Anencephaly
Aprosencephaly with open cranium
Anencephaly is the absence of a large part of the brain and the skull.
Causes
Anencephaly is one of the most common neural tube defects. Neural tube defects are birth defects that affect the tissue that becomes the spinal cord and brain.
Anencephaly occurs early in the development of an unborn baby. It results when the upper part of the neural tube fails to close. Why this happens is not known. Possible causes include environmental toxins and low intake of folic acid by the mother during pregnancy.
Toxins
Toxins are substances created by plants and animals that are poisonous to humans. Toxins also include some medicines that are helpful in small doses...

Folic acid
Folic acid is a type of B vitamin. It is the man-made (synthetic) form of folate that is found in supplements and added to fortified foods. Folate i...
The exact number of cases of anencephaly is unknown, because many of these pregnancies result in miscarriage. Having 1 infant with this condition increases the risk of having another child with neural tube defects.
Symptoms
Symptoms of anencephaly are:
- Absence of the skull
- Absence of parts of the brain
- Facial feature abnormalities
- Heart defects
Exams and Tests
An ultrasound during pregnancy is done to confirm the diagnosis. The ultrasound may reveal too much fluid in the uterus. This condition is called polyhydramnios .
Ultrasound
A pregnancy ultrasound is an imaging test that uses sound waves to create a picture of how a baby is developing in the womb. It is also used to chec...
Polyhydramnios
Polyhydramnios occurs when too much amniotic fluid builds up during pregnancy. It is also called amniotic fluid disorder, or hydramnios.
The mother may also have these tests during pregnancy:
-
Amniocentesis (to look for increased levels of
alpha-fetoprotein
)
Alpha-fetoprotein
Alpha fetoprotein (AFP) is a protein produced by the liver and yolk sac of a developing baby during pregnancy. AFP levels go down soon after birth. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Alpha-fetoprotein level (increased levels suggest a neural tube defect)
- Urine estriol level
A pre-pregnancy serum folic acid test may also be done.
Treatment
There is no current treatment. Talk to your health care provider about care decisions.
Outlook (Prognosis)
This condition usually causes death within a few days after birth.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
A provider usually detects this condition during routine prenatal testing and ultrasound. Otherwise, it is recognized at birth.
If anencephaly is detected before birth, further counseling will be needed.
Prevention
There is good evidence that folic acid can help reduce the risk of certain birth defects, including anencephaly. Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should take a multivitamin with folic acid every day. Many foods are now fortified with folic acid to help prevent these kinds of birth defects.
Getting enough folic acid can cut the chance of neural tube defects in half.
For specific recommendations, see folic acid (folate) .
Folic acid (folate)
Folic acid is a type of B vitamin. It is the man-made (synthetic) form of folate that is found in supplements and added to fortified foods. Folate i...

References
Finnell RH, George TM, Mitchell LE. Neural tube defects. In: Rimoin D, Pyeritz RE, Korf B, eds. Emery and Rimoin's Principles and Practice of Medical Genetics . 6th ed. Elsevier Ltd; 2013:chap 114.
Kinsman SL, Johnston MV. Congenital anomalies of the central nervous system. In: Kliegman, RM, Behrman RE, St. Geme JW III, Schor NF, Stanton BF, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 19th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2011:chap 585.
-
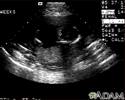
Ultrasound, normal fetus - ventricles of brain - illustration
This is a normal fetal ultrasound performed at 17 weeks gestation. The development of the brain and nervous system begins early in fetal development. During an ultrasound, the technician usually looks for the presence of brain ventricles. Ventricles are spaces in the brain that are filled with fluid. In this early ultrasound, the ventricles can be seen as light lines extending through the skull, seen in the upper right side of the image. The cross hair is pointing to the front of the skull, and directly to the right, the lines of the ventricles are visible.
Ultrasound, normal fetus - ventricles of brain
illustration
-
Ultrasound, normal fetus - ventricles of brain - illustration
This is a normal fetal ultrasound performed at 17 weeks gestation. The development of the brain and nervous system begins early in fetal development. During an ultrasound, the technician usually looks for the presence of brain ventricles. Ventricles are spaces in the brain that are filled with fluid. In this early ultrasound, the ventricles can be seen as light lines extending through the skull, seen in the upper right side of the image. The cross hair is pointing to the front of the skull, and directly to the right, the lines of the ventricles are visible.
Ultrasound, normal fetus - ventricles of brain
illustration
Review Date: 4/21/2015
Reviewed By: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Isla Ogilvie, PhD, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.