Herniated disk
Lumbar radiculopathy; Cervical radiculopathy; Herniated intervertebral disk; Prolapsed intervertebral disk; Slipped disk; Ruptured disk; Herniated nucleus pulposus: Low back pain - herniated disk; LBP - herniated disk; Sciatica - herniated disk; Herniated disk
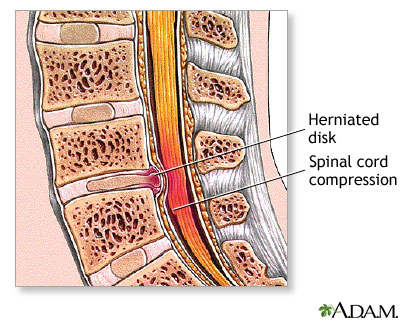
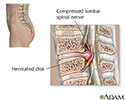
A herniated (slipped) disk occurs when all or part of a disk is forced through a weakened part of the disk. This may place pressure on nearby nerves or the spinal cord.
Causes
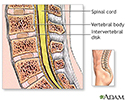
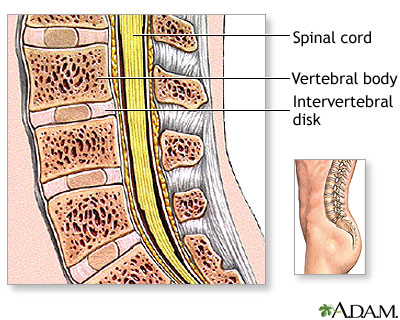
The bones (vertebrae) of the spinal column protect nerves that come out of the brain and travel down your back to form the spinal cord. Nerve roots are large nerves that branch out from the spinal cord and leave your spinal column between each vertebra.
The spinal bones are separated by disks. These disks cushion the spinal column and put space between your vertebrae. The disks allow movement between the vertebrae, which lets you bend and reach.
With herniated disk:
-
The disk may move out of place (herniate) or break open (rupture) from injury or
strain
. When this happens, there may be pressure on the spinal nerves. This can lead to pain, numbness, or weakness.
Strain
A strain is when a muscle is stretched too much and tears. It is also called a pulled muscle. A strain is a painful injury. It can be caused by an...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - The lower back (lumbar area) of the spine is the most common area affected by a slipped disk. The neck (cervical) disks are the second most commonly affected area. The upper-to-mid-back (thoracic) disks are rarely involved.
A herniated disk is a cause of radiculopathy. This is any disease that affects the spinal nerve roots.
Slipped disks occur more often in middle-aged and older men, usually after strenuous activity. Other risk factors may include:
- Lifting heavy objects
- Being overweight
- Repetitive bending or twisting the lower back
- Sitting or standing in same position for long hours
- Inactive lifestyle
- Smoking
Symptoms
The pain most often occurs on one side of the body. Symptoms vary depending on the site of injury, and may include the following:
- With a slipped disk in your lower back, you may have sharp pain in one part of the leg, hip, or buttocks and numbness in other parts. You may also feel pain or numbness on the back of the calf or sole of the foot. The same leg may also feel weak.
- With a slipped disk in your neck, you may have pain when moving your neck, deep pain near or over the shoulder blade, or pain that moves to the upper arm, forearm, and fingers. You can also have numbness along your shoulder, elbow, forearm, and fingers.
The pain often starts slowly. It may get worse:
- After standing or sitting
- At night
- When sneezing, coughing, or laughing
- When bending backward or walking more than a few yards or meters
You may also have weakness in certain muscles. Sometimes, you may not notice it until your health care provider examines you. In other cases, you will notice that you have a hard time lifting your leg or arm, standing on your toes on one side, squeezing tightly with one of your hands, or other problems. Your bladder control may be lost.
The pain, numbness, or weakness often goes away or improves a lot over weeks to months.
Exams and Tests
A careful physical exam and history is almost always the first step. Depending on where you have symptoms, your provider examines your neck, shoulder, arms, and hands, or your lower back, hips, legs, and feet.
Your provider will check:
- For numbness or loss of feeling
- Your muscle reflexes, which may be slower or missing
- Your muscle strength, which may be weaker
- Your posture, or the way your spine curves
Your provider may also ask you to:
- Sit, stand, and walk. While you walk, your provider may ask you to try walking on your toes and then your heels.
