Trichinosis
Parasite infection - trichinosis; Trichiniasis; Trichinellosis; Roundworm - trichinosis
Trichinosis is an infection with the roundworm Trichinella spiralis .
Causes
Trichinosis is a disease caused by eating meat that has not been thoroughly cooked and contains cysts (larvae, or immature worms) of Trichinella spiralis . Trichinella spiralis can be found in pork, bear, walrus, fox, rat, horse, and lion.
Wild animals, especially carnivores (meat eaters) or omnivores (animals that eat both meat and plants), should be considered possible sources of roundworm disease. Domestic meat animals raised specifically for eating under United States Department of Agriculture (government) guidelines and inspection can be considered safe. For this reason, trichinosis is rare in the United States, but it is a common infection worldwide.
When a person eats meat from an infected animal, trichinella cysts break open in the intestine and grow into adult roundworms. The roundworms produce other worms that move through the gut wall and into the bloodstream. The worms invade muscle tissues, including the heart and diaphragm (the breathing muscle under the lungs). They can also infect the lungs and brain. The cysts remain alive for years.
Symptoms
Symptoms of trichinosis include:
- Abdominal discomfort, cramping
- Diarrhea
- Facial swelling around the eyes
- Fever
-
Muscle pain
(especially muscle pain with breathing, chewing, or using large muscles)
Muscle pain
Muscle aches and pains are common and can involve more than 1 muscle. Muscle pain also can involve ligaments, tendons, and fascia. Fascia are the s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Muscle weakness
Exams and Tests
Tests to diagnose this condition include:
-
Complete blood count (
CBC
)
CBC
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The tota...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Eosinophil count (a type of white blood cell)
- Creatine kinase level (an enzyme found in muscle cells)
-
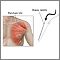
Muscle biopsy
to check for worms in the muscle
Muscle biopsy
A muscle biopsy is the removal of a small piece of muscle tissue for examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood antibody test
Treatment
Medicines can be used to treat infections in the intestines, though mild infection does not usually need treatment. Pain medicine can help relieve muscle soreness after the larvae have invaded the muscles.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most people with trichinosis have no symptoms and the infection goes away by itself. More severe infections may be difficult to treat, especially if the lungs, heart, or brain is involved.
Possible Complications
Possible complications include:
- Encephalitis (brain infection and inflammation)
-
Heart failure
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart rhythm problems from heart inflammation
- Pneumonia
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you have symptoms of trichinosis and you recently ate undercooked or raw meat that might have been contaminated.
Prevention
Pork and meat from wild animals should be cooked until well done (no traces of pink). Freezing pork at subzero temperatures (5°F, or -15°C, or colder) for 3 to 4 weeks will kill the worms. Freezing wild game meat does not always kill the worms. Smoking, salting, and drying meat are also not reliable methods of killing the worms.
References
Diemert DJ. Tissue nematode infections. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 358.
Kazura JW. Tissue nematodes (trichinellosis, dracunculiasis, filariasis, loiasis, and onchocerciasis). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, Updated Edition . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 289.
-
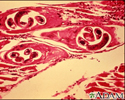
Trichinella spiralis in human muscle - illustration
Trichinella spiralis
Trichinella spiralis in human muscle
illustration
-
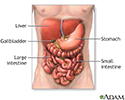
Digestive system organs - illustration
The digestive system organs in the abdominal cavity include the liver, gallbladder, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.
Digestive system organs
illustration
-
Trichinella spiralis in human muscle - illustration
Trichinella spiralis
Trichinella spiralis in human muscle
illustration
-
Digestive system organs - illustration
The digestive system organs in the abdominal cavity include the liver, gallbladder, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.
Digestive system organs
illustration
Review Date: 11/14/2016
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Assistant Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Assistant in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.