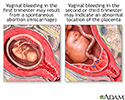
Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy
Pregnancy - vaginal bleeding; Maternal blood loss - vaginal
Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy is any discharge of blood from the vagina during pregnancy.
Considerations
Up to 1 in 4 women have vaginal bleeding at some time during their pregnancy. Bleeding is more common in the first 3 months (first trimester), especially with twins.
Causes
During the first 3 months , vaginal bleeding may be a sign of a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy. Contact the health care provider right away.
During the first 3 months
Miscarriage - vaginal bleeding; Threatened abortion - vaginal bleeding
During months 4 to 9 , bleeding may be a sign of:
-
The placenta separating from the inner wall of the uterus before the baby is born (
abruptio placentae
)
Abruptio placentae
The placenta is the organ that supplies food and oxygen to the baby during pregnancy. Placental abruption is when the placenta detaches from the wal...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Miscarriage
- The placenta is covering all or part of the opening to the cervix (placenta previa)
- Vasa previa
Other possible causes of vaginal bleeding during pregnancy:
-
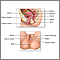
Cervical polyp
or growth
Cervical polyp
Cervical polyps are fingerlike growths on the lower part of the uterus that connects with the vagina (cervix).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Early labor (bloody show)
-
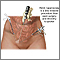
Ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy that occurs outside the womb (uterus). It is life-threatening to the mother.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection of the cervix
- Trauma to the cervix from intercourse (small amount of bleeding) or recent pelvic exam
Home Care
Avoid sexual intercourse until your provider tells you that it is safe to start having intercourse again.
Drink only fluids if the bleeding and cramping are severe.
You may need to cut down your activity or be put on bed rest at home.
- Bed rest at home may be for the rest of your pregnancy or until the bleeding stops.
- The bed rest may be complete.
- Or, you may be able to get up to go to the bathroom, walk around the house, or do light chores.
Medicine is not needed in most cases. DO NOT take any medicines without talking to your provider.
Talk to your provider about what to look for, such as the amount of bleeding and color of the blood.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have any vaginal bleeding during pregnancy. Treat this as a potential emergency.
- You have vaginal bleeding and have placenta previa (get to the hospital right away).
- You have cramps or labor pains.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will take a medical history and perform a physical exam .
Physical exam
During a physical examination, a health care provider studies your body to determine if you do or do not have a physical problem. A physical examinat...
You will probably have a pelvic exam as well.
Tests that may be done include:
- Blood tests
-
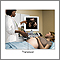
Pregnancy ultrasound
Pregnancy ultrasound
A pregnancy ultrasound is an imaging test that uses sound waves to create a picture of how a baby is developing in the womb. It is also used to chec...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ultrasound of the pelvis
References
Francois KE, Foley MR. Antepartum and postpartum hemorrhage. In: Gabbe SG, Niebyl JR, Simpson JL, et al, eds. Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:chap 19.
Houry DE, Salhi BA. Acute complications of pregnancy. In: Marx JA, Hockberger RS, Walls RM, et al, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2014:chap 178.
-
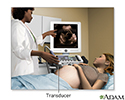
Ultrasound in pregnancy - illustration
The ultrasound has become a standard procedure used during pregnancy. It can demonstrate fetal growth and can detect increasing numbers of conditions in the fetus including meningomyelocele, congenital heart disease, kidney abnormalities, hydrocephalus, anencephaly, club feet, and other deformities. Ultrasound does not produce ionizing radiation and is considered a very safe procedure for both the mother and the fetus.
Ultrasound in pregnancy
illustration
-
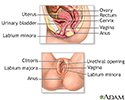
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
External structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris. Internal structures include the uterus, ovaries and cervix.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
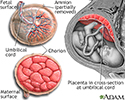
Anatomy of a normal placenta - illustration
The placenta provides the fetus with oxygen and nutrients and takes away waste such as carbon dioxide via the umbilical cord.
Anatomy of a normal placenta
illustration
-
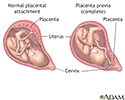
Placenta previa - illustration
Placenta previa is a condition of pregnancy when the placenta implants in the lower part of the uterus, partly or completely obstructing the cervical outlet to the vagina (birth canal).
Placenta previa
illustration
-
Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy - illustration
There are many possible causes of bleeding during pregnancy. Bleeding should always be evaluated by a health care provider.
Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy
illustration
-
Ultrasound in pregnancy - illustration
The ultrasound has become a standard procedure used during pregnancy. It can demonstrate fetal growth and can detect increasing numbers of conditions in the fetus including meningomyelocele, congenital heart disease, kidney abnormalities, hydrocephalus, anencephaly, club feet, and other deformities. Ultrasound does not produce ionizing radiation and is considered a very safe procedure for both the mother and the fetus.
Ultrasound in pregnancy
illustration
-
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
External structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris. Internal structures include the uterus, ovaries and cervix.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
Anatomy of a normal placenta - illustration
The placenta provides the fetus with oxygen and nutrients and takes away waste such as carbon dioxide via the umbilical cord.
Anatomy of a normal placenta
illustration
-
Placenta previa - illustration
Placenta previa is a condition of pregnancy when the placenta implants in the lower part of the uterus, partly or completely obstructing the cervical outlet to the vagina (birth canal).
Placenta previa
illustration
-
Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy - illustration
There are many possible causes of bleeding during pregnancy. Bleeding should always be evaluated by a health care provider.
Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy
illustration
- Vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy
- Vaginal bleeding in late pregnancy
- After vaginal delivery - in the hospital
- Common symptoms during pregnancy
- Prenatal care in your second trimester
- Prenatal care in your first trimester
- Preterm labor
- When your baby is stillborn
- Prenatal care in your third trimester
- Bed rest during pregnancy
Review Date: 4/5/2016
Reviewed By: Irina Burd, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Gynecology and Obstetrics at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.