Thrombolytic drugs for heart attack
Myocardial infarction - thrombolytic; MI - thrombolytic; ST - elevation myocardial infarction; CAD - thrombolytic; Coronary artery disease - thrombolytic; STEMI - thrombolytic
Information
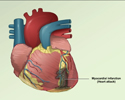
Small blood vessels called coronary arteries supply blood and oxygen to the heart.
- A heart attack can occur if a blood clot stops the flow of blood through one of these arteries.
-
Unstable angina
refers to chest pain and other warning signs that a heart attack may happen soon. It is most often caused by blood clots in the arteries.
Unstable angina
Unstable angina is a condition in which your heart doesn't get enough blood flow and oxygen. It may lead to a heart attack. Angina is a type of ches...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Some people may be given drugs to break up the clot if the artery is completely blocked.
- These drugs are called thrombolytics, or clot-busting drugs.
-
They are only given for a type of
heart attack
, where certain changes are noted on the ECG. This type of heart attack is called an ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
Heart attack
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - These drugs should be given as soon as possible after the chest pain first occurs (most often in less than 12 hours).
- The medicine is given through a vein (IV).
- Blood thinners taken by mouth may be prescribed later to prevent more clots from forming.
The main risk when receiving clot-busting drugs is bleeding, especially bleeding in the brain.
Thrombolytic therapy is not safe for people who have:
- Bleeding inside the head or a stroke
- Brain abnormalities, such as tumors or poorly-formed blood vessels
- Had a head injury within the past 3 months
- A history of using blood thinners or a bleeding disorder
- Had major surgery, a major injury, or internal bleeding within the past 3 to 4 weeks
-
Peptic ulcer
disease
Peptic ulcer
A peptic ulcer is an open sore or raw area in the lining of the stomach or intestine. A gastric ulcer occurs in the stomach. A duodenal ulcer occurs ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Severe high blood pressure
Other treatments to open blocked or narrowed vessels that may be done in place of or along with thrombolytic therapy include:
-
Angioplasty
Angioplasty
Angioplasty is a procedure to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels that supply blood to the heart. These blood vessels are called the coronary art...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Heart bypass surgery
Heart bypass surgery
Heart bypass surgery creates a new route, called a bypass, for blood and oxygen to go around a blockage to reach your heart.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, Casey DE Jr, Ganiats TG, Holmes DR Jr, Jaffe AS, Jneid H, Kelly RF, Kontos MC, Levine GN, Liebson PR, Mukherjee D, Peterson ED, Sabatine MS, Smalling RW, Zieman SJ. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol . 2014;64:e139-228. PMID: 25260718 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25260718 .
O'Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, Casey DE Jr, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol . 2013;61:e78-140. PMID: 23256913 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23256913 .
Review Date: 4/20/2015
Reviewed By: Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.