Dementia
Chronic brain syndrome; Lewy body dementia; DLB; Vascular dementia; Mild cognitive impairment; MCI
Dementia is a loss of brain function that occurs with certain diseases. It affects memory, thinking, language, judgment, and behavior.
Causes
Dementia usually occurs in older age. It is rare in people under age 60. The risk of dementia increases as a person gets older.
Most types of dementia are nonreversible (degenerative). Nonreversible means the changes in the brain that are causing the dementia cannot be stopped or turned back. Alzheimer disease is the most common type of dementia.
Alzheimer disease
Dementia is a loss of brain function that occurs with certain diseases. Alzheimer disease is one form of dementia. It affects memory, thinking, and...
Another common type of dementia is vascular dementia . It is caused by many small strokes.
Vascular dementia
Dementia is a gradual and permanent loss of brain function. This occurs with certain diseases. It affects memory, thinking, language, judgment, ...

Lewy body disease is a common cause of dementia in older adults. People with this condition have abnormal protein structures in certain areas of the brain.
The following medical conditions can also lead to dementia:
-
Huntington disease
Huntington disease
Huntington disease is a disorder in which nerve cells in certain parts of the brain waste away, or degenerate. The disease is passed down through fa...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Brain injury
-
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease that affects the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Infections such as HIV/
AIDS
,
syphilis
, and
Lyme disease
AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes AIDS. When a person becomes infected with HIV, the virus attacks and weakens the immune ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleSyphilis
Neurosyphilis is a bacterial infection of the brain or spinal cord. It usually occurs in people who have had untreated syphilis for many years....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleLyme disease
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection that is spread through the bite of one of several types of ticks.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Parkinson disease
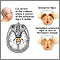
Parkinson disease
Parkinson disease causes certain brain cells to die. These are the cells that help control movement and coordination. The disease leads to shaking ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pick disease
Pick disease
Pick disease is a rare form of dementia that is similar to Alzheimer disease, except that it tends to affect only certain areas of the brain....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Progressive supranuclear palsy
Progressive supranuclear palsy
Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) is a movement disorder that occurs from damage to certain nerve cells in the brain.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Some causes of dementia may be stopped or reversed if they are found soon enough, including:
- Brain injury
- Brain tumors
- Chronic alcohol abuse
-
Changes in blood sugar, sodium, and calcium levels (
dementia due to metabolic causes
)
Dementia due to metabolic causes
Dementia is loss of brain function that occurs with certain diseases. Dementia due to metabolic causes is a loss of brain function that can occur wit...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Low
vitamin B12
level
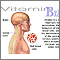
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin. Water-soluble vitamins dissolve in water. After the body uses these vitamins, leftover amounts leave the bo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Normal pressure hydrocephalus
Normal pressure hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of spinal fluid inside the fluid chambers of the brain. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "Normal pressure hydroce...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Use of certain medicines, including cimetidine and some cholesterol drugs
Symptoms
Dementia symptoms include difficulty with many areas of mental function, including:
- Emotional behavior or personality
- Language
- Memory
- Perception
- Thinking and judgment (cognitive skills)
Dementia usually first appears as forgetfulness.
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is the stage between normal forgetfulness due to aging and the development of dementia. People with MCI have mild problems with thinking and memory that do not interfere with daily activities. They often know about their forgetfulness. Not everyone with MCI develops dementia.
Symptoms of MCI include:
- Difficulty doing more than one task at a time
- Difficulty solving problems or making decisions
- Forgetting recent events or conversations
- Taking longer to do more difficult mental activities
Early symptoms of dementia can include:
- Difficulty with tasks that take some thought, but that used to come easily, such as balancing a checkbook, playing games (such as bridge), and learning new information or routines
- Getting lost on familiar routes
- Language problems, such as trouble with the names of familiar objects
- Losing interest in things previously enjoyed, flat mood
- Misplacing items
- Personality changes and loss of social skills, which can lead to inappropriate behaviors
As dementia becomes worse, symptoms are more obvious and interfere with the ability to take care of oneself. Symptoms may include:
- Change in sleep patterns, often waking up at night
- Difficulty with basic tasks, such as preparing meals, choosing proper clothing, or driving
- Forgetting details about current events
- Forgetting events in one's own life history, losing self-awareness
-
Having
hallucinations
, arguments, striking out, and violent behavior
Hallucinations
Hallucinations involve sensing things such as visions, sounds, or smells that seem real but are not. These things are created by the mind.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Having delusions, depression, agitation
- More difficulty reading or writing
- Poor judgment and loss of ability to recognize danger
- Using the wrong word, not pronouncing words correctly, speaking in confusing sentences
- Withdrawing from social contact
People with severe dementia can no longer:
- Perform basic activities of daily living, such as eating, dressing, and bathing
- Recognize family members
- Understand language
Other symptoms that may occur with dementia:
- Problems controlling bowel movements or urine
- Swallowing problems
Exams and Tests
A skilled health care provider can often diagnose dementia using the following:
- Complete physical exam, including nervous system exam
- Asking about the person's medical history and symptoms
- Mental function tests (mental status examination)
Other tests may be ordered to find out if other problems may be causing dementia or making it worse. These conditions include:
-
Anemia
Anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. Different type...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Brain tumor
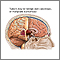
Brain tumor
A primary brain tumor is a group (mass) of abnormal cells that start in the brain.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chronic infection
- Intoxication from medicines
- Severe depression
- Thyroid disease
- Vitamin deficiency
The following tests and procedures may be done:
-
B12 level
B12 level
The vitamin B12 level is a blood test that measures how much vitamin B12 is in your blood.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blood
ammonia
levels
Ammonia
Ammonia is a strong, colorless gas. If the gas is dissolved in water, it is called liquid ammonia. Poisoning may occur if you breathe in ammonia. ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blood chemistry (
chem-20
)
Chem-20
A comprehensive metabolic panel is a group of blood tests. They provide an overall picture of your body's chemical balance and metabolism. Metaboli...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blood gas analysis
Blood gas analysis
Blood gases are a measurement of how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in your blood. They also determine the acidity (pH) of your blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis
A CSF cell count is a test to measure the number of red and white blood cells that are in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF is a clear fluid that in th...
