Mastoiditis
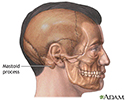
Mastoiditis is an infection of the mastoid bone of the skull. The mastoid is located just behind the ear.
Causes
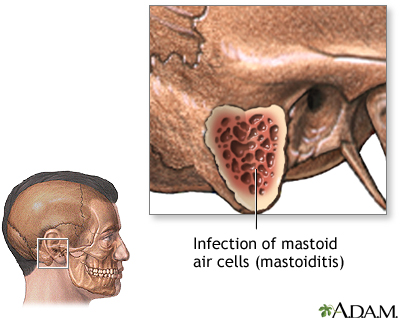
Mastoiditis is most often caused by a middle ear infection ( acute otitis media ). The infection may spread from the ear to the mastoid bone. The bone has a honeycomb-like structure that fills with infected material and may break down.
Acute otitis media
Ear infections are one of the most common reasons parents take their children to the doctor. The most common type of ear infection is called otitis ...
The condition is most common in children. Before antibiotics, mastoiditis was one of the leading causes of death in children. The condition does not occur very often today. It is also much less dangerous.
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
-
Drainage from the ear
Drainage from the ear
Ear discharge is drainage of blood, ear wax, pus, or fluid from the ear.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Ear pain or discomfort
Ear pain or discomfort
An earache is a sharp, dull, or burning pain in one or both ears. The pain may last a short time or be ongoing. Related conditions include:Otitis m...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fever, may be high or suddenly increase
- Headache
- Hearing loss
- Redness of the ear or behind the ear
- Swelling behind ear, may cause ear to stick out
Exams and Tests
An exam of the head may reveal signs of mastoiditis. The following tests may show an abnormality of the mastoid bone:
-
CT scan
of the ear
CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Head CT scan
Head CT scan
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
A culture of drainage from the ear may show bacteria.
Treatment
Mastoiditis may be hard to treat because the medicine may not reach deeply into the bone. The condition sometimes requires repeated or long-term treatment. The infection is treated with antibiotic injections, followed by antibiotics taken by mouth.
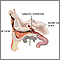
Surgery to remove part of the bone and drain the mastoid ( mastoidectomy ) may be needed if antibiotic treatment does not work. Surgery to drain the middle ear through the eardrum ( myringotomy ) may be needed to treat the middle ear infection.
Mastoidectomy
A mastoidectomy is surgery to remove cells in the hollow, air-filled spaces in the skull behind the ear. These cells are called mastoid air cells....
Myringotomy
Ear tube insertion involves placing tubes through the eardrums. The eardrum is the thin layer of tissue that separates the outer and middle ear. ...
Outlook (Prognosis)
Mastoiditis can be cured. However, it may be hard to treat and may come back.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Destruction of the mastoid bone
-
Dizziness
or vertigo
Dizziness
Dizziness is a term that is often used to describe 2 different symptoms: lightheadedness and vertigo. Lightheadedness is a feeling that you might fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Epidural abscess
Epidural abscess
An epidural abscess is a collection of pus (infected material) and germs between the outer covering of the brain and spinal cord and the bones of the...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Facial paralysis
Facial paralysis
Facial paralysis occurs when a person is no longer able to move some or all of the muscles on one side of the face.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Meningitis
Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Partial or complete
hearing loss
Hearing loss
Hearing loss is being partly or totally unable to hear sound in one or both ears.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Spread of infection to the brain or throughout the body
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you have symptoms of mastoiditis.
Also call if:
-
You have an
ear infection
that does not respond to treatment or is followed by new symptoms.
Ear infection
Otitis is a term for infection or inflammation of the ear.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Your symptoms do not respond to treatment.
Prevention
Prompt and thorough treatment of ear infections reduces the risk for mastoiditis.
References
Chole RA. Chronic otitis media, mastoiditis, and petrositis. In: Flint PW, Haughey BH, Lund VJ, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 139.
Klein JO. Otitis externa, otitis media, and mastoiditis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 62.
O'Handley JG, Tobin EJ, Shah AR. Otorhinolaryngology. In: Rakel RE, Rakel DP, eds. Textbook of Family Medicine . 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 18.
-
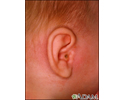
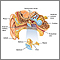
Mastoiditis - side view of head - illustration
Mastoiditis is an infection of the bony air cells in the mastoid bone, located just behind the ear. It is rarely seen today because of the use of antibiotics to treat ear infections. This child has drainage from the ear and redness (erythema) behind the ear over the mastoid bone.
Mastoiditis - side view of head
illustration
-
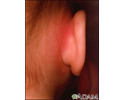
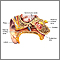
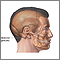
Mastoiditis - redness and swelling behind ear - illustration
Mastoiditis is an infection of the bony air cells in the mastoid bone, located just behind the ear. It is rarely seen today because of the use of antibiotics to treat ear infections. This child has noticeable swelling and redness behind his right ear because of mastoiditis.
Mastoiditis - redness and swelling behind ear
illustration
-
Mastoidectomy - series
Presentation
-
Mastoiditis - side view of head - illustration
Mastoiditis is an infection of the bony air cells in the mastoid bone, located just behind the ear. It is rarely seen today because of the use of antibiotics to treat ear infections. This child has drainage from the ear and redness (erythema) behind the ear over the mastoid bone.
Mastoiditis - side view of head
illustration
-
Mastoiditis - redness and swelling behind ear - illustration
Mastoiditis is an infection of the bony air cells in the mastoid bone, located just behind the ear. It is rarely seen today because of the use of antibiotics to treat ear infections. This child has noticeable swelling and redness behind his right ear because of mastoiditis.
Mastoiditis - redness and swelling behind ear
illustration
-
Mastoidectomy - series
Presentation
Review Date: 5/25/2016
Reviewed By: Sumana Jothi, MD, specialist in laryngology, Assistant Clinical Professor, UCSF Otolaryngology, NCHCS VA, SFVA, San Francisco, CA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.