Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome
Rubinstein syndrome, RTS
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RTS) is a genetic disease. It involves broad thumbs and toes, short stature, distinctive facial features, and varying degrees of intellectual disability.
Causes
RTS is a rare condition. Defects in the genes CREBBP and EP300 are seen in some people with this condition.
Some people are missing the gene entirely. This is more typical in people with more severe problems.
Most cases are sporadic (not passed down through families). They are likely due to a new genetic defect that occurs either in the sperm or egg cells, or at the time of conception.
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- Broadening of the thumbs and big toes
- Constipation
- Excess hair on body (hirsutism)
- Heart defects, possibly requiring surgery
-
Intellectual disability
Intellectual disability
Intellectual disability is a condition diagnosed before age 18 that includes below-average intellectual function and a lack of skills necessary for d...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Seizures
-
Short stature
that is noticeable after birth
Short stature
A child who has short stature is much shorter than children who are the same age and sex. Your health care provider will go over your child's growth ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Slow development of cognitive skills
- Slow development of motor skills accompanied by low muscle tone
Other signs and symptoms may include:
- Absent or extra kidney, and other problems with kidney or bladder
- An underdeveloped bone in the midface
- Unsteady or stiff walking gait
- Downward-slanted eyes
-
Low-set ears
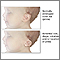
or malformed ears
Low-set ears
Low-set ears and pinna abnormalities refer to an abnormal shape or position of the outer ear (pinna or auricle).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Drooping eyelid (
ptosis
)
Ptosis
Eyelid drooping is excess sagging of the upper eylid. The edge of the upper eyelid may be lower than it should be (ptosis) or there may be excess ba...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cataracts
-
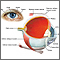
Coloboma
(a defect in the iris of the eye)
Coloboma
Coloboma of the iris is a hole or defect of the iris of the eye. Most colobomas are present since birth (congenital).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Extra fingers (polydactyly)
-
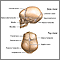
Macrocephaly
(excessively large head) or
microcephaly
(excessively small head)
Macrocephaly
Increased head circumference is when the measured distance around the widest part of the skull is larger than expected for the child's age and backgr...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMicrocephaly
Microcephaly is a condition in which a person's head size is much smaller than that of others of the same age and sex. Head size is measured as the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Narrow, small, or recessed mouth with crowded teeth
- Prominent or "beaked" nose
- Thick and arched eyebrows with long eyelashes
-
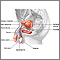
Undescended testicle (
cryptorchidism
), or other testicular problems
Cryptorchidism
Undescended testicle occurs when one or both testicles fail to move into the scrotum before birth.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam. Blood tests and x-rays may also be done.
Genetic tests can be done to determine if the genes involved in this disease are missing or changed.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for RTS. Surgery to repair the bones in the thumbs or toes can sometimes improve grasp or relieve discomfort.
Support Groups
Rubinstein-Taybi Parents Group USA: www.rubinstein-taybi.com
Outlook (Prognosis)
The majority of children can learn to read at an elementary level. The majority have delayed motor development, but on average, they learn to walk by 2 1/2 years of age.
Possible Complications
Complications depend on what part of the body is affected. Complications may include:
- Feeding problems in infants
- Repeated ear infections and hearing loss
- Problems with the shape of the heart
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Scarring of the skin
When to Contact a Medical Professional
An appointment with a geneticist is recommended if the provider finds signs of RTS.
Prevention
Genetic counseling is advised for couples with a family history of this disease who are planning a pregnancy.
References
Nussbaum RL, McInnes RR, Willard HF. Develomental genetics and birth defects. In: Nussbaum RL, McInnes RR, Willard HF, eds. Thompson & Thompson Genetics in Medicine . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 14.
Stevens CA. Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome. Gene Reviews. 2014;8. PMID: 20301699 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20301699 . Accessed August 1, 2015.
-
Polydactyly - an infant's hand - illustration
Extra digits may be present as an isolated finding, or they may occur as part of a syndrome, in which case other abnormalities are usually present.
Polydactyly - an infant's hand
illustration
Review Date: 8/1/2015
Reviewed By: Chad Haldeman-Englert, MD, FACMG, Fullerton Genetics Center, Asheville, NC. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

