Hepatocerebral degeneration
Chronic acquired (Non-Wilsonian) hepatocerebral degeneration
Hepatocerebral degeneration is a brain disorder that occurs in people with liver damage.
Causes
This condition may occur in any case of acquired liver failure, including severe hepatitis .
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is swelling and inflammation of the liver.
Liver damage can lead to the buildup of ammonia and other toxic materials in the body. This happens when the liver doesn't work properly. It does not break down and eliminate these chemicals. The toxic materials can damage brain tissue.
Specific areas of the brain, such as the basal ganglia, are more likely to be injured from liver failure. The basal ganglia help control movement. This condition is the "non-Wilsonian" type. This means that the liver damage is not caused by copper deposits in the liver. This is a key feature of
Wilson disease
.
Wilson disease
Wilson disease is an inherited disorder in which there is too much copper in the body's tissues. The excess copper damages the liver and nervous sys...

Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Difficulty walking
- Impaired intellectual function
- Jaundice
- Muscle spasm (myoclonus)
- Rigidity
- Shaking of arms, head (tremor)
- Twitching
-
Uncontrolled body movements (
chorea
)
Chorea
Jerky body movement is a condition in which a person makes fast movements that they cannot control and that have no purpose. These movements interru...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Unsteady walking (
ataxia
)
Ataxia
Uncoordinated movement is due to a muscle control problem that causes an inability to coordinate movements. It leads to a jerky, unsteady, to-and-fr...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Signs include:
-
Coma
Coma
Decreased alertness is a state of reduced awareness. A coma is a state of decreased alertness from which a person cannot be awakened. A long-term co...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fluid in the abdomen that causes swelling (
ascites
)
Ascites
Ascites is the build-up of fluid in the space between the lining of the abdomen and abdominal organs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Gastrointestinal bleeding from enlarged veins in the food pipe (esophageal varices)
A nervous system (neurological) exam may show signs of:
-
Dementia
Dementia
Dementia is a loss of brain function that occurs with certain diseases. It affects memory, thinking, language, judgment, and behavior.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Involuntary movements
- Walking instability
Laboratory tests may show a high ammonia level in the bloodstream and abnormal liver function.
Other tests may include:
-
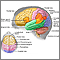
MRI of the head
MRI of the head
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
EEG
(may show general slowing of brain waves)
EEG
An electroencephalogram is a test to measure the electrical activity of the brain.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CT scan of the head
CT scan of the head
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment helps reduce the toxic chemicals that build up from liver failure. It may include antibiotics or a medicine such as lactulose, which lowers the level of ammonia in the blood.
A treatment called branched-chain amino acid therapy may also:
- Improve symptoms
- Reverse brain damage
There is no specific treatment for the neurologic syndrome, because it is caused by irreversible liver damage. A liver transplant may cure the liver disease. However, this operation may not reverse the symptoms of brain damage.
Outlook (Prognosis)
This is a long-term (chronic) condition that may lead to irreversible nervous system (neurological) symptoms.
The person may continue to get worse and die without a liver transplant. If a transplant is done early, the neurological syndrome may be reversible.
Possible Complications
Complications include:
-
Hepatic coma
Hepatic coma
Loss of brain function occurs when the liver is unable to remove toxins from the blood. This is called hepatic encephalopathy. This problem may occ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Severe brain damage
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you have any symptoms of liver disease.
Prevention
It is not possible to prevent all forms of liver disease. However, alcoholic and viral hepatitis may be prevented.
To reduce your risk of getting alcoholic or viral hepatitis:
- Avoid risky behaviors, such as IV drug use or unprotected sex.
- Don't drink, or drink only in moderation.
References
Garcia-Tiso G. Cirrhosis and its sequelae. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 153.
Haq IU, Tate JA, Siddiqui MS, Okun MS. Clinical overview of movement disorders. In: Winn HR, ed. Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery . 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 84.
-
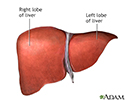
Liver anatomy - illustration
The liver serves a wide variety of body functions, including detoxifying blood and producing bile that aids in digestion.
Liver anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 12/1/2016
Reviewed By: Subodh K. Lal, MD, gastroenterologist with Gastrointestinal Specialists of Georgia, Austell, GA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.