Pierre Robin sequence
Pierre Robin syndrome; Pierre Robin complex; Pierre Robin anomaly
Pierre Robin sequence (or syndrome) is a condition in which an infant has a smaller than normal lower jaw, a tongue that falls back in the throat, and difficulty breathing. It is present at birth.
Causes
The exact causes of Pierre Robin sequence are unknown. It may be part of many genetic syndromes.
The lower jaw develops slowly before birth, but may grow faster during the first few years of life.
Symptoms
Symptoms of this condition include:
- Cleft soft palate
- High-arched palate
- Jaw that is very small with a small chin
- Jaw that is far back in the throat
- Repeated ear infections
- Small opening in the roof of the mouth, which may cause choking or liquids coming back out through the nose
- Teeth that appear when the baby is born
- Tongue that is large compared to the jaw
Exams and Tests
A health care provider can often diagnose this condition during a physical exam. Consulting with a genetic specialist can rule out other problems linked to this syndrome.
Treatment
Do NOT put infants with this condition on their back. This is to prevent their tongue from falling back into their airway.
In moderate cases, the child will need to have a tube placed through their nose and into their airways to avoid airway blockage. In severe cases, surgery is needed to prevent a blockage in the upper airway. Some children need surgery to make a hole in their airway or to move their jaw forward.
Feeding must be done very carefully to avoid choking and breathing liquids into the airways. The child may need to be fed through a tube to prevent choking.
Support Groups
For support and information, the following organizations may be helpful:
- The Pierre Robin Network
- The Cleft Palate Foundation -- www.cleftline.org .
Outlook (Prognosis)
Choking and feeding problems may go away on their own over the first few years as the lower jaw grows to a more normal size. There is a high risk for problems if the child's airways are not kept from getting blocked.
Possible Complications
These complications can occur:
- Breathing difficulties, especially when the child sleeps
- Choking episodes
- Congestive heart failure
- Death
- Feeding difficulties
- Low blood oxygen and brain damage (due to difficulty breathing)
- Type of high blood pressure called pulmonary hypertension
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Babies born with this condition are often diagnosed at birth.
Call your provider if your child has choking episodes or breathing problems. A blockage of the airways may cause a high-pitched noise when the child breathes in. It can also lead to blueness of the skin (cyanosis).
Also call if your child has other breathing problems.
Prevention
There is no known prevention. Treatment may reduce breathing problems and choking.
References
Tinanoff N. Syndromes with oral manifestations. In: Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St Geme JW III, Schor NF, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics . 20th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 311.
-
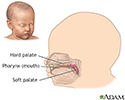
Infant hard and soft palates - illustration
The roof of the mouth is comprised of the hard palate and the soft palate. These structures separate the nasal cavity from the mouth.
Infant hard and soft palates
illustration
Review Date: 10/27/2015
Reviewed By: Chad Haldeman-Englert, MD, FACMG, Fullerton Genetics Center, Asheville, NC. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.