Funnel-web spider bite
This article describes the effects of a bite from the funnel-web spider. Male funnel-web spiders are more poisonous than females.
This article is for information only. DO NOT use it to treat or manage a bite from this type of spider. If you or someone you are with has an exposure, call your local emergency number (such as 911), or your local poison center can be reached directly by calling the national toll-free Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) from anywhere in the United States.
Poisonous Ingredient
The venom in the funnel-web spider contains the poison.
Where Found
Funnel-web spiders are found in southeast Australia, around Sydney. They are not native to the United States, although some people may keep them as exotic pets.
Symptoms
Funnel-web spider bites are very painful and dangerous. They have been known to cause these symptoms in different parts of the body:
Eyes, ears, nose, and throat
- Drooling
- Drooping eyelids
- Double vision
- Swallowing difficulty
- Tingling or numbness in the mouth or lips within 10 to 15 minutes
Heart and blood
- Collapse
- Rapid heart rate
Lungs
- Difficulty breathing
Muscles and joints
- Joint pain
- Severe muscle spasms, usually in the legs and belly area
Nervous system
- Agitation
- Confusion
- Coma
- Headache
- Numbness of mouth and lips
- Tremors
- Shivering (chills)
Skin
- Heavy sweating
- Redness around the site of the bite
Stomach and intestines
- Diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
Home Care
Funnel-web spider bites are very poisonous. Seek medical help right away. Call the Poison Control Center for guidance.
Follow these steps until medical help is given:
- Apply a bandage and put firm pressure over the bite.
- Keep the affected area still, if possible, to prevent the venom from spreading. A homemade splint may be helpful if the bite was on the arms, legs, hands, or feet.
- Loosen clothing and remove rings and other tight jewelry.
Before Calling Emergency
Have this information ready:
- Person's age, weight, and condition
- Time the bite occurred
- Type of spider, if possible
Poison Control
Your local poison center can be reached directly by calling the national toll-free Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) from anywhere in the United States. They will give you further instructions.
Poison Help hotline
For a POISON EMERGENCY call:1-800-222-1222ANYWHERE IN THE UNITED STATESThis national hotline number will let you talk to experts in poisoning. This ...

This is a free and confidential service. All local poison control centers in the United States use this national number. You should call if you have any questions about poisoning or poison prevention. It does NOT need to be an emergency. You can call for any reason, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
What to Expect at the Emergency Room
The health care provider will measure and monitor the person's vital signs, including temperature, pulse, breathing rate, and blood pressure. The wound will be treated as appropriate.
The person may receive:
- Antivenin, a medicine to reverse the effects of the venom, if available
- Breathing support, including oxygen, tube through the mouth into the throat, and breathing machine
- Blood and urine tests
- Chest x-ray
- EKG (electrocardiogram, or heart tracing)
- Intravenous fluids (through a vein)
- Medicines to treat symptoms
Outlook (Prognosis)
Funnel-web spider bites can be life threatening, especially in children. They must be treated quickly with antivenin by an experienced provider. Even with appropriate and quick treatment, symptoms may last for several days to weeks.
References
Boyer LV, Greta J. Binford GJ, Degan JA. Spider bites. In: Auerbach PS, ed. Wilderness Medicine . 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; 2011:chap 52.
Nogar JN, Clark RF. Arthropod bites and stings. In: Adams JG, ed. Emergency Medicine . 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2013:chap 140.
Otten EJ. Venomous animal bites. In: Marx JA, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice . 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2014:chap 62.
-
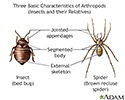
Arthropods, basic features - illustration
Many arthropods are capable of carrying disease. This illustration shows some of the general characteristics of arthropods.
Arthropods, basic features
illustration
-
Arachnids, basic features - illustration
This picture shows the basic features of spiders (arachnids).
Arachnids, basic features
illustration
-
Arthropods, basic features - illustration
Many arthropods are capable of carrying disease. This illustration shows some of the general characteristics of arthropods.
Arthropods, basic features
illustration
-
Arachnids, basic features - illustration
This picture shows the basic features of spiders (arachnids).
Arachnids, basic features
illustration
Review Date: 7/13/2015
Reviewed By: Jacob L. Heller, MD, MHA, Emergency Medicine, Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.