- Bend forward, backward, and sideways.
- Move your neck forward, backward, and sideways.
- Raise your shoulders, elbow, wrist, and hand, and check your strength during these tasks.
Leg pain that occurs when you sit on an exam table and lift your leg straight up usually suggests a slipped disk in your lower back.
In another test, you will bend your head forward and to the sides while the provider puts slight downward pressure on the top of your head. Increased pain or numbness during this test is usually a sign of pressure on a nerve in your neck.
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
Tests done may include:
-
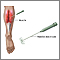
Electromyography
(EMG) may be done to determine the exact nerve root that is involved.
Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Myelogram
may be done to determine the size and location of disk herniation.
Myelogram
A lumbosacral spine x-ray is a picture of the small bones (vertebrae) in the lower part of the spine. This area includes the lumbar region and the s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Nerve conduction velocity
test may also be done.
Nerve conduction velocity
Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a test to see how fast electrical signals move through a nerve.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Spine MRI
or
spine CT
will show where the herniated disk is pressing on the spinal canal.
Spine MRI
A lumbar magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan uses energy from strong magnets to create pictures of the lower part of the spine (lumbar spine). An M...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleSpine CT
A lumbosacral spine CT is a computed tomography scan of the lower spine and surrounding tissues.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Spine x-ray
may be done to rule out other causes of back or neck pain. However, it is not possible to diagnose a herniated disk by a spine x-ray alone.
Spine x-ray
A thoracic spine x-ray is an x-ray of the twelve chest (thoracic) bones (vertebrae). The vertebrae are separated by flat pads of cartilage called di...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The first treatment for a slipped disk is a short period of rest and taking medicines for the pain. This is followed by physical therapy. Most people who follow these treatments recover and return to normal activities. Some people will need to have more treatment. This may include steroid injections or surgery.
MEDICINES
Medicines can help with your pain . Your provider may prescribe any of the following:
Medicines can help with your pain
Back pain often goes away on its own over several weeks. In some people, back pain persists. It may not go away completely or it may get more painf...
- NSAIDs for long-term pain control
-
Narcotics
if the pain is severe and does not respond to NSAIDs
Narcotics
Opiates or opioids are drugs used to treat pain. The term narcotic refers to either type of drug. If you stop or cut back on these drugs after heavy...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Medicines to calm the nerves
- Muscle relaxants to relieve back spasms
LIFESTYLE CHANGES
If you are overweight, diet and exercise are very important for improving back pain.
Physical therapy is important for nearly everyone with disk disease. Therapists will teach you how to properly lift, dress, walk, and perform other activities. They teach you how to strengthen muscles that help support the spine. You will also learn how to increase flexibility in your spine and legs.
Take care of your back at home :
Take care of your back at home
Low back pain refers to pain that you feel in your lower back. You may also have back stiffness, decreased movement of the lower back, and difficult...

- Reduce activity for the first few days. Slowly restart your usual activities.
- Avoid heavy lifting or twisting your back for the first 6 weeks after the pain starts.
- After 2 to 3 weeks, gradually start exercising again.
INJECTIONS
Steroid medicine injections into the back in the area of the herniated disk may help control pain for several months. These injections reduce swelling around the spinal nerve and disk and relieve many symptoms. They do not solve the underlying problem and your pain may return after weeks or months. Spinal injections are an outpatient procedure.
Steroid medicine injections
An epidural steroid injection (ESI) is the delivery of powerful anti-inflammatory medicine directly into the space outside of the sac of fluid around...
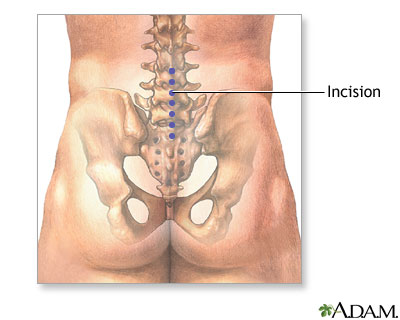
SURGERY
Surgery may be an option if your symptoms do not go away with other treatments and time.
