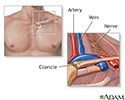
Thoracic outlet syndrome
Thoracic outlet syndrome is a rare condition that involves:
- Pain in the neck and shoulder
-
Numbness and tingling
of the fingers
Numbness and tingling
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - A weak grip
The thoracic outlet is the area between the ribcage and collarbone.
Causes
Nerves coming from the spine and major blood vessels of the body pass through a narrow space near your shoulder and collarbone on the way to the arms. Sometimes, there is not enough space for the nerves to pass by through the collarbone and upper ribs.
Pressure (compression) on these blood vessels or nerves can cause symptoms in the arms or hands.
Pressure may happen if you have:
- An extra rib above the first one.
- An abnormal tight band connecting the spine to the ribs.
People with this syndrome often have injured the area in the past or overused the shoulder.
People with long necks and droopy shoulders may be more likely to develop this condition because of extra pressure on the nerves and blood vessels.
Symptoms
Symptoms of thoracic outlet syndrome may include:
- Pain, numbness, and tingling in the pinky and ring fingers, and the inner forearm
- Pain and tingling in the neck and shoulders (carrying something heavy may make the pain worse)
- Signs of poor circulation in the hand or forearm (a bluish color, cold hands, or a swollen arm)
- Weakness of the muscles in the hand
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine you and ask about your medical history and symptoms.
The following tests may be done to confirm the diagnosis:
-
Electromyography
(EMG)
Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT angiogram
-
MRI
MRI
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Nerve conduction velocity
study
Nerve conduction velocity
Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a test to see how fast electrical signals move through a nerve.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
X-ray
X-ray
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray particles through the body. The im...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Tests are also done to rule out other problems, such as carpal tunnel syndrome or a damaged nerve due to problems in the neck.
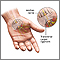
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in which there is excessive pressure on the median nerve. This is the nerve in the wrist that allows feeling a...
Treatment
Physical therapy is often used to treat thoracic outlet syndrome. It helps:
- Make your shoulder muscles stronger
- Improve your range of motion in the shoulder
- Promote better posture
Your provider may prescribe pain medicine.
If there is pressure on a vein, your provider may give you a blood thinner to prevent a blood clot.
You may need surgery if physical therapy and changes in activity do not improve your symptoms. The surgeon may make a cut either under your armpit or just above your collarbone.
During surgery, the following may be done:
- An extra rib is removed and certain muscles are cut.
- A section of the first rib is removed to release pressure in the area.
- Bypass surgery is done to reroute blood around the compression or remove the area that is causing the symptoms.
Your doctor may also suggest other alternatives, including angioplasty , if the artery is narrowed.
Angioplasty
The blood vessels that bring blood to your brain and face are called the carotid arteries. You have a carotid artery on each side of your neck. The...
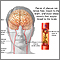
Outlook (Prognosis)
Surgery to remove the extra rib and break up tight fiber bands may ease symptoms in some people. Some people have symptoms that return after surgery.
Possible Complications
Complications can occur with any surgery, and depend on the type of procedure and anesthesia.
Risks related to this surgery include:
- Damage to nerves or blood vessels, causing muscle weakness
- Lung collapse
- Failure to relieve the symptoms
References
Filler AG. Brachial plexus nerve entrapments and thoracic outlet syndromes. In: Winn HR, ed. Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery . 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 250.
Posner MA, Roach CJ, Owens BD. Vascular problems and thoracic outlet syndrome. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR, eds. DeLee and Drez's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine . 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 59.
-
Thoracic outlet anatomy - illustration
Thoracic outlet syndrome is a rare condition that occurs when there is compression of vessels and nerves in the area of the clavicle. This can happen when there is an extra cervical rib or because of a tight fibrous band that connects the spinal vertebra to the rib. There may be pain in the neck and shoulders, and numbess in the last 3 fingers and inner forearm. Thoracic outlet syndrome is usually treated with physical therapy which helps strengthen and straighten out the shoulders.
Thoracic outlet anatomy
illustration
-
Thoracic outlet anatomy - illustration
Thoracic outlet syndrome is a rare condition that occurs when there is compression of vessels and nerves in the area of the clavicle. This can happen when there is an extra cervical rib or because of a tight fibrous band that connects the spinal vertebra to the rib. There may be pain in the neck and shoulders, and numbess in the last 3 fingers and inner forearm. Thoracic outlet syndrome is usually treated with physical therapy which helps strengthen and straighten out the shoulders.
Thoracic outlet anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 11/11/2016
Reviewed By: Mary C. Mancini, MD, PhD, Department of Surgery, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center-Shreveport, Shreveport, Louisiana. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.