Gallbladder removal - laparoscopic
Cholecystectomy - laparoscopic; Surgery - gallbladder - laparoscopic
Laparoscopic gallbladder removal is surgery to remove the gallbladder using a medical device called a laparoscope.
Description
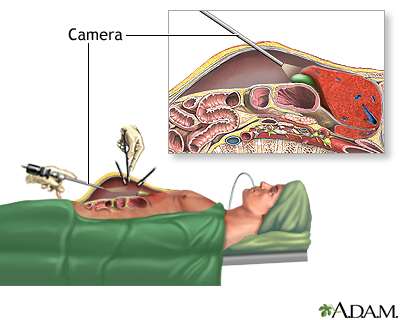
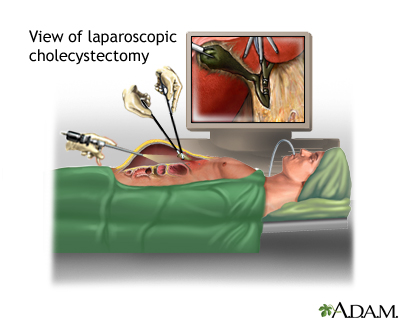
Surgery using a laparoscope is the most common way to remove the gallbladder. A laparoscope is a thin, lighted tube that lets the doctor see inside your belly.
Gallbladder removal surgery is done while you are under general anesthesia so you will be asleep and pain-free. To perform the surgery:
General anesthesia
General anesthesia is treatment with certain medicines that puts you into a deep sleep so you do not feel pain during surgery. After you receive the...
The operation is done the following way:
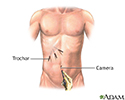
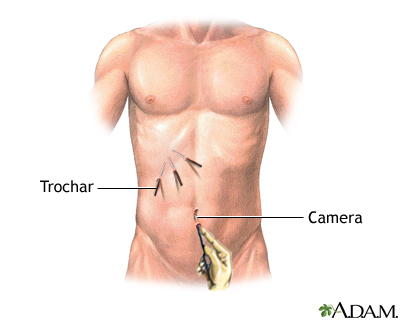
- The surgeon makes 3 to 4 small cuts in your belly.
- The laparoscope is inserted through one of the cuts.
- Other medical instruments are inserted through the other cuts.
- Gas is pumped into your belly to expand the space. This gives the surgeon more room to see and work.
The gallbladder is then removed using the laparoscope and other instruments.
An x-ray called a cholangiogram may be done during your surgery.
Cholangiogram
A percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram (PTCA) is an x-ray of the bile ducts. These are the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladde...
- To do this test, dye is injected into your common bile duct and an x-ray picture is taken. The dye helps find stones that may be outside your gallbladder.
- If other stones are found, the surgeon may remove them with a special instrument.
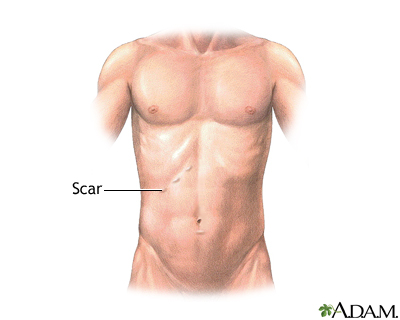
Sometimes the surgeon cannot safely take out the gallbladder using a laparoscope. In this case, the surgeon will use open surgery , in which a larger cut is made.
Open surgery
Open gallbladder removal is surgery to remove the gallbladder through a large cut in your abdomen.
Why the Procedure Is Performed
You may need this surgery if you have pain or other symptoms from gallstones . You may also need it if your gallbladder is not working normally.
Gallstones
Gallstones are hard deposits that form inside the gallbladder. Gallstones may be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball.

Common symptoms may include:
-
Indigestion
, including bloating, heartburn, and gas
Indigestion
Indigestion (dyspepsia) is a mild discomfort in the upper belly or abdomen. It occurs during or right after eating. It may feel like:Heat, burning,...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pain after eating, usually in the upper right or upper middle area of your belly (epigastric pain)
-
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up is forcing the contents of the stomach ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Most people have a quicker recovery and fewer problems with laparoscopic surgery than with open surgery.
