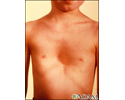
LEOPARD syndrome
LEOPARD syndrome is a very rare inherited disorder in which there are problems with the skin, face, and heart.
Causes
LEOPARD syndrome is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. This means the person only needs the abnormal gene from one parent in order to inherit the disease.
Symptoms
LEOPARD stands for the different problems (signs and symptoms) of this disorder:
- L entigines – large number of brown or black freckle-like skin markings that mainly affect the neck and upper chest but can appear all over the body
-
Electrocardiograph
conduction abnormalities – problems with the electrical and pumping functions of the heart
Electrocardiograph
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - O cular hypertelorism – eyes that are spaced wide apart
-
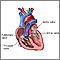
Pulmonary valve stenosis
– narrowing of the pulmonary heart valve, resulting in less blood flow to the lungs and causing shortness of breath
Pulmonary valve stenosis
Pulmonary valve stenosis is a heart valve disorder that involves the pulmonary valve. This is the valve separating the right ventricle (one of the ch...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
A
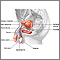
bnormalities of the genitals – such as
undescended testicles
Undescended testicles
Undescended testicle occurs when one or both testicles fail to move into the scrotum before birth.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
R
etardation of growth (
delayed growth
) – including bone growth problems of the chest and spine
Delayed growth
Delayed growth is poor or abnormally slow height or weight gains in a child younger than age 5. This may just be normal, and the child may outgrow i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - D eafness – hearing loss may vary between mild and severe
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and listen to the heart with a stethoscope.
Tests that may be done include:
-
ECG and
echocardiogram
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hearing test
- CT scan of the brain
- Skull x-ray
- EEG
- Blood tests to check certain hormone levels
Treatment
Symptoms are treated as appropriate. A hearing aid may be needed. Hormone treatment may be necessary at the expected time of puberty to cause the normal changes to occur.
Laser, cryosurgery (freezing), or bleaching creams may help lighten some of the brown spots on the skin.
Possible Complications
Complications vary and include:
- Deafness
- Delayed puberty
- Heart problems
- Infertility
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if there are symptoms of this disorder.
Call for an appointment with your provider if you have a family history of this disorder and plan to have children.
Prevention
Genetic counseling is recommended for people with a family history of LEOPARD syndrome who want to have children.
References
Martínez-Quintana E, Rodríguez-González F. LEOPARD syndrome: clinical features and gene mutations. Mol Syndromol . 2012;3:145-57. PMID: 23239957 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23239957 .
Porciello R, Divona L, Strano S, Carbone A, Calvieri C, Giustini S. LEOPARD syndrome. Dermatol Online J . 2008;14(3):7. PMID: 18627709 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18627709 .
Sarkozy A, Digilio MC, Dallapiccola B. LEOPARD syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis . 2008;3:13. PMID: 18505544 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18505544 .
-
Pectus excavatum - illustration
Pectus excavatum is a condition in which the "breast bone" (sternum) appears sunken and the chest concave. It is sometimes called "funnel chest". The majority of these cases are not associated with any other condition (isolated findings). However, some genetic conditions include pectus excavatum.
Pectus excavatum
illustration
-
Pectus excavatum - illustration
Pectus excavatum is a condition in which the "breast bone" (sternum) appears sunken and the chest concave. It is sometimes called "funnel chest". The majority of these cases are not associated with any other condition (isolated findings). However, some genetic conditions include pectus excavatum.
Pectus excavatum
illustration
Review Date: 4/14/2015
Reviewed By: Kevin Berman, MD, PhD, Atlanta Center for Dermatologic Disease, Atlanta, GA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.