Newborn head molding
Newborn cranial deformation; Molding of the newborn's head; Neonatal care - head molding
Newborn head molding is an abnormal head shape that results from pressure on the baby's head during childbirth.
Information
The bones of a newborn baby's skull are soft and flexible, with gaps between the plates of bone.
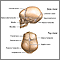
The spaces between the bony plates of the skull are called cranial sutures . The front ( anterior ) and back (posterior) fontanelles are 2 gaps that are particularly large. These are the soft spots you can feel when you touch the top of your baby's head.
Cranial sutures
Cranial sutures are fibrous bands of tissue that connect the bones of the skull.
Anterior
Anterior means "in front of" or "the front surface of. " It usually refers to the front side of the body. For example, your knee caps are on the ant...
Fontanelles
Cranial sutures are fibrous bands of tissue that connect the bones of the skull.

When a baby is born in a head-first position, pressure on the head in the birth canal may mold the head into an oblong shape. These spaces between the bones allow the baby's head to change shape. Depending on the amount and length of pressure, the skull bones may even overlap.
These spaces also allow the brain to grow inside the skull bones. They will close as the brain reaches its full size.
Fluid may also collect in the baby's scalp ( caput succedaneum ), or blood may collect beneath the scalp (cephalohematoma). This may further distort the shape and appearance of the baby's head. Fluid and blood collection in and around the scalp is common during delivery. It will most often go away in a few days.
Caput succedaneum
Caput succedaneum is swelling of the scalp in a newborn. It is most often brought on by pressure from the uterus or vaginal wall during a head-first...
If your baby is born breech (buttocks or feet first) or by Cesarean delivery , the head is most often round. Very severe abnormalities in head size are NOT related to molding.
Cesarean delivery
A C-section is the delivery of a baby through a surgical opening in the mother's lower belly area. It is also called a cesarean delivery.
Related topics include:
-
Craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis is a birth defect in which one or more of the sutures on a baby's head closes earlier than usual. The skull of an infant or young c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Macrocephaly
(abnormally large head size)
Macrocephaly
Increased head circumference is when the measured distance around the widest part of the skull is larger than expected for the child's age and backgr...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Microcephaly
(abnormally small head size)
Microcephaly
Microcephaly is a condition in which a person's head size is much smaller than that of others of the same age and sex. Head size is measured as the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Graham JM, Sanchez-Lara P. Vertex birth molding. In: Graham JM, Sanchez-Lara PA, eds. Smiths' Recognizable Patterns of Human Deformation . 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 35.
Smith J. Initial evaluation. In: Gleason CA, Devaskar SU, eds. Avery's Diseases of the Newborn . 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:chap 25.
-
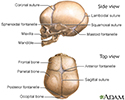
Skull of a newborn - illustration
The "sutures" or anatomical lines where the bony plates of the skull join together can be easily felt in the newborn infant. The diamond shaped space on the top of the skull and the smaller space further to the back are often referred to as the "soft spot" in young infants.
Skull of a newborn
illustration
-
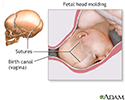
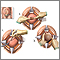
Fetal head molding - illustration
During a head first birth, pressure on the head caused by the tight birth canal may "mold" the head into an oblong rather than round shape. This is a common occurrence that usually disappears after a few days.
Fetal head molding
illustration
-
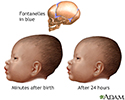
Newborn head molding - illustration
During a head first birth, pressure on the head caused by the tight birth canal may 'mold' the head into an oblong rather than round shape. Newborn head molding is a common occurrence that usually disappears after a few days.
Newborn head molding
illustration
-
Skull of a newborn - illustration
The "sutures" or anatomical lines where the bony plates of the skull join together can be easily felt in the newborn infant. The diamond shaped space on the top of the skull and the smaller space further to the back are often referred to as the "soft spot" in young infants.
Skull of a newborn
illustration
-
Fetal head molding - illustration
During a head first birth, pressure on the head caused by the tight birth canal may "mold" the head into an oblong rather than round shape. This is a common occurrence that usually disappears after a few days.
Fetal head molding
illustration
-
Newborn head molding - illustration
During a head first birth, pressure on the head caused by the tight birth canal may 'mold' the head into an oblong rather than round shape. Newborn head molding is a common occurrence that usually disappears after a few days.
Newborn head molding
illustration
Review Date: 11/19/2015
Reviewed By: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.