Eye floaters
Specks in your vision
Information
The floating specks you sometimes see in front of your eyes are not on the surface of your eyes, but inside them. These floaters are bits of cell debris that drift around in the fluid that fills the back of your eye. They may look like spots, specks, bubbles, threads, or clumps. Most adults have at least a few floaters. There are times when they may be more visible than at other times, such as when you are reading.
Most of the time floaters are harmless. However, they can be a symptom of a tear in the retina. (The retina is the layer in the back of the eye.) If you notice a sudden increase in floaters or if you see floaters along with flashes of light in your side vision, this may be a symptom of a retinal tear or detachment. Go to an eye doctor or emergency room if you have these symptoms.
References
Crouch ER Jr, Crouch ER, Grant TR Jr. Ophthalmology. In: Rakel RE, Rakel D, eds. Textbook of Family Medicine . 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 17.
Sebag J, Yee KMP. Vitreous: from biochemistry to clinical relevance. In: Tasman W, Jaeger EA, eds. Duane's Foundations of Clinical Ophthalmology . 2013 ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2013:vol 1;chap 16.
-
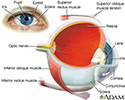
Eye - illustration
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer or tunic (sclera, or white, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle tunic layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (the retina) is nervous or sensory. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
Eye
illustration
-
Eye - illustration
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer or tunic (sclera, or white, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle tunic layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (the retina) is nervous or sensory. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
Eye
illustration
Review Date: 11/4/2015
Reviewed By: Franklin W. Lusby, MD, ophthalmologist, Lusby Vision Institute, La Jolla, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.