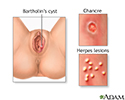
Genital sores - female
Sores on the female genitals
Sores or lesions on the female genitalia or in the vagina may occur for many reasons.
Considerations
Genital sores may be painful or itchy, or may produce no symptoms. Other symptoms that may be present include pain when you urinate or painful sexual intercourse. Depending on the cause, a discharge from the vagina may be present.
Causes
Infections spread through sexual contact can cause these sores:
- Herpes is a common cause of painful sores.
-
Genital warts
may cause painless sores.
Genital warts
Genital warts are soft growths on the skin and mucus membranes of the genitals. They may be found on the penis, vulva, urethra, vagina, cervix, and ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Less common infections such as chancroid , granuloma inguinale , molluscum contagiosum , and syphilis may also cause sores.
Chancroid
Chancroid is a bacterial infection that is spread through sexual contact.
Granuloma inguinale
Donovanosis (granuloma inguinale) is a sexually transmitted disease that is rarely seen in the United States.
Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection that causes raised, pearl-like papules or nodules on the skin.
Changes that may lead to cancer of the vulva (vulvar dysplasia) may appear as white, red, or brown patches on the vulva. These areas may itch. Skin cancers such as melanoma and basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas may also be found, but are less common.
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer. It is the leading cause of death from skin disease. Melanoma can also involve the colored part o...
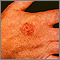
Squamous cell carcinomas
Squamous cell cancer is the second most common type of cancer in the United States. Other common types of skin cancer are:Basal cellMelanoma
Other common causes of genital sores include:
-
Long-term (chronic) skin disorder that involves scaly and itchy rashes. (
atopic dermatitis
)
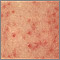
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a long-term (chronic) skin disorder that involves scaly and itchy rashes. It is a type of eczema. Other forms of eczema include...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Skin that becomes red, sore, or inflamed after contact with perfumes, detergents, fabric softeners, feminine sprays, ointments, creams, douches. (
contact dermatitis
)
Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a condition in which the skin becomes red, sore, or inflamed after direct contact with a substance.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
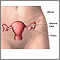
Cysts or
abscesses of the Bartholin
or other glands
Abscesses of the Bartholin
Bartholin abscess is the buildup of pus that forms a lump (swelling) in one of the Bartholin glands. These glands are found on each side of the vagi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Trauma or scratches
- Flu-type viruses that can cause genital sores or ulcers in some cases
Home Care
See a health care provider before treating yourself. Self-treatment may make it harder for the provider to find the source of the problem.
A sitz bath may help relieve itching and crusting.
Sitz bath
A sitz bath is a warm water bath used for healing or cleansing purposes. You sit in the bath. The water covers only your hips and buttocks. The wa...

If the sores are caused by a sexually transmitted infection, your sexual partner may need to be tested and treated as well. Do not have any type of sexual activity until your provider says the sores can no longer be spread to others.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your provider if you:
- Find any unexplained genital sore
- Have a change in a genital sore
- Have genital itching that does not go away with home care
- Think you might have a sexually transmitted infection
- Have pelvic pain, fever, vaginal bleeding, or other new symptoms as well genital sores
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical examination. The physical exam most often includes a pelvic examination. You will be asked about your symptoms and medical history. Questions may include:
- What does the sore look like? Where is it located?
- When did you first notice it?
- Do you have more than 1?
- Does it hurt or itch? Has it grown bigger?
- Have you ever had 1 before?
- How often do you have sexual activity?
- Do you have painful urination or pain during sexual intercourse?
- Do you have abnormal vaginal drainage?
The following tests may be done:
-
Complete blood count
(CBC)
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The tota...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blood differential
Blood differential
The blood differential test measures the percentage of each type of white blood cell (WBC) that you have in your blood. It also reveals if there are...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Skin or mucosal biopsy culture
Skin or mucosal biopsy culture
A skin or nail culture is a laboratory test to look for and identify germs that cause problems with the skin or nails. It is called a mucosal culture...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment may include medicines that you put on the skin or take by mouth. The type of medicine depends on the cause.
References
Augenbraun MH. Genital skin and mucous membrane lesions. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 108.
Eckert LO, Lentz GM. Infections of the lower genital tract. In: Lentz GM, Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Katz VL, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2012:chap 23.
Frumovitz M, Bodurka DC. Neoplastic diseases of the vulva. In: Lentz GM, Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Katz VL, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2012:chap 30.
Link RE, Rosen T. Cutaneous diseases of the external genitalila. In: Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Partin AW, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh Urology . 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 16.
-
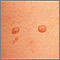
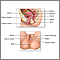
Genital sores (female) - illustration
Sores or lesions on the female genitalia may have many causes. Often, the lesions of most concern are those seen with sexually transmitted diseases.
Genital sores (female)
illustration
-
Herpes simplex virus
(Alt. Medicine)
Review Date: 11/5/2015
Reviewed By: Cynthia D. White, MD, Fellow American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, Group Health Cooperative, Bellevue, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.