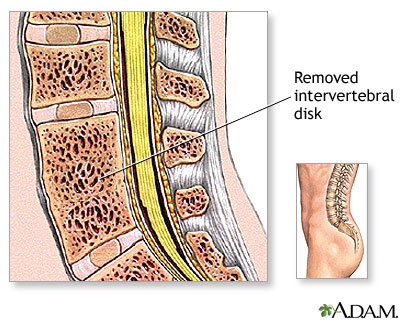
Diskectomy is surgery to remove all or part of a disk.
Diskectomy
Diskectomy is surgery to remove all or part of the cushion that helps support part of your spinal column. These cushions are called disks, and they ...
Discuss with your provider which treatment options are best for you.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most people improve with treatment. But you may have long-term back pain even after treatment.
It may take several months to a year or more to go back to all of your activities without having pain or straining your back. People who work in jobs that involve heavy lifting or back strain may need to change their job activities to avoid injuring their back again.
Possible Complications
In rare cases, the following problems can occur:
- Long-term back pain or leg pain
- Loss of movement or feeling in the legs or feet
- Loss of bowel and bladder function
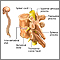
-
Permanent
spinal cord injury
(very rare)
Spinal cord injury
Spinal cord trauma is damage to the spinal cord. It may result from direct injury to the cord itself or indirectly from disease of the nearby bones,...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if you have:
- Severe back pain that does not go away
- Any numbness, loss of movement, weakness, or bowel or bladder changes
Prevention
To help prevent back injury:
- Use proper lifting techniques.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Do exercises to keep your abdominal (core) and back muscles strong.
Your provider may suggest a back brace to help support the spine. A brace may prevent injuries in people who lift heavy objects at work. But using these devices too much can weaken the muscles that support your spine and make the problem worse.
References
Gardocki RJ, Park AL. Lower back pain and disorders of intervertebral discs. In: Canale ST, Beaty JH, eds. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics . 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2013:chap 42.
Magee DJ. Lumbar spine. In: Magee DJ, ed. Orthopaedic Physical Assessment . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2014:chap 9.
Safran MR, Zachazewski J, Stone DA. Herniated disk (ruptured disk). In: Safran MR, Zachazewski J, Stone DA, eds. Instructions for Sports Medicine Patients . 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:462-470.
-
Herniated nucleus pulposus (slipped disk)
Animation
-
Herniated disk
Animation
-
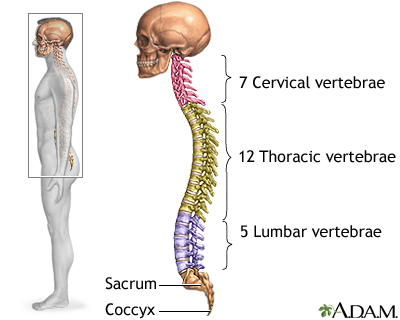
Skeletal spine - illustration
The spine is divided into several sections. The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. The thoracic vertebrae comprise the chest section and have ribs attached. The lumbar vertebrae are the remaining vertebrae below the last thoracic bone and the top of the sacrum. The sacral vertebrae are caged within the bones of the pelvis, and the coccyx represents the terminal vertebrae or vestigial tail.
Skeletal spine
illustration
-
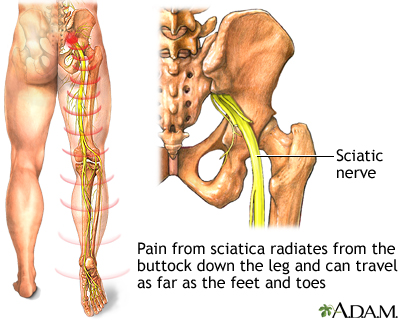
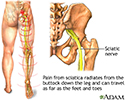
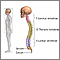
Sciatic nerve - illustration
The main nerve traveling down the leg is the sciatic nerve. Pain associated with the sciatic nerve usually originates higher along the spinal cord when nerve roots become compressed or damaged from narrowing of the vertebral column or from a slipped disk. Symptoms can include tingling, numbness, or pain, which radiates to the buttocks legs and feet.