Risks
Risks for anesthesia and surgery in general include:
- Reactions to medicines
-
Breathing problems
Breathing problems
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathingUncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bleeding
,
blood clots
Bleeding
Bleeding is the loss of blood. Bleeding may be:Inside the body (internally) Outside the body (externally)Bleeding may occur:Inside the body when blo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleBlood clots
Blood clots are clumps that occur when blood hardens from a liquid to a solid. A blood clot that forms inside one of your veins or arteries is calle...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection
Risks for gallbladder surgery include:
- Damage to the blood vessels that go to the liver
- Injury to the common bile duct
- Injury to the small intestine
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas)
Before the Procedure
You may have the following tests done before your surgery:
-
Blood tests (
complete blood count
,
electrolytes
, and kidney tests)
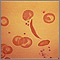
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The tota...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleElectrolytes
The electrolytes - urine test measures specific chemicals called electrolytes in urine. It usually measures the levels of calcium, chloride, potassi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest x-ray
or
electrocardiogram
(EKG), for some people
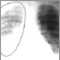
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleElectrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Several x-rays of the gallbladder
- Ultrasound of the gallbladder
Tell your health care provider:
- If you are or might be pregnant
- What medicines, vitamins, and other supplements you are taking, even ones you bought without a prescription
During the week before surgery:
- You may be asked to stop taking aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), vitamin E, warfarin (Coumadin), and any other drugs that put you at higher risk of bleeding during surgery.
- Ask your doctor which drugs you should still take on the day of your surgery.
-
Prepare your home
for any problems you might have getting around after the surgery.
Prepare your home
Getting your home ready after you have been in the hospital often requires much preparation. Set up your home to make your life is easier and safer w...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Your doctor or nurse will tell you when to arrive at the hospital.
On the day of surgery:
- Follow instructions about when to stop eating and drinking.
- Take the drugs your doctor told you to take with a small sip of water.
- Shower the night before or the morning of your surgery.
- Arrive at the hospital on time.
After the Procedure
If you do not have any problems, you will be able to go home when you are able to drink liquids easily and your pain can be treated with pain pills. Most people go home on the same day or the day after this surgery.
If there were problems during surgery, or if you have bleeding, a lot of pain, or a fever, you may need to stay in the hospital longer.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most people recover quickly and have good results from this procedure.
References
Glasgow RE, Mulvihill SJ. Treatment of gallstone disease: In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management . 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 66.
Jackson PG, Evans SRT. Biliary system. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery . 19th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:chap 55.
-
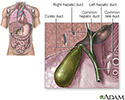
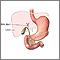
Gallbladder - illustration
The gallbladder is a sac located under the liver. It stores and concentrates the bile produced in the liver. Bile is released from the gallbladder in response to food, especially fats, in the upper small intestine.
Gallbladder
illustration
-
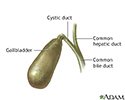
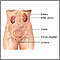
Gallbladder anatomy - illustration
The gallbladder is a sac located under the liver. It stores and concentrates the bile produced in the liver.
Gallbladder anatomy
illustration
-
Incision
Presentation
-
Gallbladder - illustration
The gallbladder is a sac located under the liver. It stores and concentrates the bile produced in the liver. Bile is released from the gallbladder in response to food, especially fats, in the upper small intestine.
Gallbladder
illustration
-
Gallbladder anatomy - illustration
The gallbladder is a sac located under the liver. It stores and concentrates the bile produced in the liver.
Gallbladder anatomy
illustration
-
Incision
Presentation
-
Gallstones and gallbladder disease
(In-Depth)
Review Date: 7/28/2015
Reviewed By: Debra G. Wechter, MD, FACS, general surgery practice specializing in breast cancer, Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.