Cervical polyps
Vaginal bleeding - polyps
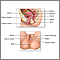
Cervical polyps are fingerlike growths on the lower part of the uterus that connects with the vagina ( cervix ).
Cervix
The cervix is the lower end of the womb (uterus). It is at the top of the vagina. It is about 2 inches (5 centimeters) long. The cervical canal pa...
Causes
The exact cause of cervical polyps is not known. They may occur with:
- An abnormal response to increased levels of the female hormone estrogen
-
Chronic
inflammation
Chronic
Chronic refers to something that continues over an extended period of time. A chronic condition is usually long-lasting and does not easily or quick...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Clogged blood vessels in the cervix
Cervical polyps are common. They are often found in women over age 20 who have had children. Polyps are rare in young women who have not started having their period (menstruation).
Most women have only one polyp, but some women have two or three.
Symptoms
Polyps do not always cause symptoms. When symptoms are present, they may include:
- Very heavy menstrual periods
- Vaginal bleeding after douching or intercourse
-
Abnormal vaginal bleeding after
menopause
or between periods
Menopause
Menopause is the time in a woman's life when her periods (menstruation) stop. Most often, it is a natural, normal body change that most often occurs...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - White or yellow mucus (leukorrhea)
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will see smooth, red or purple fingerlike growths on the cervix during a pelvic exam.
A cervical biopsy will be performed. Most of the time, the biopsy will show cells that are consistent with a benign polyp. Rarely, there may be abnormal, precancerous, or cancer cells in a polyp.
Biopsy
A colposcopy is a special way of looking at the cervix. It uses a light and a low-powered microscope to make the cervix appear much larger. This he...

Treatment
The provider can remove polyps during a simple, outpatient procedure.
- Smaller polyps may be removed with gentle twisting.
- Electrocautery may be needed to remove larger polyps.
The removed polyp tissue should be sent to a lab for further tests.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most polyps are not cancerous (benign) and are easy to remove. Polyps do not grow back most of the time. Women who have polyps are at risk of growing more polyps.
Possible Complications
There may be bleeding and slight cramping for a few days after removal of a polyp. Some cervical cancers may first appear as a polyp. Certain uterine polyps may be associated with uterine cancer.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if you have:
- Abnormal bleeding from the vagina, including bleeding after sex or between periods
- Abnormal discharge from the vagina
- Abnormally heavy periods
Call your provider to schedule regular gynecological exams. Ask how often you should receive a Pap test .
Pap test
The Pap test checks for cervical cancer. Cells scraped from the opening of the cervix are examined under a microscope. The cervix is the lower part...

Prevention
See your provider to treat infections as soon as possible.
References
Choby BA. Cervical polyps. In: Pfenninger JL, Fowler GC, eds. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care . 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2011:chap 135.
Ellenson LHl, Pirog EC. The female genital tract. In: Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC, eds. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease . 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 22.
Katz VL. Benign gynecologic lesions. In: Lentz GM, Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Katz VL, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2012:chap 18.
-
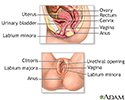
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
External structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris. Internal structures include the uterus, ovaries and cervix.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
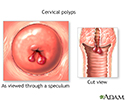
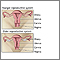
Cervical polyps - illustration
Cervical polyps are small fingerlike growths originating from the mucosal surface of the cervix. The small fragile growths hang from a stalk and protrude through the cervical opening.
Cervical polyps
illustration
-
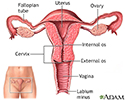
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
-
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
External structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris. Internal structures include the uterus, ovaries and cervix.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
Cervical polyps - illustration
Cervical polyps are small fingerlike growths originating from the mucosal surface of the cervix. The small fragile growths hang from a stalk and protrude through the cervical opening.
Cervical polyps
illustration
-
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
Review Date: 4/5/2016
Reviewed By: Irina Burd, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Gynecology and Obstetrics at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.