Sciatic nerve
illustration
-
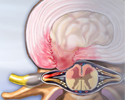
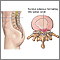
Herniated nucleus pulposus - illustration
Herniated nucleus pulposus is a condition in which part or all of the soft, gelatinous central portion of an intervertebral disk is forced through a weakened part of the disk, resulting in back pain and nerve root irritation.
Herniated nucleus pulposus
illustration
-
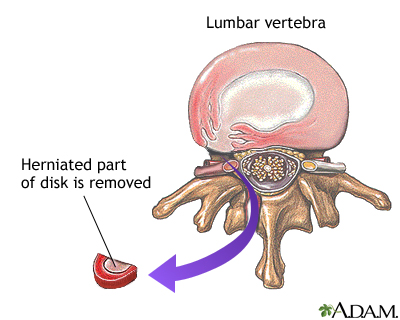
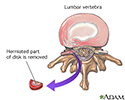
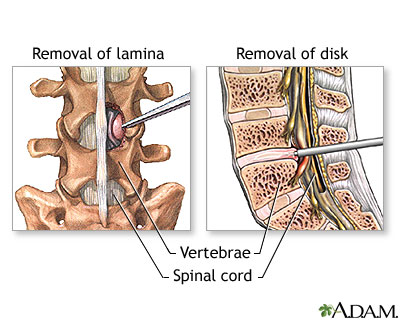
Herniated disk repair - illustration
When the soft, gelatinous central portion of an intervertebral disk is forced through a weakened part of a disk, it is a condition known as a slipped disk. Most herniation takes place in the lumbar area of the spine, and it is one of the most common causes of lower back pain. The mainstay of treatment for herniated disks is an initial period of rest with pain and anti-inflammatory medications followed by physical therapy. If pain and symptoms persist, surgery to remove the herniated portion of the intervertebral disk is recommended.
Herniated disk repair
illustration
-
Lumbar spinal surgery - Series
Presentation
-
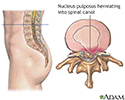
Herniated lumbar disk - illustration
Herniated lumbar disk is a condition in which part or all of the soft, gelatinous central portion of an intervertebral disk (the nucleus pulposus) is forced through a weakened part of the disk, resulting in back pain and nerve root irritation.
Herniated lumbar disk
illustration
-
Skeletal spine - illustration
The spine is divided into several sections. The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. The thoracic vertebrae comprise the chest section and have ribs attached. The lumbar vertebrae are the remaining vertebrae below the last thoracic bone and the top of the sacrum. The sacral vertebrae are caged within the bones of the pelvis, and the coccyx represents the terminal vertebrae or vestigial tail.
Skeletal spine
illustration
-
Sciatic nerve - illustration
The main nerve traveling down the leg is the sciatic nerve. Pain associated with the sciatic nerve usually originates higher along the spinal cord when nerve roots become compressed or damaged from narrowing of the vertebral column or from a slipped disk. Symptoms can include tingling, numbness, or pain, which radiates to the buttocks legs and feet.
Sciatic nerve
illustration
-
Herniated nucleus pulposus - illustration
Herniated nucleus pulposus is a condition in which part or all of the soft, gelatinous central portion of an intervertebral disk is forced through a weakened part of the disk, resulting in back pain and nerve root irritation.
Herniated nucleus pulposus
illustration
-
Herniated disk repair - illustration
When the soft, gelatinous central portion of an intervertebral disk is forced through a weakened part of a disk, it is a condition known as a slipped disk. Most herniation takes place in the lumbar area of the spine, and it is one of the most common causes of lower back pain. The mainstay of treatment for herniated disks is an initial period of rest with pain and anti-inflammatory medications followed by physical therapy. If pain and symptoms persist, surgery to remove the herniated portion of the intervertebral disk is recommended.
Herniated disk repair
illustration
-
Lumbar spinal surgery - Series
Presentation
-
Herniated lumbar disk - illustration
Herniated lumbar disk is a condition in which part or all of the soft, gelatinous central portion of an intervertebral disk (the nucleus pulposus) is forced through a weakened part of the disk, resulting in back pain and nerve root irritation.
Herniated lumbar disk
illustration
-
Back pain and sciatica
(In-Depth)
Review Date: 9/22/2016
Reviewed By: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.