Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Lou Gehrig disease; ALS; Upper and lower motor neuron disease; Motor neuron disease
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, is a disease of the nerve cells in the brain, brain stem and spinal cord that control voluntary muscle movement.
ALS is also known as Lou Gehrig disease.
Causes
One out of 10 cases of ALS is due to a genetic defect. The cause is unknown in most other cases.
In ALS, motor nerve cells (neurons) waste away or die, and can no longer send messages to muscles. This eventually leads to muscle weakening, twitching, and an inability to move the arms, legs, and body. The condition slowly gets worse. When the muscles in the chest area stop working, it becomes hard or impossible to breathe.
ALS affects approximately 5 out of every 100,000 people worldwide.
Having a family member who has a hereditary form of the disease is a risk factor for ALS. Other risks include military service. Some risk factors are controversial.
Symptoms
Symptoms usually do not develop until after age 50, but they can start in younger people. People with ALS have a loss of muscle strength and coordination that eventually gets worse and makes it impossible for them to do routine tasks such as going up steps, getting out of a chair, or swallowing.
Weakness can first affect the arms or legs, or the ability to breathe or swallow. As the disease gets worse, more muscle groups develop problems.
ALS does not affect the senses (sight, smell, taste, hearing, touch). Most people are able to think normally, although a small number develop dementia, causing problems with memory.
Muscle weakness starts in one body part, such as the arm or hand, and slowly gets worse until it leads to the following:
- Difficulty lifting, climbing stairs, and walking
- Difficulty breathing
- Difficulty swallowing -- choking easily, drooling, or gagging
- Head drop due to weakness of the neck muscles
- Speech problems, such as a slow or abnormal speech pattern (slurring of words)
- Voice changes, hoarseness
Other findings include:
- Depression
-
Muscle cramps
Muscle cramps
Muscle cramps are when a muscle gets tight (contracts) without you trying to tighten it, and it does not relax. Cramps may involve all or part of on...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Muscle stiffness, called spasticity
-
Muscle contractions
, called fasciculations
Muscle contractions
Muscle cramps are when a muscle gets tight (contracts) without you trying to tighten it, and it does not relax. Cramps may involve all or part of on...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weight loss
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will examine you and ask about your medical history and symptoms.
The physical exam may show:
- Weakness, often beginning in one area
- Muscle tremors, spasms, twitching, or loss of muscle tissue
- Twitching of the tongue (common)
- Abnormal reflexes
- Stiff or clumsy walk
- Decreased or increased reflexes at the joints
- Difficulty controlling crying or laughing (sometimes called emotional incontinence)
- Loss of gag reflex
Tests that may be done include:
- Blood tests to rule out other conditions
- Breathing test to see if lung muscles are affected
-
Cervical spine CT
or MRI to be sure there is no disease or injury to the neck, which can mimic ALS
Cervical spine CT
A computed tomography (CT) scan of the cervical spine makes cross-sectional pictures of the neck. It uses x-rays to create the images.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
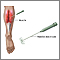
Electromyography
to see which nerves or muscles do not work properly
Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Genetic testing, if there is a family history of ALS
-
Head CT
or
MRI
to rule out other conditions
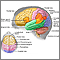
Head CT
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swallowing studies
- Spinal tap (lumbar puncture)
Treatment
There is no known cure for ALS. A medicine called riluzole helps slow the symptoms and helps people live slightly longer.
Treatments to control other symptoms include:
-
Baclofen or diazepam for
spasticity
that interferes with daily activities
Spasticity
Spasticity is stiff or rigid muscles. It may also be called unusual tightness or increased muscle tone. Reflexes (for example, a knee-jerk reflex) ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Trihexyphenidyl or amitriptyline for people with problems swallowing their own saliva
Physical therapy, rehabilitation, use of braces or a wheelchair, or other measures may be needed to help with muscle function and general health.
People with ALS tend to lose weight. The illness itself increases the need for food and calories. At the same time, problems with choking and swallowing make it hard to eat enough. To help with feeding, a tube may be placed into the stomach. A dietitian who specializes in ALS can give advice on healthy eating.
Breathing devices include machines that are used only at night, and constant mechanical ventilation.
Medicine for depression may be needed if a person with ALS is feeling sad. They also should discuss their wishes regarding artificial ventilation with their families and providers.
Support Groups
Emotional support is vital in coping with the disorder, because mental functioning is not affected. Groups such as the ALS Association may be available to help people who are coping with the disorder.
Groups
The following organizations are good resources for information on amyotrophic lateral sclerosis:Muscular Dystrophy Association -- www. mda. org/disea...

Support for people who are caring for someone with ALS is also available, and may be very helpful.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Over time, people with ALS lose the ability to function and care for themselves. Death often occurs within 3 to 5 years of diagnosis. About 1 in 4 people survive for more than 5 years after diagnosis. Some people live much longer, but they typically need help breathing from a ventilator or other device.
Possible Complications
Complications of ALS include:
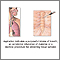
-
Breathing in food or fluid (
aspiration
)
Aspiration
Aspiration means to draw in or out using a sucking motion. It has two meanings:Breathing in a foreign object (sucking food into the airway). A medic...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Loss of ability to care for self
- Lung failure
-
Pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a breathing (respiratory) condition in which there is an infection of the lung. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pressure sores
- Weight loss
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if:
- You have symptoms of ALS, particularly if you have a family history of the disorder
- You or someone else has been diagnosed with ALS and symptoms get worse or new symptoms develop
Increased difficulty swallowing, difficulty breathing, and episodes of apnea are symptoms that require immediate attention.
Apnea
Breathing that stops from any cause is called apnea. Slowed breathing is called bradypnea. Labored or difficult breathing is known as dyspnea....
Prevention
You may want to see a genetic counselor if you have a family history of ALS.
References
Fearon C, Murray B, Mitsumoto H. Disorders of upper and lower motor neurons. In: Daroff RB, Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, eds. Bradley's Neurology in Clinical Practice . 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 98.
Shaw PJ. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other motor neuron diseases. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 419.
-
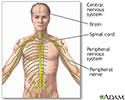
Central nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes all peripheral nerves.
Central nervous system
illustration
Review Date: 5/30/2016
Reviewed By: Amit M. Shelat, DO, FACP, Attending Neurologist and Assistant Professor of Clinical Neurology, SUNY Stony Brook, School of Medicine, Stony Brook, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.