup of a substance called me...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a blood cancer that starts in the plasma cells in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue found inside most bone...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency
-
Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia is softening of the bones. It most often occurs because of a problem with vitamin D, which helps your body absorb calcium. Your body n...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Propionic acidemia
-
Rickets
Rickets
Rickets is a disorder caused by a lack of vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate. It leads to softening and weakening of the bones.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tyrosinemia type 1
- Tyrosinemia type 2
-
Viral
hepatitis
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is swelling and inflammation of the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Wilson disease
Wilson disease
Wilson disease is an inherited disorder in which there is too much copper in the body's tissues. The excess copper damages the liver and nervous sys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Considerations
Screening infants for increased levels of amino acids can help detect problems with metabolism. Early treatment for these conditions may prevent complications in the future.
References
Hortin GL. In: Burtis CA ed. Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics . 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:chap 21.
-
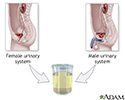
Urine sample - illustration
A "clean-catch" urine sample is performed by collecting the sample of urine in midstream. Men or boys should wipe clean the head of the penis. Women or girls need to wash the area between the lips of the vagina with soapy water and rinse well. A small amount of urine should initially fall into the toilet bowl before it is collected (this clears the urethra of contaminants). Then, in a clean container, catch about 1 to 2 ounces of urine and remove the container from the urine stream. The container is then given to the health care provider.
Urine sample
illustration
-
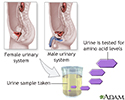
Aminoaciduria urine test - illustration
Aminoaciduria is a test that screens for increased levels of amino acid excretion in the urine which may indicate inborn errors of metabolism caused by a specific enzyme deficiency.
Aminoaciduria urine test
illustration
-
Urine sample - illustration
A "clean-catch" urine sample is performed by collecting the sample of urine in midstream. Men or boys should wipe clean the head of the penis. Women or girls need to wash the area between the lips of the vagina with soapy water and rinse well. A small amount of urine should initially fall into the toilet bowl before it is collected (this clears the urethra of contaminants). Then, in a clean container, catch about 1 to 2 ounces of urine and remove the container from the urine stream. The container is then given to the health care provider.
Urine sample
illustration
-
Aminoaciduria urine test - illustration
Aminoaciduria is a test that screens for increased levels of amino acid excretion in the urine which may indicate inborn errors of metabolism caused by a specific enzyme deficiency.
Aminoaciduria urine test
illustration
Review Date: 4/20/2015
Reviewed By: Chad Haldeman-Englert, MD, FACMG, Wake Forest School of Medicine, Department of Pediatrics, Section on Medical Genetics, Winston-Salem, NC. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.