Biofeedback
Biofeedback is a technique that measures bodily functions and gives you information about them in order to help train you to control them.
Information
Biofeedback is most often based on measurements of:
- Blood pressure
-
Brain waves (
EEG
)
EEG
An electroencephalogram is a test to measure the electrical activity of the brain.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Breathing
-
Heart rate
Heart rate
The pulse is the number of heartbeats per minute.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Muscle tension
- Skin conductivity of electricity
- Skin temperature
By watching these measurements, you can learn how to change these functions by relaxing or by holding pleasant images in your mind.
Patches, called electrodes, are placed on different parts of your body. They measure your heart rate, blood pressure, or other function. A monitor displays the results. A tone or other sound may be used to let you know when you have reached a goal or certain state.
Your health care provider will describe a situation and guide you through relaxation techniques. The monitor lets you see how your heart rate and blood pressure change in response to being stressed or remaining relaxed.
Biofeedback teaches you how to control and change these bodily functions. By doing so, you feel more relaxed or more able to cause specific muscle relaxation processes. This may help treat conditions such as:
- Anxiety and insomnia
- Constipation
-
Tension and
migraine headaches
Migraine headaches
A migraine is a type of headache. It may occur with symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light and sound. In many people, a throbbi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence
Urinary (or bladder) incontinence happens when you are not able to keep urine from leaking out of your urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Haas DJ. Complementary and alternative medicine. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 131.
Perlman A. Complementary and alternative medicine. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 39.
Turk DC. Psychological interventions. In: Benzon HT, Rathmell JP, Wu CL, Turk DC, Argoff CE, Hurley RW, eds. Practical Management of Pain . 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2014:chap 45.
-
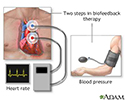
Biofeedback - illustration
Biofeedback is a process for monitoring a body function such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure and altering that function through relaxation or imagery.
Biofeedback
illustration
-
Biofeedback - illustration
An EKG is an external electronic monitoring device which gives an immediate and continuous readout of the beating of the heart.
Biofeedback
illustration
-
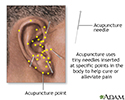
Acupuncture - illustration
Acupuncture, hypnosis and biofeedback are all alternative ways to control pain. Acupuncture involves the insertion of tiny sterile needles, slightly thicker than a human hair, at specific points on the body.
Acupuncture
illustration
-
Biofeedback - illustration
Biofeedback is a process for monitoring a body function such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure and altering that function through relaxation or imagery.
Biofeedback
illustration
-
Biofeedback - illustration
An EKG is an external electronic monitoring device which gives an immediate and continuous readout of the beating of the heart.
Biofeedback
illustration
-
Acupuncture - illustration
Acupuncture, hypnosis and biofeedback are all alternative ways to control pain. Acupuncture involves the insertion of tiny sterile needles, slightly thicker than a human hair, at specific points on the body.
Acupuncture
illustration
-
Biofeedback
(Alt. Medicine)
Review Date: 1/5/2016
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Division of Neurology, Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.