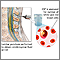 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Drug or alcohol levels (
toxicology screen
)
Toxicology screen
A toxicology screen refers to various tests that determine the type and approximate amount of legal and illegal drugs a person has taken.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Electroencephalograph
(EEG)
Electroencephalograph
An electroencephalogram is a test to measure the electrical activity of the brain.
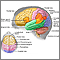 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Head CT
Head CT
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Mental status test
-
MRI of head
MRI of head
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Thyroid function tests
, including thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Thyroid function tests
Thyroid function tests are used to tell whether your thyroid is working normally. The most common thyroid function tests are:Total, or free T4 (the m...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Thyroid stimulating hormone
level
Thyroid stimulating hormone
A TSH test measures the amount of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) in your blood. TSH is produced by the pituitary gland. It tells the thyroid gla...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment depends on the condition causing the dementia. Some people may need to stay in the hospital for a short time.
Sometimes, dementia medicine can make a person's confusion worse. Stopping or changing these medicines is part of the treatment.
Certain mental exercises can help with dementia.
Treating conditions that can lead to confusion often greatly improve mental function. Such conditions include:
- Anemia
- Congestive heart failure
-
Decreased blood oxygen (
hypoxia
)
Hypoxia
Cyanosis is a bluish color to the skin or mucous membrane that is usually due to a lack of oxygen in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Depression
-
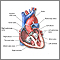
Heart failure
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infections
- Nutritional disorders
- Thyroid disorders
Medicines may be used to:
- Slow the rate at which symptoms get worse, though improvement with these drugs may be small
- Control problems with behavior, such as loss of judgment or confusion
Someone with dementia will need support in the home as the disease gets worse. Family members or other caregivers can help by helping the person cope with memory loss and behavior and sleep problems . It is important to make sure the homes of people who have dementia are safe for them .
Support in the home
Dementia is a loss of brain function that occurs with certain diseases. It affects memory, thinking, and behavior.
Outlook (Prognosis)
People with MCI do not always develop dementia. When dementia does occur, it usually gets worse over time. Dementia often decreases quality of life and lifespan. Families will likely need to plan for their loved one's future care .
Future care
Dementia is a loss of brain function that occurs with certain diseases. It affects memory, thinking, and behavior.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if:
-
Dementia develops or a sudden
change in mental status
occurs
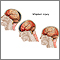
Change in mental status
Confusion is the inability to think as clearly or quickly as you normally do. You may feel disoriented and have difficulty paying attention, remembe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - The condition of a person with dementia gets worse
- You are unable to care for a person with dementia at home
Prevention
Most causes of dementia are not preventable.
The risk of vascular dementia may be reduced by preventing strokes through:
- Eating healthy foods
- Exercising
- Quitting smoking
- Controlling high blood pressure
- Managing diabetes
References
Galvin JE, Sadowsky CH; NINCDS-ADRDA. Practical guidelines for the recognition and diagnosis of dementia. J Am Board Fam Med . 2012;25(3):367-382. PMID: 22570400 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22570400 .
Knopman DS. Alzheimer disease and other dementias. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman's Cecil Medicine . 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 402.
Mitchell SL. CLINICAL PRACTICE. Advanced Dementia. N Engl J Med . 2015;372(26):2533-2540. PMID: 26107053 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26107053 .
Peterson R, Graff-Radford J. Alzheimer disease and other dementias. In: Daroff RB, Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, eds. Bradley's Neurology in Clinical Practice . 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 95.
-
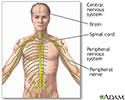
Central nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes all peripheral nerves.
Central nervous system
illustration
-
Dementia
(Alt. Medicine)
-
Alzheimer disease
(In-Depth)
Review Date: 8/13/2015
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Division of Neurology, Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Internal review and update on 09/01/2016 by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.